Routine use of antibiotics in animal feed has been common practice in livestock farming, but is now no longer widely practised.
Which statements best explain why?
Use of antibiotics allows sub-standard hygiene conditions for farm animals to be kept in
It encourages antibiotic resistance
It is expensive
Farm animals get more nutrition from antibiotic-free feed
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Next Question
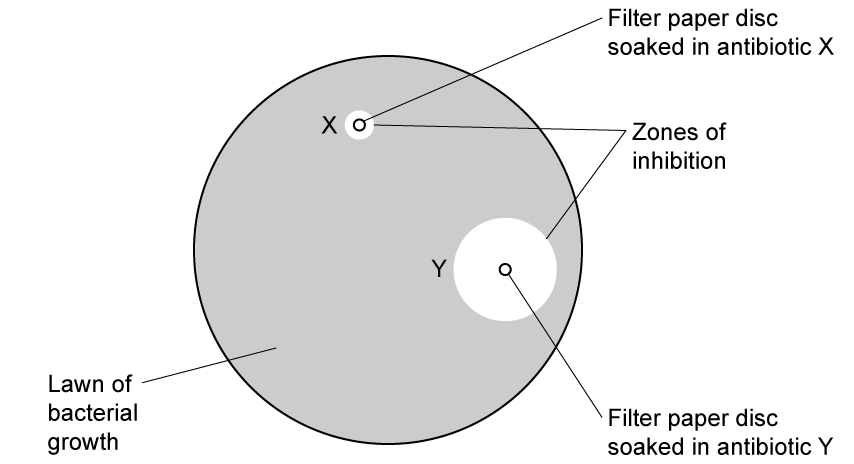
The image below shows a petri dish viewed from above. A lawn of bacteria is growing across the whole surface of the agar.
Different antibiotics, X and Y were applied to the agar before inoculating it with bacteria. Both antibiotics were applied to the discs of filter paper at the same concentration.
The plates were then incubated for 24 hours at 25°C. Zones of inhibition (areas of the dish with no bacterial growth) are shown on the diagram.
After growth, the following results were obtained.
Antibiotic Diameter of zone of inhibition / cm
X
2.0
Y
6.0
How many times more effective was antibiotic Y versus antibiotic X in this study?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Which is a reason why fungi such as Penicillium have evolved to produce antibiotics?
To destroy bacteria that could otherwise feed on Penicillium
To destroy bacteria that could otherwise harm the fungus's host organisms
To destroy saprophytic bacteria as a way of Penicillium out-competing bacterial competitors for food
To kill viruses that may otherwise be pathogenic to the fungus
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Some bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics by forming biofilms, which are large colonies of bacteria clumped together.
Which statement best explains how forming a biofilm might give a bacterial species resistance to antibiotics?
Antibiotic molecules are physically unable to reach all bacterial cells in a biofilm
Biofilms secrete chemicals which break down the antibiotic
Biofilms remain in a host organism for many years
Bacterial cells in a biofilm go into a suspended state but can become infectious again at a later stage
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Lefamulin™ is a newly-developed antibiotic that binds to the 50S bacterial ribosomal subunit.
It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in August 2019 for the treatment of pneumonia.
Which is the mode of action of Lefamulin™?
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis
Perforates the bacterial cell membrane
Prevents the bacterial cell wall forming
Inhibits replication of bacterial DNA
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question