Question 1
Identify which answer gives the correct labels when describing how the skeleton can act as a lever.
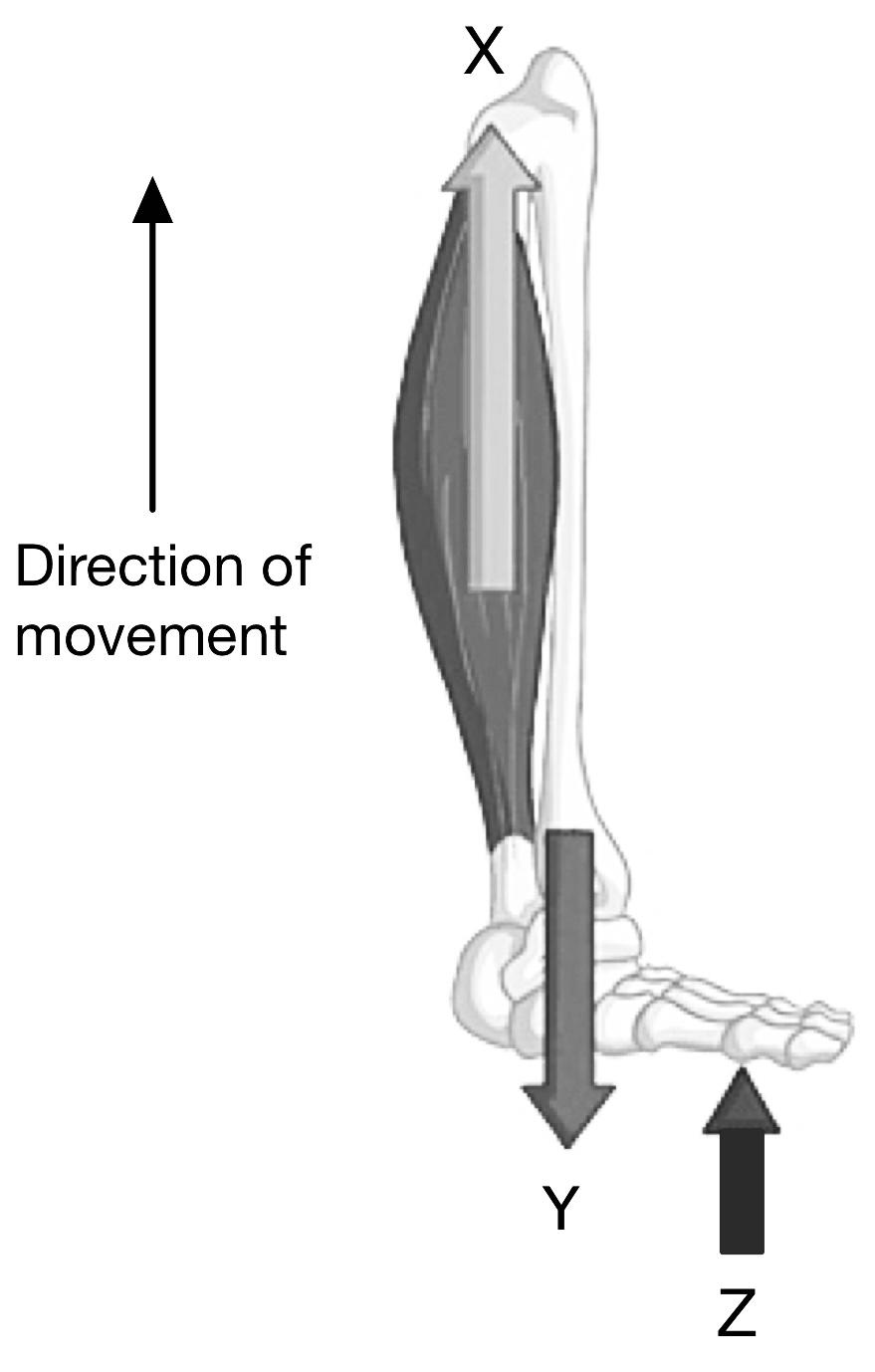
| X | Y | Z | |
| A | Fulcrum | Effort | Load |
| B | Effort | Load | Fulcrum |
| C | Fulcrum | Load | Effort |
| D | Load | Fulcrum | Effort |
Identify which answer gives the correct labels when describing how the skeleton can act as a lever.

| X | Y | Z | |
| A | Fulcrum | Effort | Load |
| B | Effort | Load | Fulcrum |
| C | Fulcrum | Load | Effort |
| D | Load | Fulcrum | Effort |
Select the correct answer to describe what is happening to the muscles in the insect leg to move from position 1 to position 2.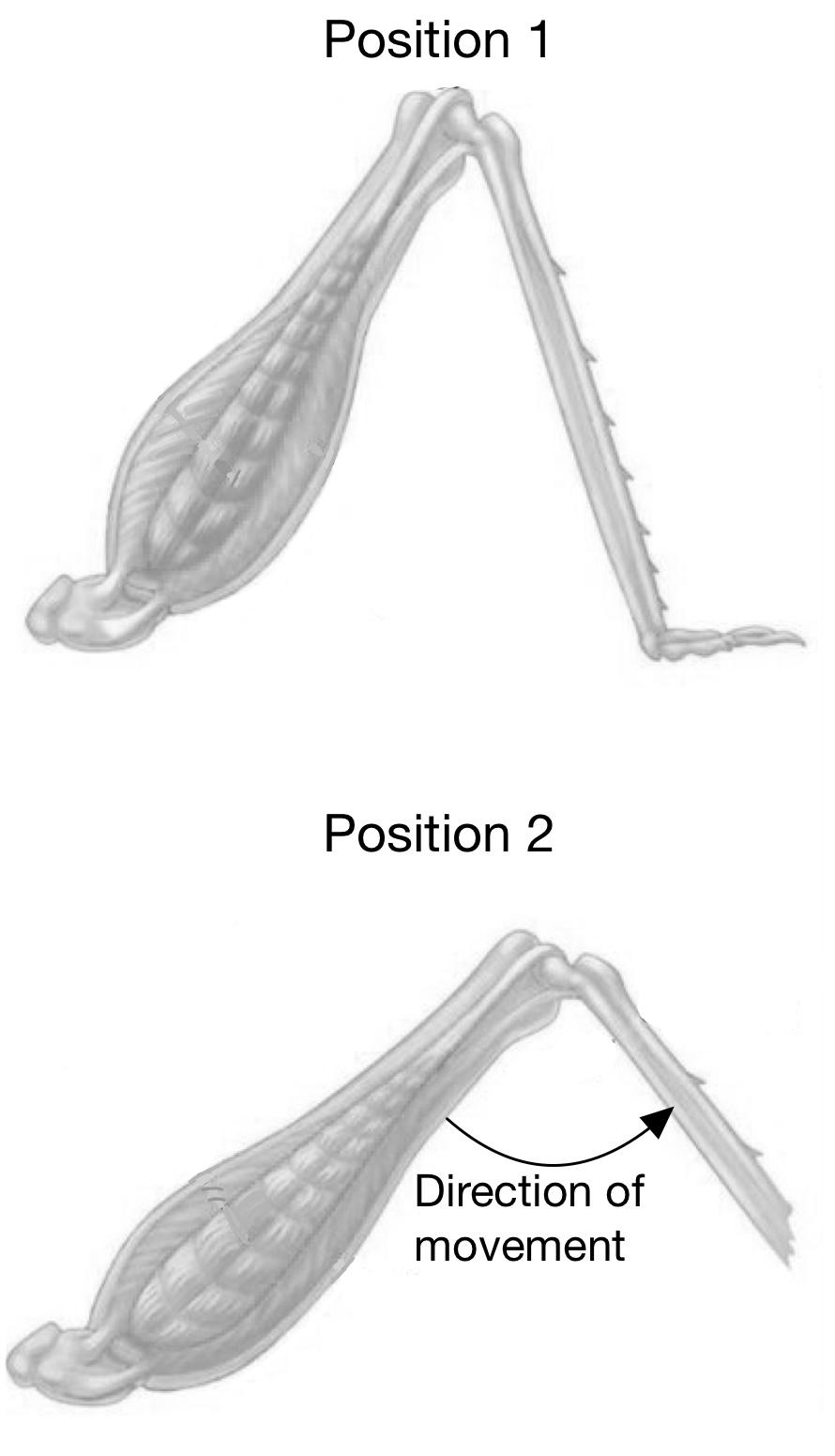
| A | Flexor contracts | Extensor relaxes |
| B | Flexor relaxes | Extensor Relaxes |
| C | Flexor Contracts | Extensor contracts |
| D | Flexor relaxes | Extensor contracts |
Which of the following is not a range of movement demonstrated by a synovial joint such as an elbow or knee joint?
Abduction
Flexion
Extension
Inversion
The diagram below shows the sarcomere of a muscle fibre.
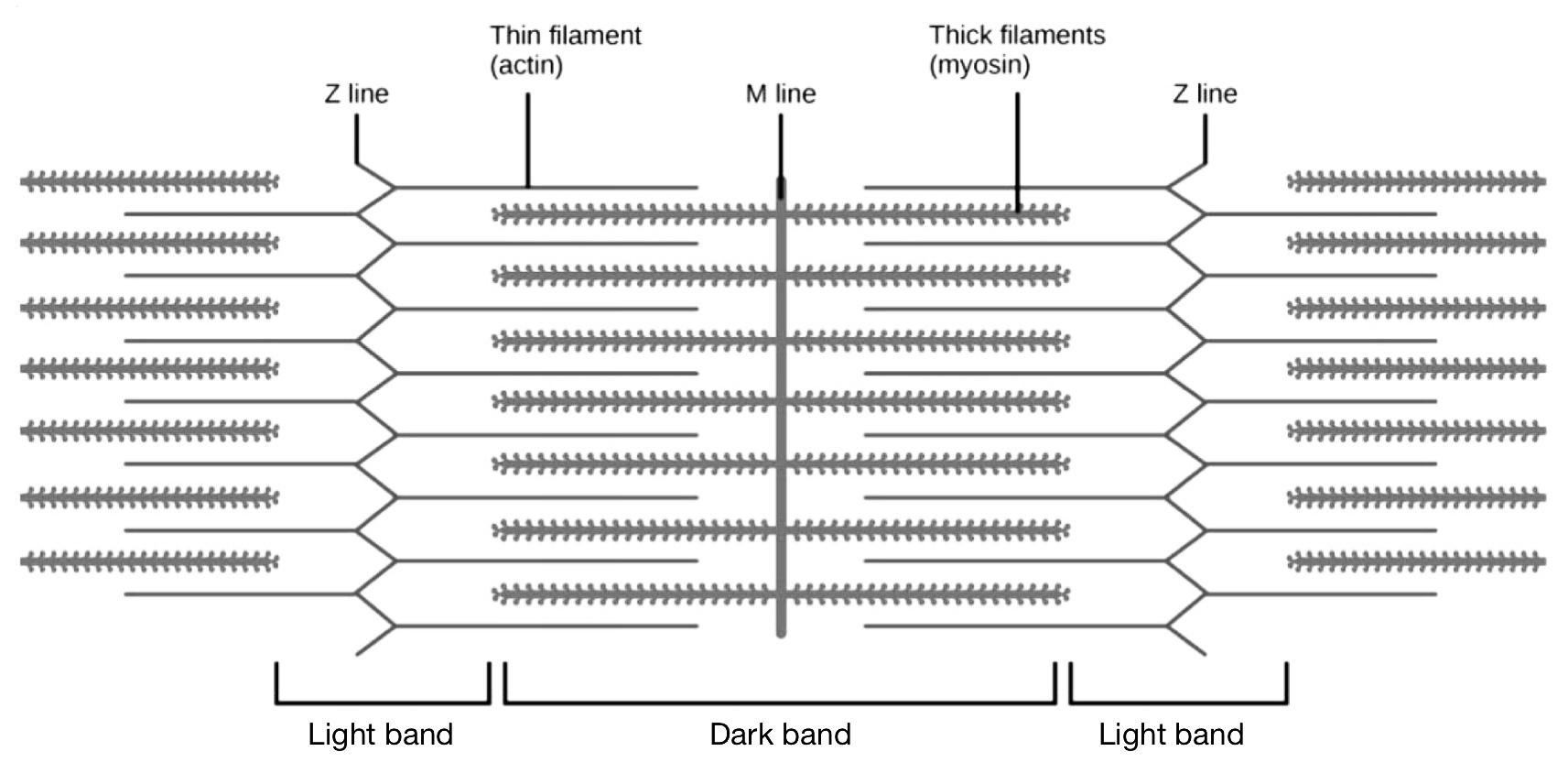
Which of the following statements correctly describes the events observed during a muscle contraction?
The length of the sarcomere stays the same, the dark band gets longer and the light bands stay the same
The length of the sarcomere gets shorter, the dark band gets shorter and the distance between the two Z lines gets shorter
The length of the sarcomere stays the same, the dark band gets longer and the distance between the two Z lines gets shorter
The length of the sarcomere gets shorter, the dark band stays the same and the light bands get shorter
One myosin powerstroke requires hydrolysis of one molecule of ATP and moves one actin filament 20 nm.
How many ATP molecules would be required to move a single actin filament 0.3 µm when the sarcomere contracts?
150 ATP
15 ATP
20 ATP
1.5 ATP
What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
It initiates hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and phosphate
It binds to tropomyosin causing a conformational change in the tropomyosin protein
It binds to troponin resulting in myosin binding sites being exposed
It binds to receptors on the myosin causing cocking of the myosin head
Which of the following describes a function of ATP in muscle contraction?
To actively transport calcium ions into myofibrils from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
To move tropomyosin and expose myosin binding sites
To allow crossbridge formation
To cause cocking of the myosin head
Phosphocreatine is a chemical found in the muscles of vertebrates. It provides a store of phosphate ions used during muscle contraction. The graph shows the effect of phosphocreatine production on the force of muscle contraction in mice.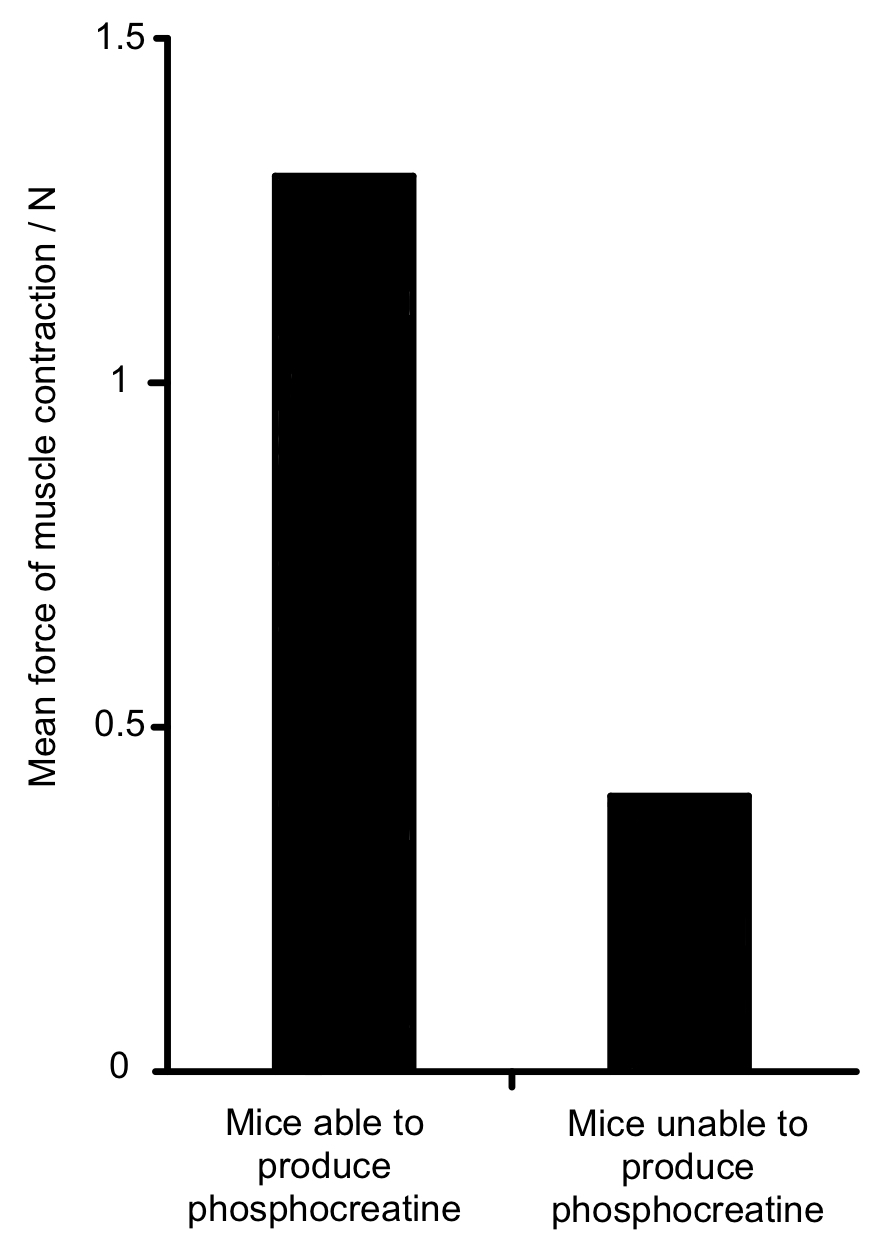
Which of the following best explains the results shown in the graph?
Mice that can produce phosphocreatine can run faster.
Phosphate ions can be combined with ADP to make ATP for contraction.
Phosphate ions initiate the formation of crossbridges.
Phosphate ions inhibit muscle contraction by creating an electrochemical gradient.
Fluorescent proteins can be used to study muscle fibres during contraction.
What is the reason for the fluorescence shown as the muscle contracts?
Fluorescent protein reacts with calcium ions released during contractions
Fluorescent protein binds to the myosin filaments when cross-bridges form
Fluorescent proteins bind to the ADP released during muscle contraction
Energy from ATP activates fluorescent proteins during muscle contraction
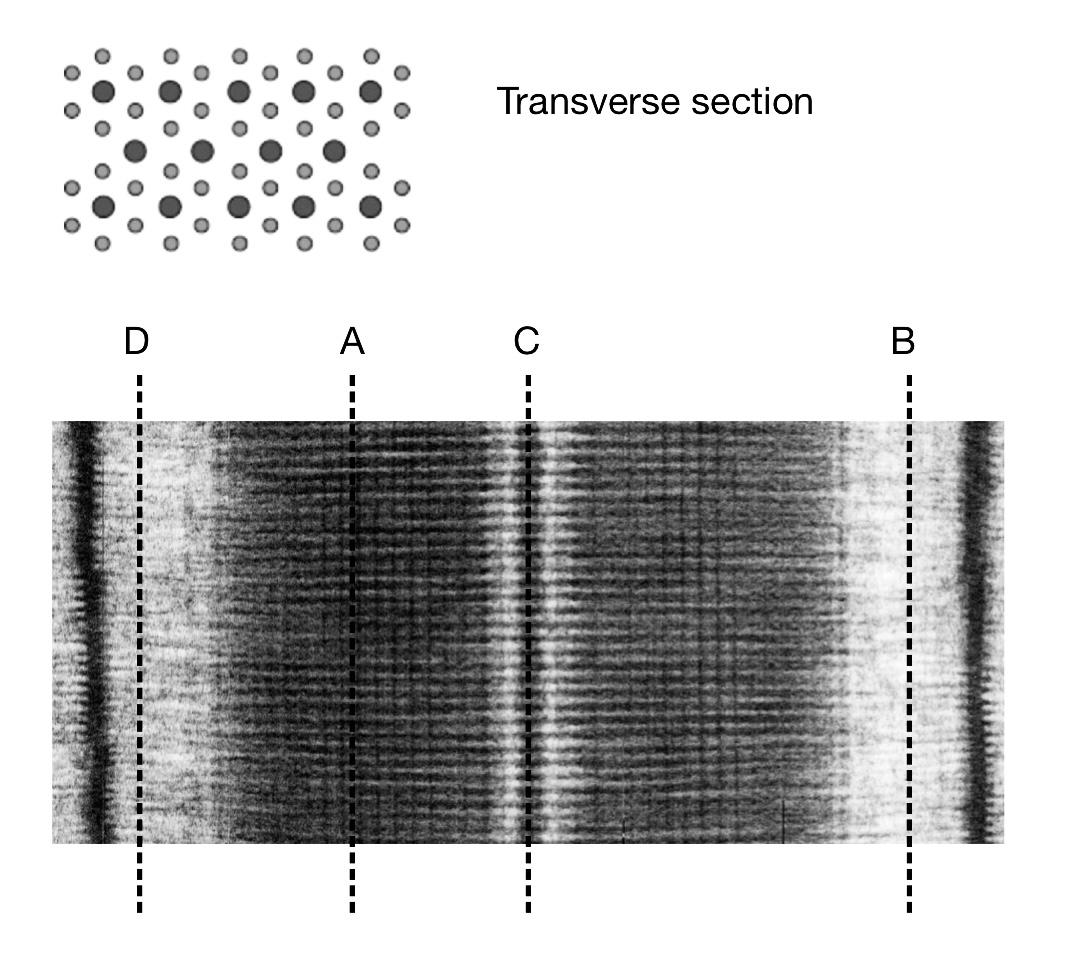
Identify the correct label from the electron micrograph which correctly represents the transverse section of muscle fibre shown.