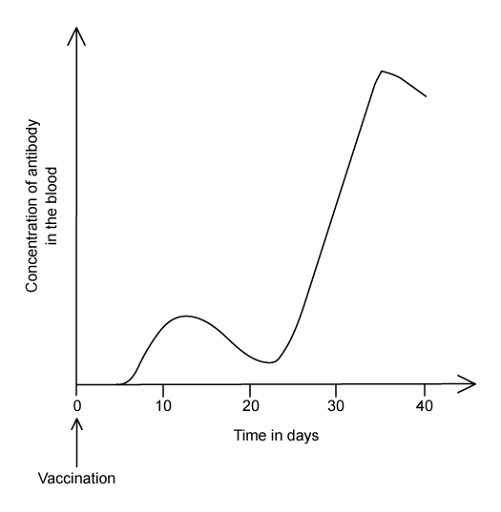
A child is given a vaccine for a viral disease. A few months later she is in contact with the same virus.
What is the expected response to the second contact with the virus?
Increased number of T-lymphocytes.
Large numbers of antibodies are released.
Large numbers of antigens are released.
Increased number of B-lymphocytes.
When a B-lymphocyte is activated by an antigen, what action is taken?
It engulfs the infected body cell which displays a complementary antigen.
It secretes signalling proteins that stimulate T-lymphocytes to produce plasma cells.
It divides repeatedly to form clones of genetically identical plasma cells.
It attaches to the infected cell displaying the antigen and destroys it.
Which type of molecule is most important to directly identify a cell as non-self?