Which of the following will lead to the termination of translation?
Once the ribosome disassembles into the large and small subunit
When the ribosome encounters a stop codon
Releasing the free polypeptide from the last tRNA molecule
When the ribosome detaches from the mRNA molecule
The diagram below shows the structure of a tRNA molecule.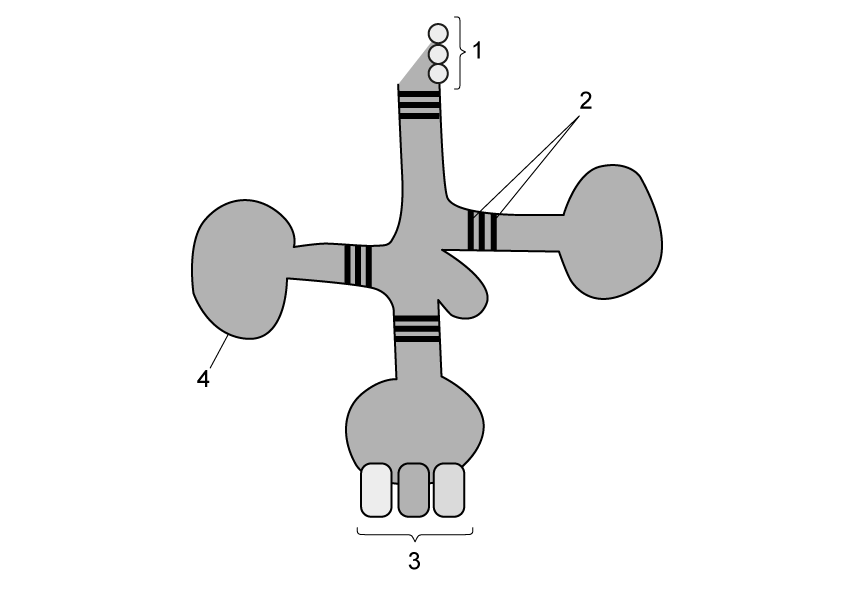
Which of the following correctly identifies the different parts of the tRNA molecule?
| |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| A. |
Amino acid binding site |
Hydrogen bonds |
Anticodon |
Sugar-phosphate backbone |
| B. |
Amino acids |
Hydrogen bonds |
Anticodon |
Covalent bonds |
| C. |
Amino acid binding site |
Covalent bonds |
Anticodon |
Sugar-phosphate backbone |
| D. |
Amino acids |
Hydrogen bonds |
Codon |
Covalent bonds |
Which of the following is involved in the secondary structure of a protein?
- Double helix
- β-pleated sheets
- Hydrogen bonds
- Hydrophobic interactions
Which of the following would apply to the polysomes of prokaryotes?
Polysomes, containing 80S ribosomes, will appear on the growing mRNA strand along the DNA molecule
Polysomes, containing 70S ribosomes, will appear on the growing mRNA strand in the absence of DNA
Polysomes, containing 80S ribosomes, will appear on the growing mRNA strand in the absence of DNA
Polysomes, containing 70S ribosomes, will appear on the growing mRNA strand along the DNA molecule
Bioinformatics involves the use of computers to generate and store large amounts of biological data.
Which of the following would not be an application of bioinformatics?
Comparing sequence similarities to determine if an unknown DNA sequence codes for a gene
Sequencing DNA to determine protein sequences
To determine the rate of aerobic respiration within the mitochondria of an organism
Comparing gene sequences between organisms to determine how closely related they are
