a)
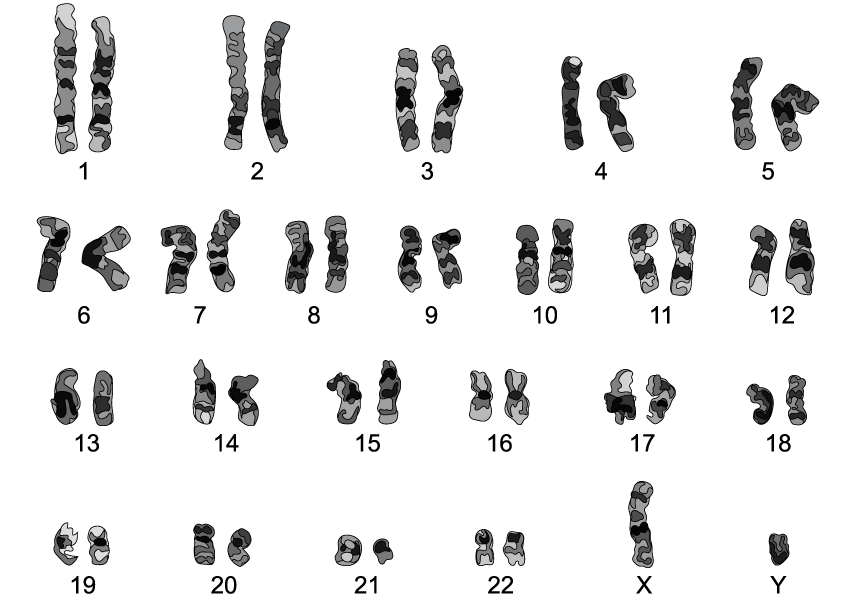
The following diagram shows the karyogram of an individual.
i)
Identify the sex of this individual.
[1 mark]
ii)
State a reason for your answer in part i).
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Cells in metaphase of mitosis were used to construct the karyogram from part a).
Explain the reason for this.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
List two characteristics of the chromosomes that are used to arrange them in a karyogram.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Apart from sex determination, state one other use of studying the karyotype of an individual.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
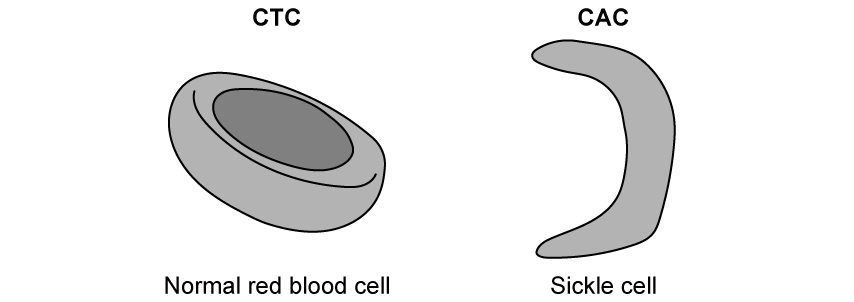
Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disease where a DNA triplet base in the gene coding for alpha-globin in haemoglobin changes from CTC to CAC. This mutation results in sickle shaped red blood cells that can cause a range of different symptoms.
The diagram below shows the DNA base triplet change and the resulting change in the structure of red blood cells.
i)
Identify the type of mutation that is illustrated in the diagram.
[1 mark]
ii)
State a reason for your answer in part i).
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
List two consequences of the change in shape of the red blood cells in a person suffering from sickle cell anaemia.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Some mutations, such as those causing sickle cell anaemia, may be inherited by offspring.
Describe how mutations can be inherited by offspring.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Gene mutations lead to the formation of new alleles in a population.
Define the term 'allele'.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
During the process of fertilisation, haploid sperm and egg cells fuse together to form a diploid zygote.
Define the term 'haploid'.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
There are certain advantages to cells being diploid.
List two advantages of cells containing two sets of chromosomes.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
A couple is expecting a child and wondering which sex the baby will be.
The following genetic diagram shows the sex chromosomes present in the gametes of both parents.
Calculate the percentage chance of the baby being a girl by completing the genetic diagram.
Show your working.
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
One of the genes carried on the Y chromosome is the SRY gene.
State one role of this gene in the development of male embryos.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
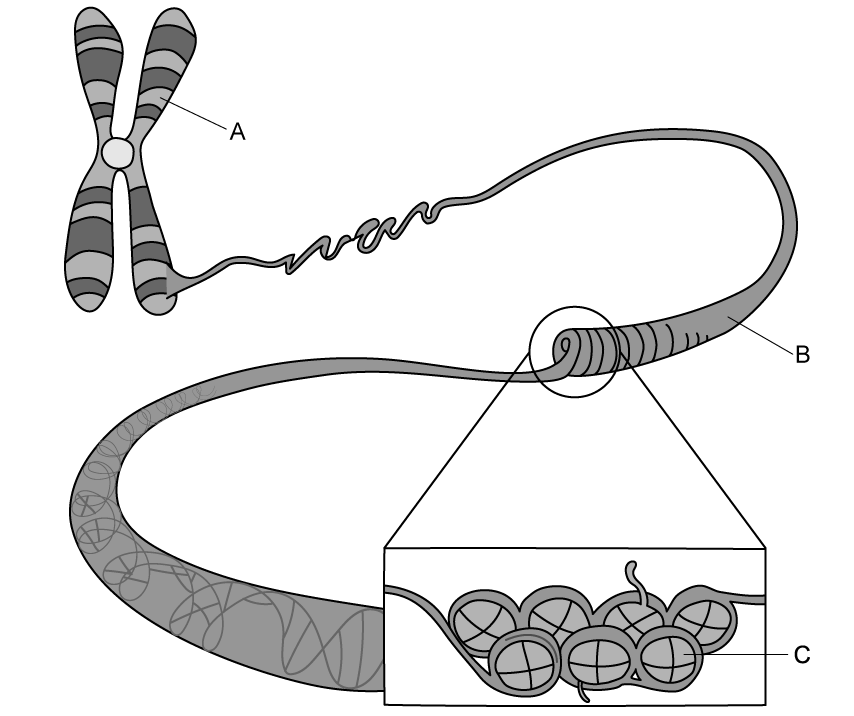
The following diagram shows the arrangement of DNA in a eukaryotic chromosome.
i)
Label structure A in the diagram.
[1 mark]
ii)
State what is represented by the banding pattern on structure A .
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Use the information in the diagram in part a) to:
i)
Identify structures B and C .
[1 mark]
ii)
Describe the relationship between structures B and C .
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Chromosomes in diploid cells will occur in homologous pairs.
Define the term 'homologous chromosomes'.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
One mark is available for clarity of communication throughout this question.
a)
The Human Genome Project was an international, collaborative research programme to sequence the entire human genome.
List four of the main applications of the Human Genome Project.
[4 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Plasmids are small, circular DNA molecules commonly found in prokaryotic cells.
Describe the role of a plasmid.
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Advancements in genome sequencing has led to developments in scientific research.
Outline the technique used to sequence a genome.
[8 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question