Question 1
Which of these is not a function of plasmodesmata in plant cells?
To allow movement of water via the symplast pathway
To enable cell recognition
To allow communication between cells
To allow movement of nutrients between cells
Which of these is not a function of plasmodesmata in plant cells?
To allow movement of water via the symplast pathway
To enable cell recognition
To allow communication between cells
To allow movement of nutrients between cells
Certain plants have developed a mutualistic relationship with soil fungi, in which the plant provides sugars to the fungus for respiration.
In what way does the plant receive a benefit in return?
The fungus helps to stabilise the plant's root network in poor / stony soils.
The fungus acts like a sponge to retain water in dry soils after (infrequent) rainfall.
The fungus fixes atmospheric nitrogen and supplies nitrate ions to the plant.
The fungus accesses mineral ions in mineral-deficient soils and supplies them to the plant's roots.
Which table gives the most accurate summary of the movement of water via the apoplast and symplast pathways?
| Apoplast pathway | Symplast pathway | |
| Route travelled | Cell walls | Cytoplasm |
| Speed of flow | Slow | Fast |
| Method of flow | Mass flow | Osmosis |
| Volume of water transported | Low | High |
| Apoplast pathway | Symplast pathway | |
| Route travelled | Cell walls | Cytoplasm |
| Speed of flow | Fast | Slow |
| Method of flow | Mass flow | Osmosis |
| Volume of water transported | High | Low |
| Apoplast pathway | Symplast pathway | |
| Route travelled | Cytoplasm | Cell walls |
| Speed of flow | Fast | Slow |
| Method of flow | Mass flow | Osmosis |
| Volume of water transported | High | Low |
| Apoplast pathway | Symplast pathway | |
| Route travelled | Cell walls | Cytoplasm |
| Speed of flow | Fast | Slow |
| Method of flow | Osmosis | Mass flow |
| Volume of water transported | High | Low |
The following data were gathered from an experiment into the rate of transpiration in samples of plants in the genus Coelus, commonly grown by gardeners for herbaceous borders. Coelus grows easily in UK gardens and thrives in the relatively high rainfall that the UK experiences. 
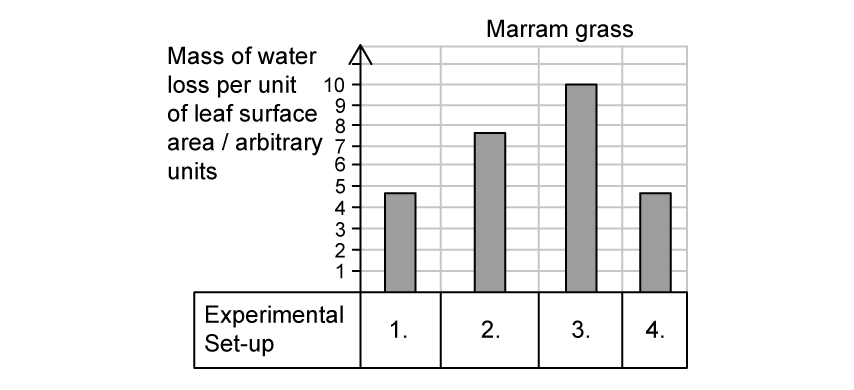
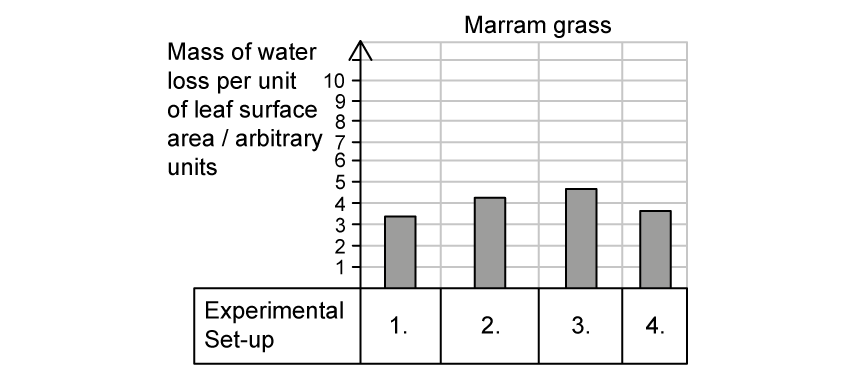
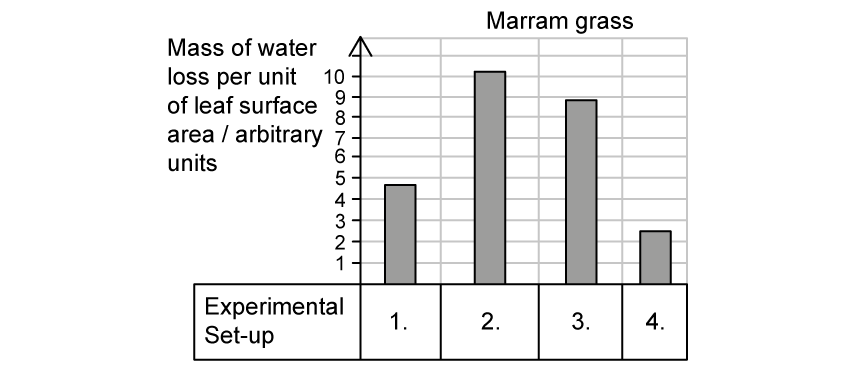
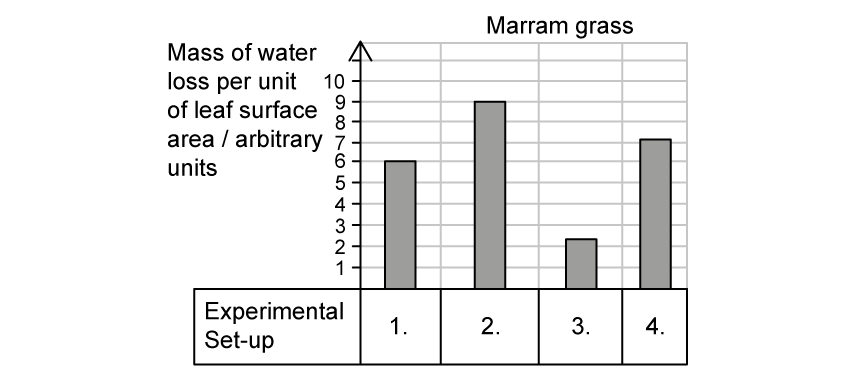
Marram grass is a xerophyte that is found on sand dunes and other fast-draining soils in coastal areas. The same experimental set-up was repeated with marram grass.
Which graph of A - D would be the most likely graph for a comparable experiment carried out on marram grass?
The diagram shows a potometer set up to measure the rate of transpiration in a piece of cut plant.
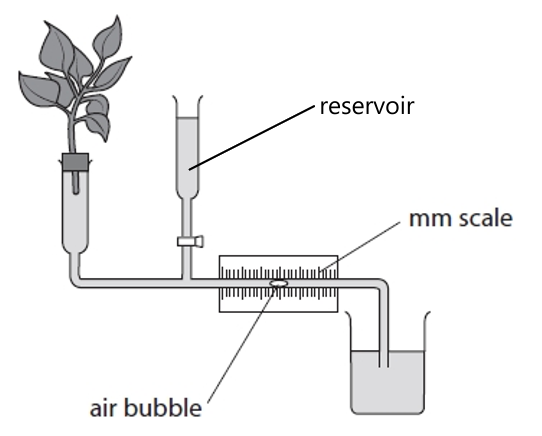
For a potometer with a cylindrical capillary of the internal diameter of d mm, the bubble was measured to travel h mm in an experimental time of s seconds.
Which is the correct formula to calculate the rate of transpiration (as a volume of water uptake per unit time) in this experiment?