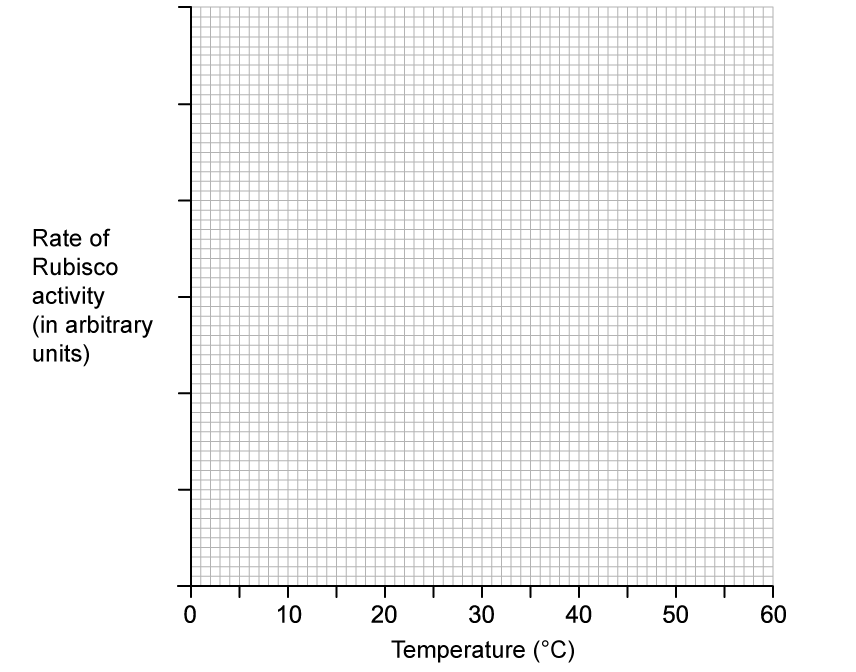a)
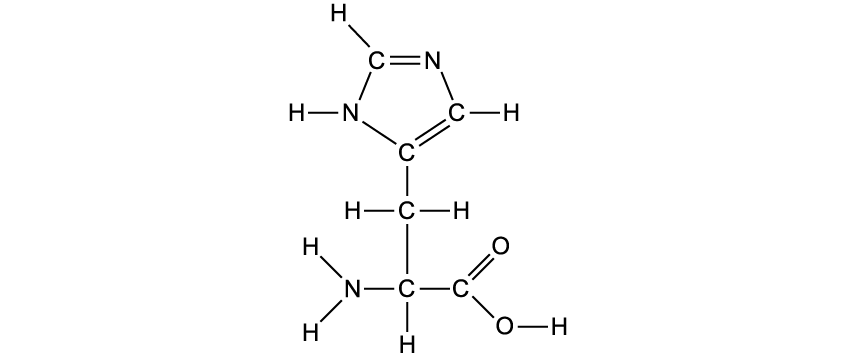
The image below shows the amino acid histidine.
Circle the section of the amino acid that is unique to histidine.
[1 mark]
b)
State the type of reaction that occurs when two amino acids bond with each other.
[1 mark]
c)
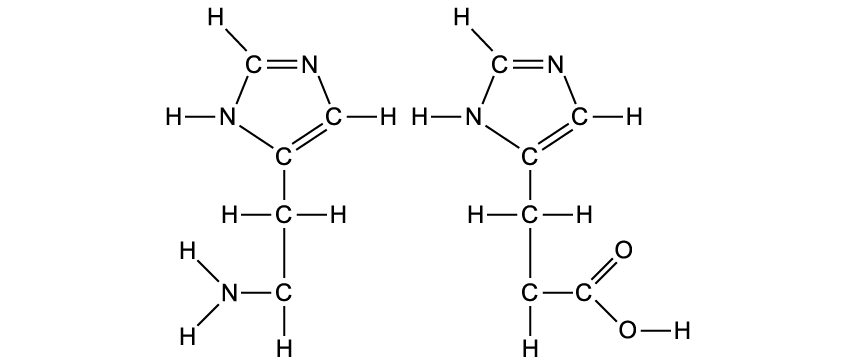
The image shows two histidine amino acids with the diagrams not fully complete.
Complete the image to include the structure of a peptide bond joining the two amino acids together into a dipeptide.
[1 mark]
d)
In a polypeptide with 100 amino acids, how many peptide bonds exist within the chain?
[1 mark]
a)
The protein Rubisco is an enzyme.
What is the function of the enzyme Rubisco in living organisms?
[2 marks]
b)
Enzymes have a specific three-dimensional conformation that enables them to carry out their roles in living organisms.
Which part of the amino acid determines the conformation of the protein?
[1 mark]
c)
In certain conditions, such as high temperatures, the 3D conformation of proteins can be lost.
i) What is the scientific name given to when a protein loses its 3D conformation?
[1 mark]
ii) State one condition, other than temperature, that can cause the 3D conformation of a protein to be lost.
[1 mark]
d)
Sketch a graph to show how the rate of reaction of Rubisco changes over a range of temperatures.
Use the axes provided below.
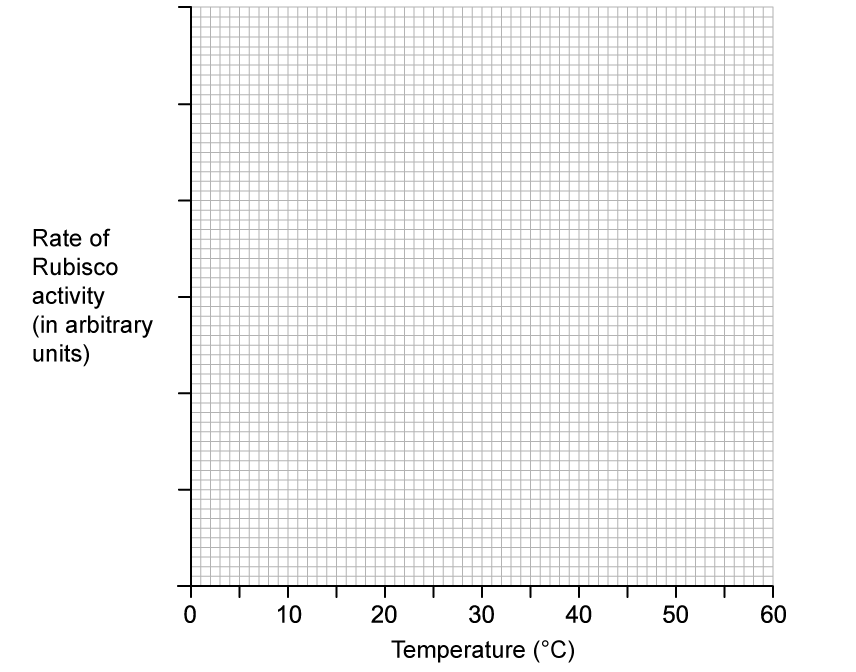
[2 marks]
a)
What is the name of the part of the cell where polypeptide synthesis takes place?
[1 mark]
b)
When a polypeptide is synthesised it is important that the amino acids are combined in the correct order to produce a functional protein.
Outline the process that allows the amino acids to be added to the polypeptide in the correct order.
[3 marks]
c)
After a polypeptide has been synthesised it must undergo a series of changes before it can become a functional protein.
Describe the changes that occur between polypeptide synthesis and the formation of the functional protein.
[3 marks]
d)
How might a change in the DNA affect the way that the process of protein folding occurs?
[2 marks]
a)
What is meant by the term proteome?
[1 mark]
b)
There are two main categories of proteins: globular and fibrous.
The protein insulin is a hormone.
State whether insulin is a globular or a fibrous protein, and give a reason for your choice.
[2 marks]
c)
The image below shows the structure of collagen at various levels of detail.
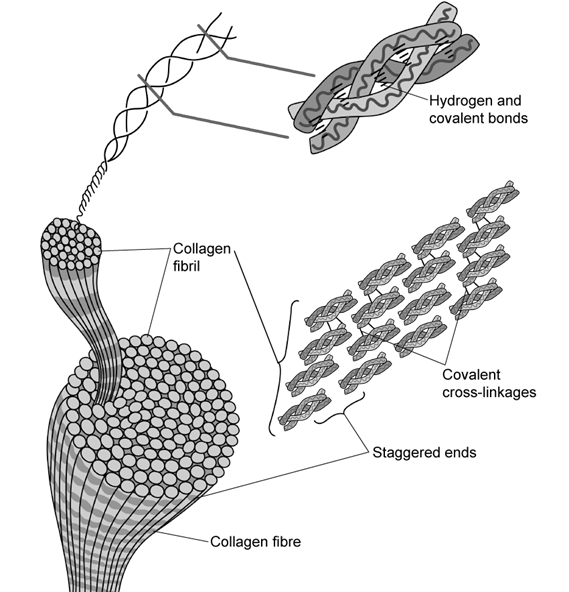
Use the image to suggest two features of collagen that enable it to be a strong, structural protein.
[2 marks]
d)
One of the polypeptide chains that forms a molecule of collagen contains 1049 peptide bonds.
Assuming all the chains that form collagen are identical in length, how many amino acids would be found in a single molecule of collagen?
Explain your answer.
[3 marks]
One mark is available for clarity of communication throughout this question.
a)
Every individual has a unique proteome.
Explain how this is possible.
[3 marks]
b)
Describe the process of protein denaturing.
[4 marks]