a)
Give the definition of a species.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
The image shows a woodland food web.
What word is used to collectively describe all the interbreeding foxes in the woodland represented by this food web?
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Identify all the primary consumers from the forest food web.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Consumers in this forest food web obtain organic molecules through eating organisms in the trophic level before.
Which two elements do all organic molecules contain?
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
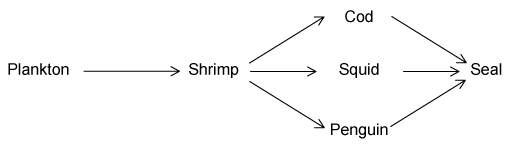
This is a simple food web found in an ocean ecosystem.
Identify an example of an organism from the food web which obtains food using the method of nutrition named in the table.
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Identify an organism (or a group of organisms), not shown in the ocean food web, which feeds on all trophic levels of the food chain.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Each of the three sentences about ecosystems contains one error.
In a functioning ecosystem, organisms are constantly recycled.
Detritivores obtain inorganic nutrients from the abiotic environment and convert them to organic molecules during photosynthesis.
Decomposition is fundamental in ensuring that ecosystems remain unsustainable over long periods of time.
Identify and replace the incorrect word in each sentence.
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Where does the organism in the first trophic level of this ocean food web obtain the carbon that it uses to build organic molecules?
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Place a (✓) or (X) in the correct columns for each of the factors listed in the table below:
Biotic Abiotic
Sunlight
Predation
Food availability
Mineral availability
Temperature
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
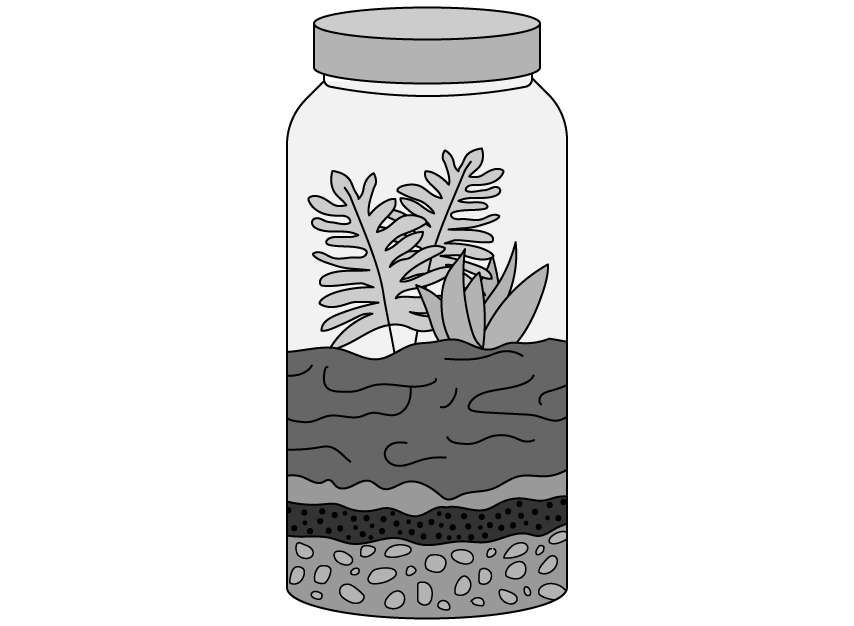
Abiotic factors can be controlled in order to study the response of a naturally occurring ecosystem using the set up below.
What is the name given to the set up shown in the image which allows the study of ecosystems?
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Suggest why the experiment set up in part b) should include the following features:
A transparent container
A lid to seal the container
Minimal primary consumers and no secondary consumers
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
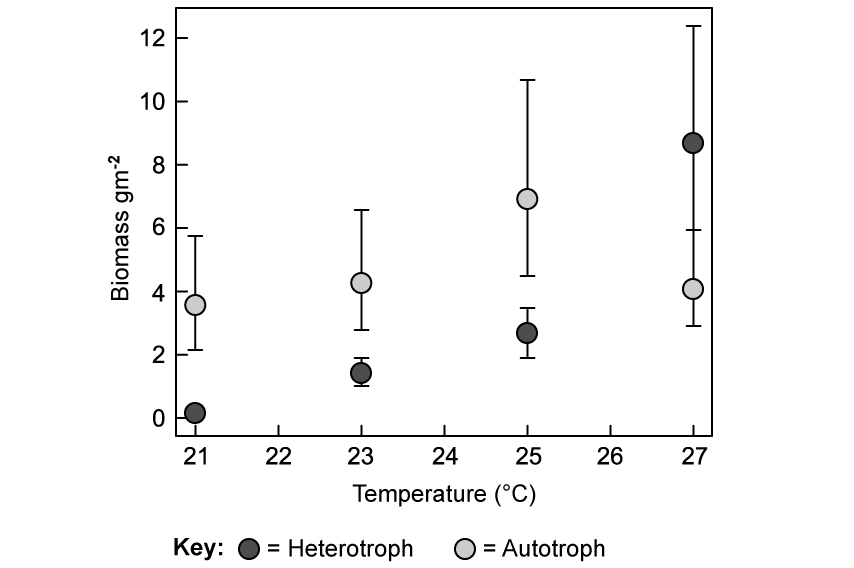
A mesocosm was set up to study the effect of increasing global temperatures on the biomass of aquatic autotrophs and heterotrophs.
The graph shows the data collected.
Describe what happened to the biomass of heterotrophs and autotrophs as temperatures increased from 21 °C to 27 °C.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
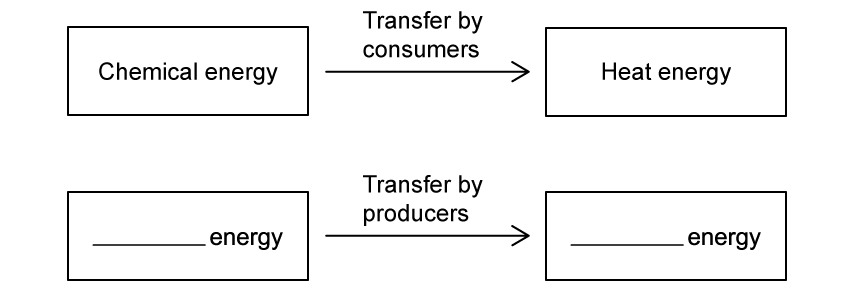
When a consumer eats another organism, it converts chemical energy into other forms of energy, such as heat energy. This is represented in the energy transfer diagram below.
Complete the diagram to identify the main energy transfer carried out by producers in a food chain.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
A blackbird ate snails containing 1150 kJ of energy. Only 10% of this energy was transferred to the blackbird.
Calculate the energy transferred from the snails to the blackbird.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Identify three functions of life which rely on energy transferred in respiration.
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
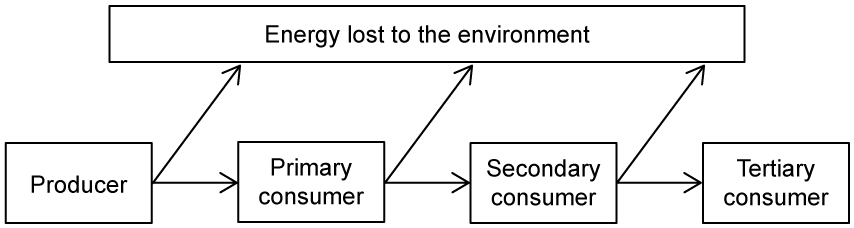
The diagram shows the movement of energy through a food web.
Explain why energy is transferred to the environment at each trophic level.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
One mark is available for clarity of communication throughout this question.
a)
Describe how a quadrat could be used to study the distribution of a particular species of clover plant in a meadow compared to a forest.
[5 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Outline some of the reasons that energy is lost between each trophic level of the food chain.
[4 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Describe, with examples, the different modes of nutrition used by organisms.
[6 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question