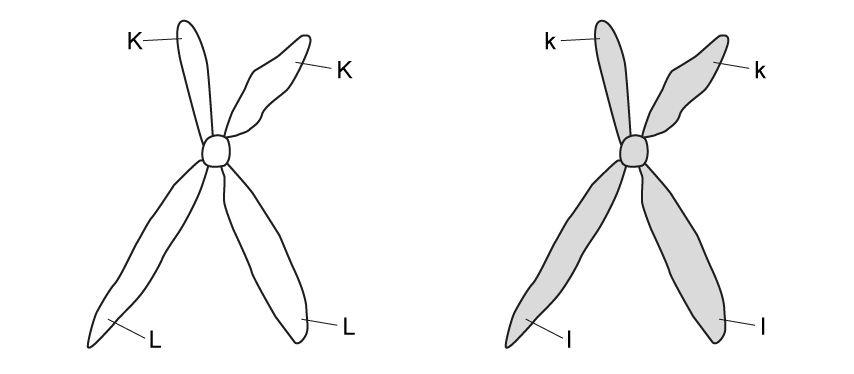Consider the following pair of chromosomes at the start of meiosis.
Which table gives the distribution of alleles in the gametes that would be most realistic, in percentage terms?
Genotype KL
Kl
kL
kl
% distribution 25
25
25
25
Genotype KL
Kl
kL
kl
% distribution 50
0
0
50
Genotype KL
Kl
kL
kl
% distribution 45
5
5
45
Genotype KL
Kl
kL
kl
% distribution 10
40
40
10
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Next Question
Which of the following statements about meiosis are true?
Gene locus can affect the chances of new allele combinations being formed
Gene locus can affect the rate of mutation giving rise to new allele combinations
Crossing over can occur between a chromatid and either of its non-sister chromatids lying alongside it
Independent assortment gives rise to far less variation than crossing over
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Which event causes genetic variety in the gametes formed during meiosis?
Linkage of genes in prophase 1 and crossing over in metaphase 1
Crossing over during prophase 1 and independent assortment of chromosomes during metaphase 1
Linkage of genes in metaphase 1 and independent assortment of chromosomes in prophase 1
Crossing over during metaphase 1 and independent assortment of chromosomes during prophase 1
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Use your knowledge of the number of events that occur in the various stages of meiosis I and meiosis II to suggest which stage occupies around 90% of the time required for a full cycle of human meiosis.
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Which of the following is the best explanation of why the lengths of DNA exchanged during crossing-over tend to be of the same length as each other?
Because breakages occur where distinct alleles fail to line up accurately with each other in the formation of a tetrad.
Because if uneven lengths of DNA are crossed over, restriction enzymes will trim off the unnecessary DNA from the longer chromatid.
Because there is a lack of space in the tightly-packed ball of condensed chromosomes in prophase I, so only short lengths of DNA can cross over.
Because breaks occur in the same base sequences on each non-sister chromatid.
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question