Question 1a
Define the following terms:
i) hydrophilic
ii) hydrophobic
[2 marks]
Question 1b
[2 marks]
Question 1c
[1 mark]
Question 1d
[2 marks]
Define the following terms:
i) hydrophilic
ii) hydrophobic
[2 marks]
[2 marks]
[1 mark]
[2 marks]
[3 marks]
State the name of the process by which materials are transported from structures S to R in the diagram below.
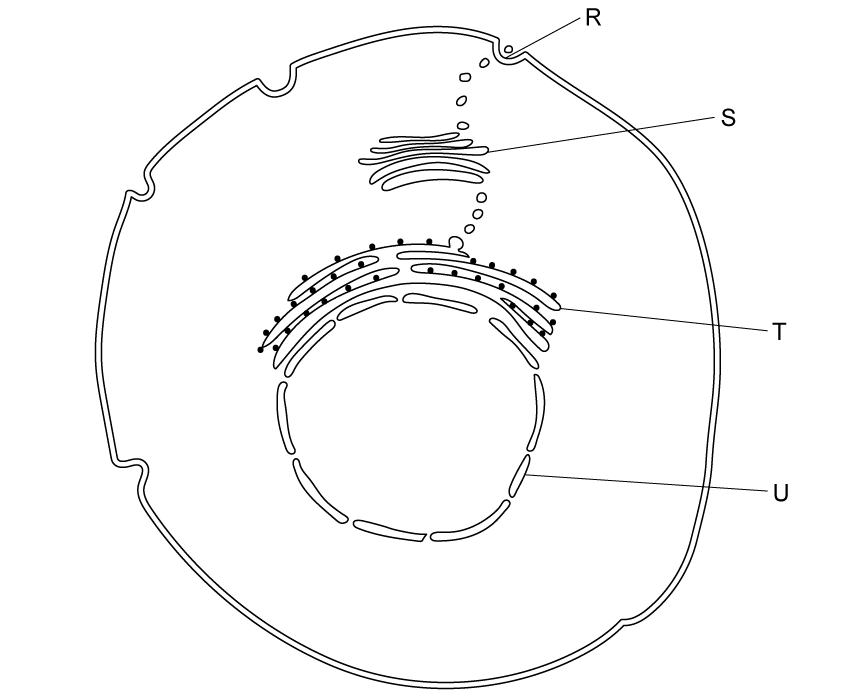
[1 mark]
[1 mark]
The below diagram shows the plasma membrane of an Amoeba sp and some molecules of a small, nonpolar substance known as substance X.
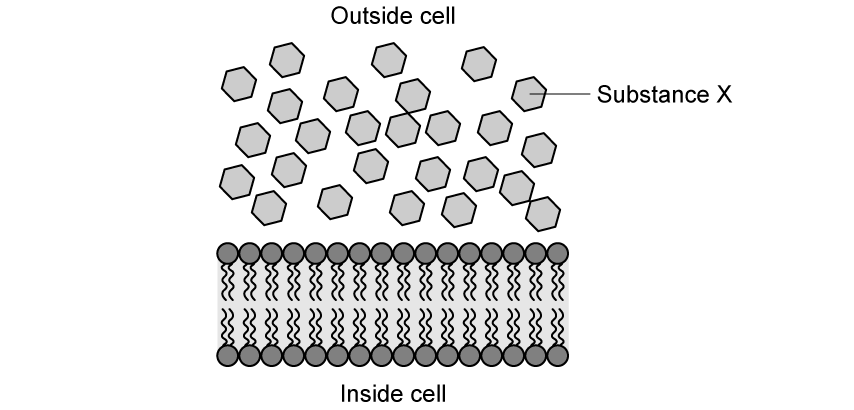
State:
i) the direction substance X would move
ii) the process by which substance X would move
[2 marks]
Amoeba requires potassium ions to assist with detecting prey.
Outline how these ions would be transported across the membrane shown in part (a).
[2 marks]
To feed upon bacteria, Amoeba uses pseudopodia to engulf the bacteria.
State the process used to engulf the bacteria.
[1 mark]
During class, a group of students investigating the impact of different salt concentrations on the mass of celery, collected the results into the table below.
|
Concentration of salt / mol dm-3 |
Initial mass / g |
Final mass / g |
Mass change / g |
Mass change / % |
|
0.0 |
12.2 |
14.5 |
+ 2.3 |
+ 18.9 |
|
0.2 |
10.0 |
11.7 |
+ 1.7 |
+ 17.0 |
|
0.4 |
9.6 |
9.3 |
- 0.3 |
- 3.1 |
|
0.6 |
11.3 |
10.5 |
- 0.8 |
|
|
0.8 |
12.5 |
11.2 |
- 1.3 |
- 10.4 |
|
1.0 |
10.7 |
8.5 |
- 2.2 |
- 20.6 |
i) Calculate the percentage change in mass for 0.6 mol dm-3
[1 mark]
ii) Estimate, with a reason, the osmolarity of the celery tissue
[2 marks]
The diagram below is a student's drawing of three celery cells seen under a light microscope at the end of the investigation from part (c).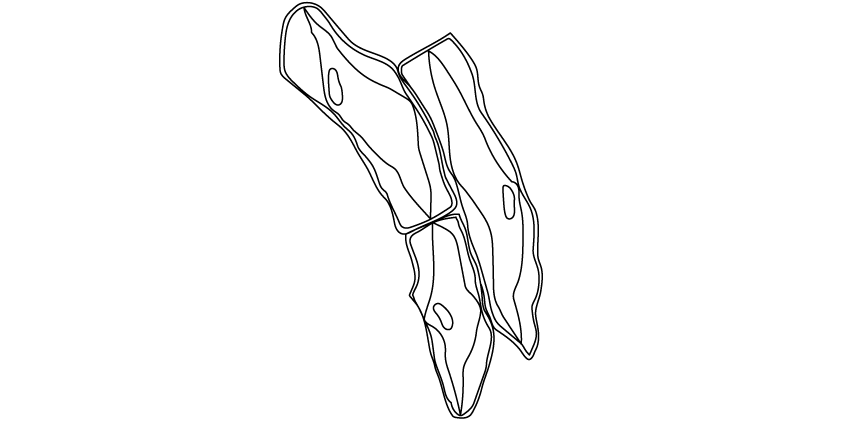
Deduce, with a reason, which salt concentration/s these cells have been immersed in.
[2 marks]
One mark is available for clarity of communication throughout this question.
Outline the functions of five different membrane proteins.
[5 marks]
Distinguish between the following two models of the plasma membrane:
Davson-Danielli and Singer-Nicolson.
[4 marks]
Compare the passive transport of substances across membranes, using named examples.
[6 marks]