Question 1
Between which structures do sensory neurones transmit electrical impulses?
From effectors to the central nervous system (CNS).
From effectors to receptors.
From receptors to effectors.
From receptors to the central nervous system (CNS).
Between which structures do sensory neurones transmit electrical impulses?
From effectors to the central nervous system (CNS).
From effectors to receptors.
From receptors to effectors.
From receptors to the central nervous system (CNS).
Where would myelin be found?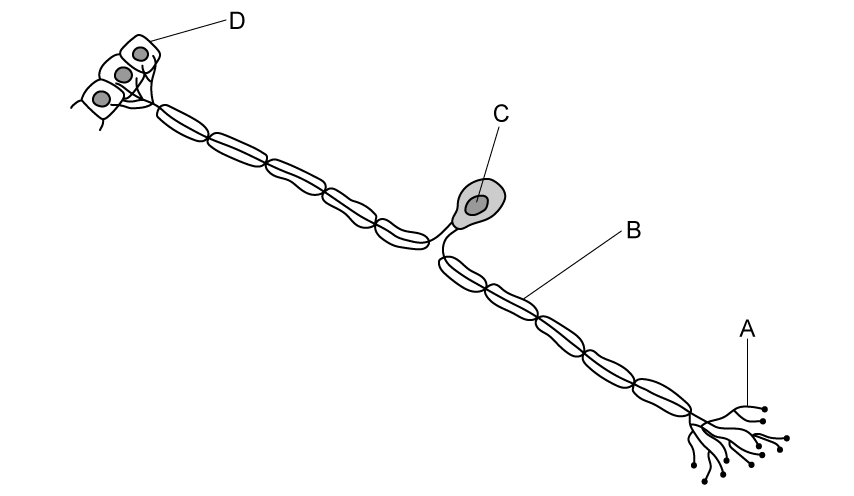
Which event directly results in the production of an action potential?
Diffusion of neurotransmitter across the synaptic cleft.
Fusion of vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
Membrane potential reaches the resting potential.
Membrane potential reaches the threshold potential.
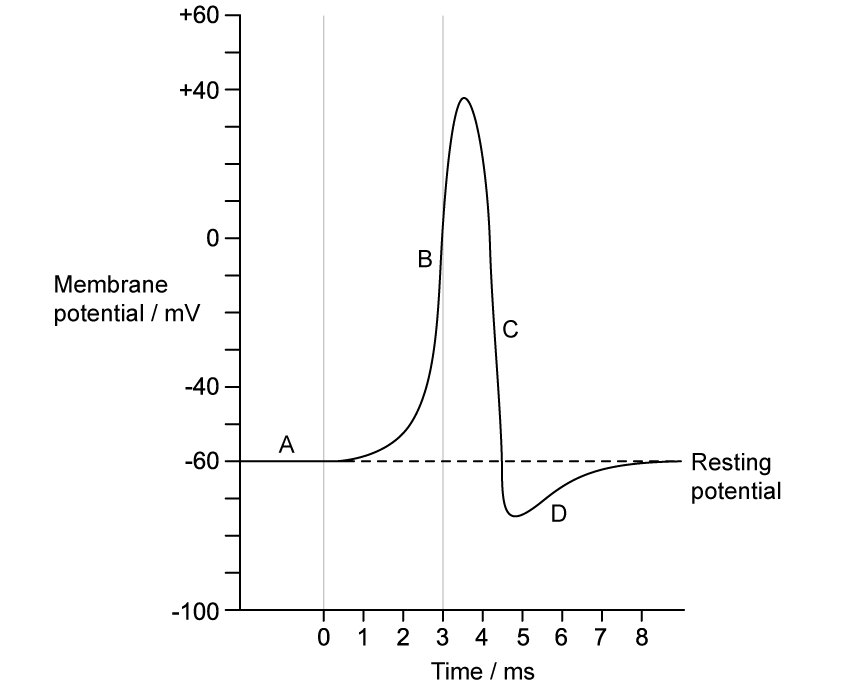
Identify where depolarisation is occurring.
Neurotransmitters leave the presynaptic neurone and enter the synaptic cleft. After this, they travel across the cleft to a receptor on the postsynaptic neurone membrane.
Identify the processes that are required for this to occur.
| Neurotransmitters enter synaptic cleft | Neurotransmitters travel across cleft | |
| A. | Endocytosis | Diffusion |
| B. | Endocytosis | Active transport |
| C. | Exocytosis | Diffusion |
| D. | Exocytosis | Active transport |