a)
The ends of a DNA strand are referred to as the 3’ end and the 5’ end.
Describe the aspects of DNA structure that give rise to this naming system.
[ 3 marks ]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Adenine/thymine and guanine/cytosine form hydrogen-bonds with each other in complementary base-pairing within the DNA double helix. These bases can also form bonds with other molecules in order to carry out their function.
i)
Suggest one other molecule that might form bonds with the bases in a DNA molecule.
[1 mark]
ii)
State the role of the molecule identified in part i).
[ 1 mark ]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
The structure of DNA has many characteristics that enable it to carry out its function.
i)
Identify two structural features that help DNA to carry out its function.
[2 marks]
ii)
For each feature identified at part i), explain how it assists with DNA function.
[ 2 marks ]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
Explain why only bases that are complementary to the bases on the template strand can be added to the new DNA strand during DNA replication.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Ultraviolet exposure can cause guanine to be oxidised to 8-oxyguanine, which is no longer complementary to cytosine. Instead, during replication, 8-oxyguanine can form bonds with adenine, resulting in a base pair.
Outline the possible consequences of this change.
[ 3 marks ]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
In the absence of mutagens, the rate of mutations during DNA replication is very low, approximately 160 bases per cell cycle.
Given that the human genome contains 3.2 billion base pairs, calculate the percentage copying error rate of each cell cycle.
[ 1 mark ]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Even the smallest DNA molecules are very long.
A kilobase (Kb) is a unit equivalent to 1000 base pairs of a DNA molecule.
One Kb of double stranded DNA has a length of 0.34 μm.
The DNA in the nucleus of a cell from a fruit fly ( Drosophila ) is 5.6 cm long.
Calculate the number of Kb in the DNA of the fruit fly. Give your answer to the nearest whole number.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
The amount of DNA found in the nucleus of cells can vary amongst people, with each human chromosome containing between 5 x 104 and 26 x 104 Kb of DNA.
Suggest one reason why people might have different quantities of DNA to each other.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Other than for use in replication, explain one advantage of DNA molecules having two strands.
[ 1 mark ]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
A section of DNA contains 1,200 base pairs.
The number of guanine molecules on strand one was counted as 156. The number of cytosine molecules on strand one was counted as 209. The number of adenine molecules on strand two was counted as 264.
Complete the table below to include the total number of each base present in the section, and the % composition of each base.
Number of molecules present % composition
Adenine
Cytosine
Guanine
Thymine
[4 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
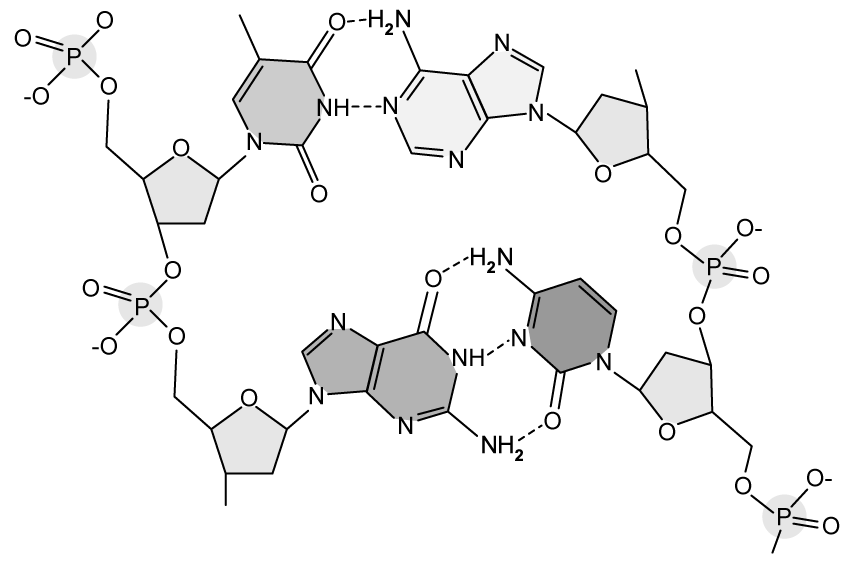
The image below shows a section of the skeletal formula of a DNA molecule.
Number the carbon atoms of all the pentose sugars shown in the image using the standard numbering format.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
The DNA nucleotides are covalently bonded together in the sugar-phosphate backbone between the pentose sugar and the phosphate group, however, they are hydrogen bonded together between the bases.
Explain why both types of bonds are important for the functioning of DNA.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
During DNA replication both DNA strands act as a template, whereas in transcription only one strand acts as a template.
Outline what is meant by the word 'template' in this context.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
One mark is available for clarity of communication throughout this question.
a)
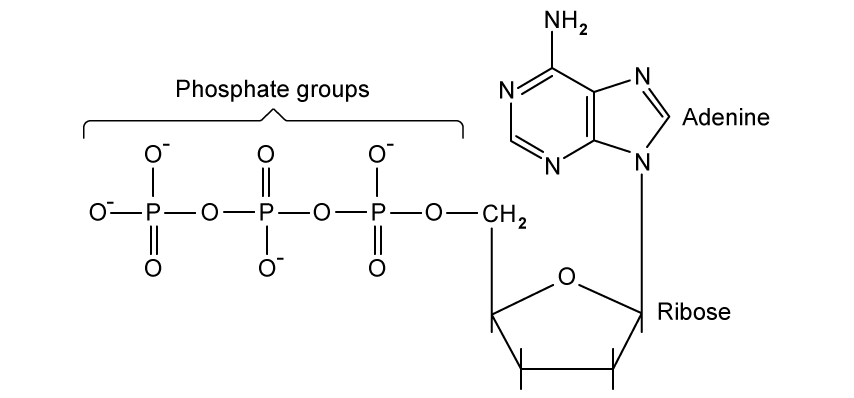
ATP is a source of energy used in cells and is produced from processes such as respiration.
The structure of ATP is shown in the diagram below.
Use the information in the diagram, as well as your own knowledge, to compare and contrast the structure of ATP with an adenine DNA nucleotide.
[4 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Explain how the structure of DNA allows replication.
[4 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Outline the steps in the experiment that Meselson and Stahl carried out to determine the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication.
[7 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question