Question 1a
A scientist is investigating two substances, X and Y, which may affect the growth of new roots from a cut plant stem. They used a ringing experiment to investigate the transport of substances X and Y through the stems taken from a grapefruit plant. A length of the stem was cut from each grapefruit plant and a small block of agar was placed at the top of each stem. Substance X or Y was added to some of the agar blocks.
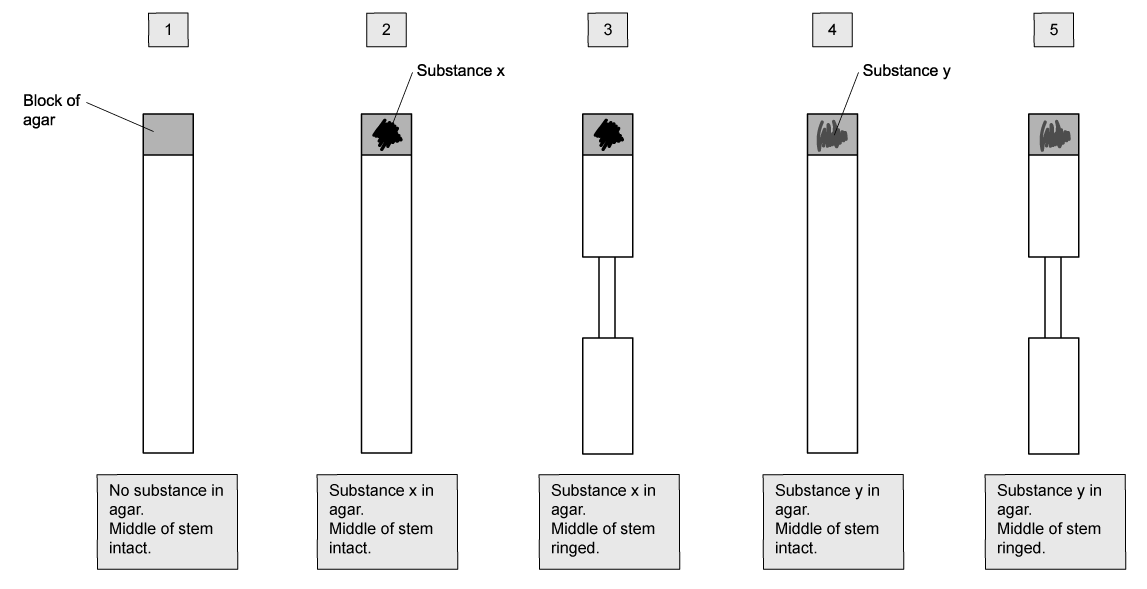
The stems were grown in the same environmental conditions for 5 weeks and then the number of roots per stem was recorded. The roots grew at the opposite end to where the agar block was located. The table shows the results of the experiment.
| Treatment | Mean number of roots per stem |
| 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 13 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 6 |
Agar delivers substances X and Y in treatments 2 - 5. Suggest one other reason why agar is present in all of the treatments.
[1 mark]
Question 1b
Suggest a conclusion that can be drawn about the action of substance Y, using the information from the diagram at part a).
[2 marks]
Question 1c
The movement of substances through the phloem can be explained using the mass flow hypothesis.
Evaluate whether the data from this experiment supports the mass flow hypothesis. Note that no statistical analysis is required.
[4 marks]
Question 1d
Upon further research, it was discovered that substance Y could be sprayed onto the leaves of a plant and it would be absorbed into the phloem sap.
Using this information, outline the mechanism by which substance Y could act as weed control.
[3 marks]
Question 1e
Suggest, with a reason, a better measure of the dependent variable in the investigation in part a) of this question.
[2 marks]