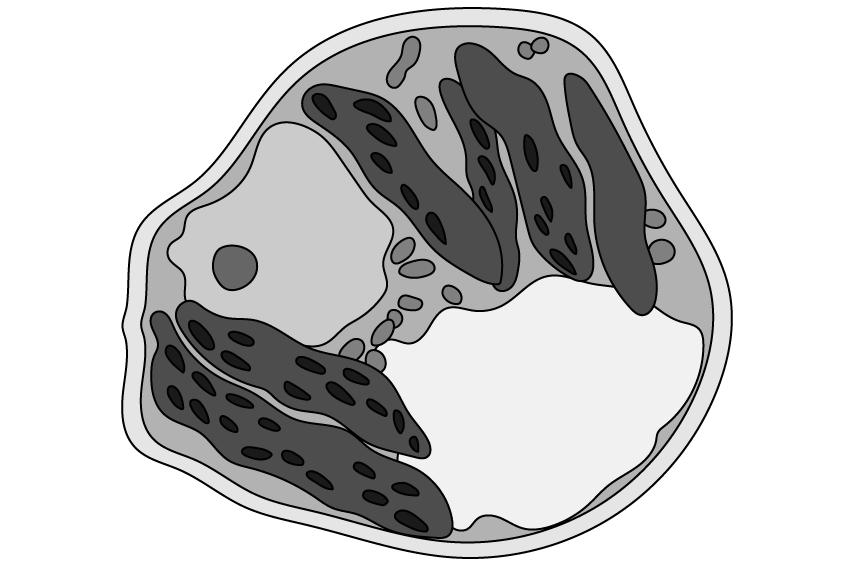
a)
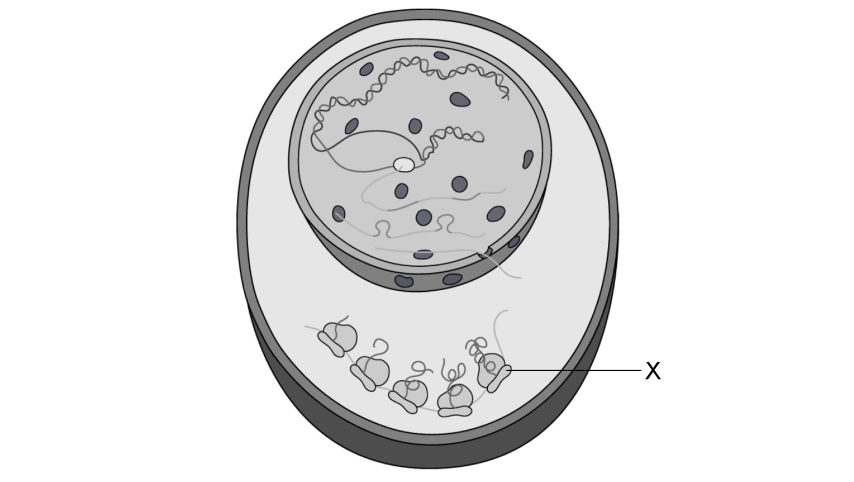
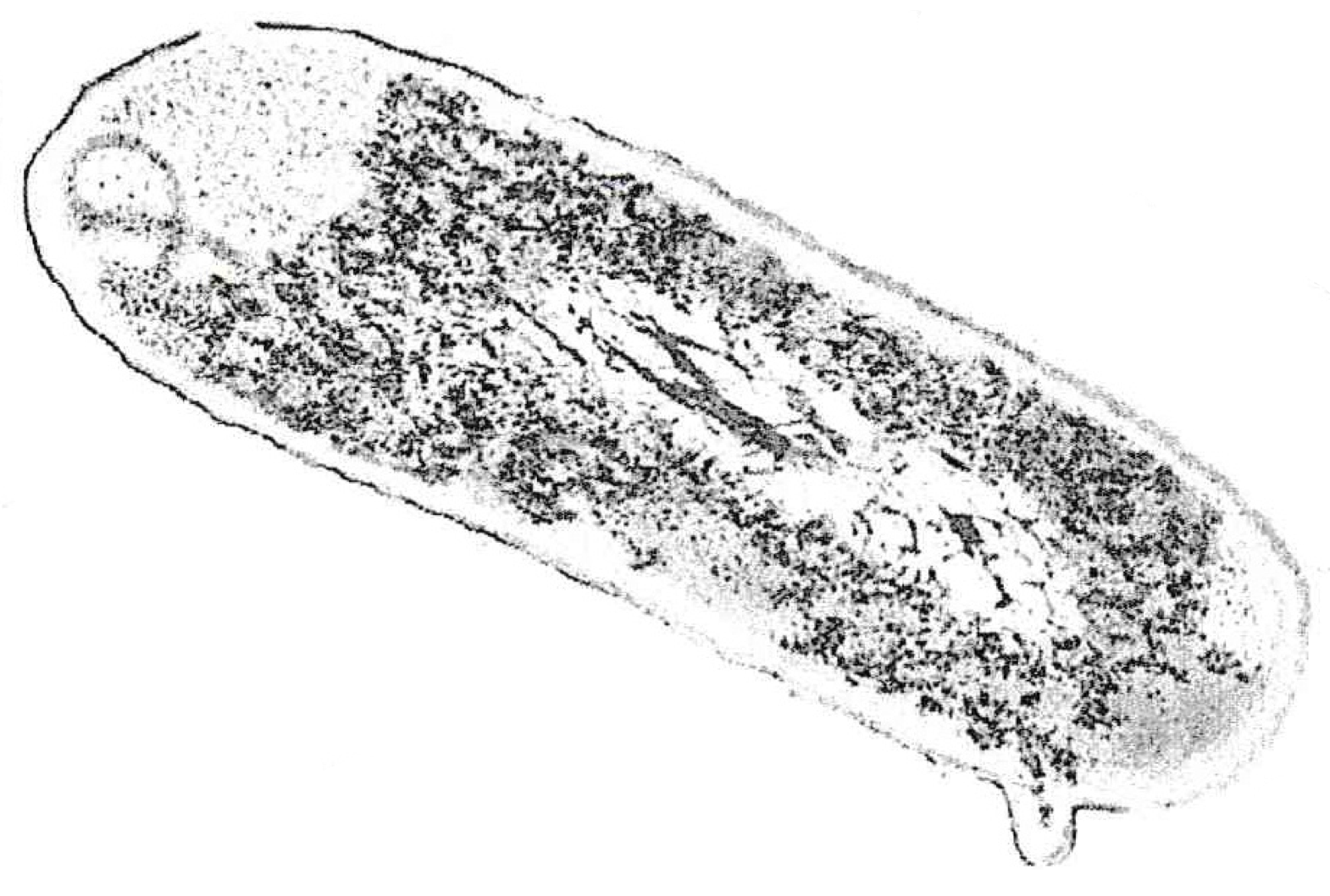
The diagram below is a drawing of an electron micrograph of a cell.
Determine, with a reason, whether the cell is a eukaryotic cell.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Outline why compartmentalisation is an advantage for this cell.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
During class, a student was examining structure X in the cell shown in part (a), and suggested that they could clearly see every detail at the highest magnification with their light microscope.
Explain why the student is not correct.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Determine which process cell Y, seen in part (a), is undergoing.
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
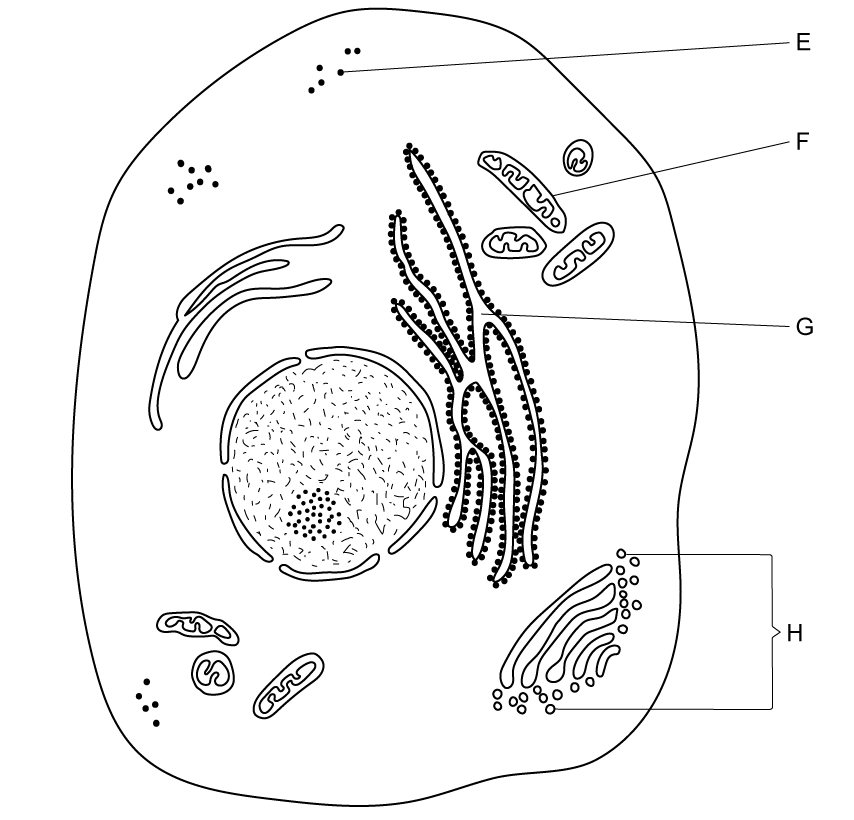
A student drew this eukaryotic cell.
Identify the structures E and G .
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Distinguish between the function of the structures identified in part (a).
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Spontaneous generation was once the widely accepted theory explaining the origin of life. It is now universally accepted that cells come from pre-existing cells.
Outline the evidence that has allowed this change in universal acceptance.
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Miller and Urey’s experiments recreated the conditions thought to have existed on Earth prior to life.
Explain how the apparatus they used provided evidence for how the first cells could have formed.
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
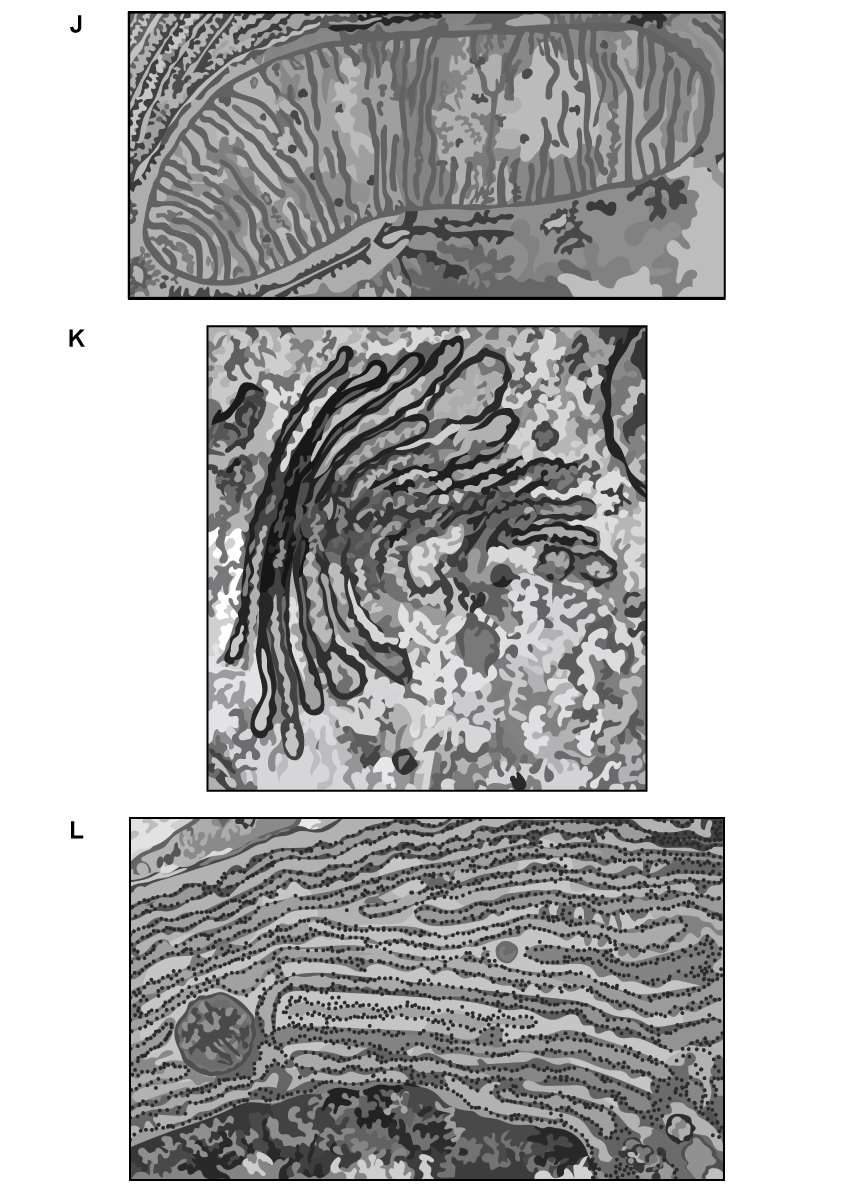
Below are three electron micrographs showing organelles found within a cell.
i) Identify the organelles J, K, and L.
ii) Suggest how the structure of these organelles enables them to function efficiently.
[4 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Compare the structure and function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
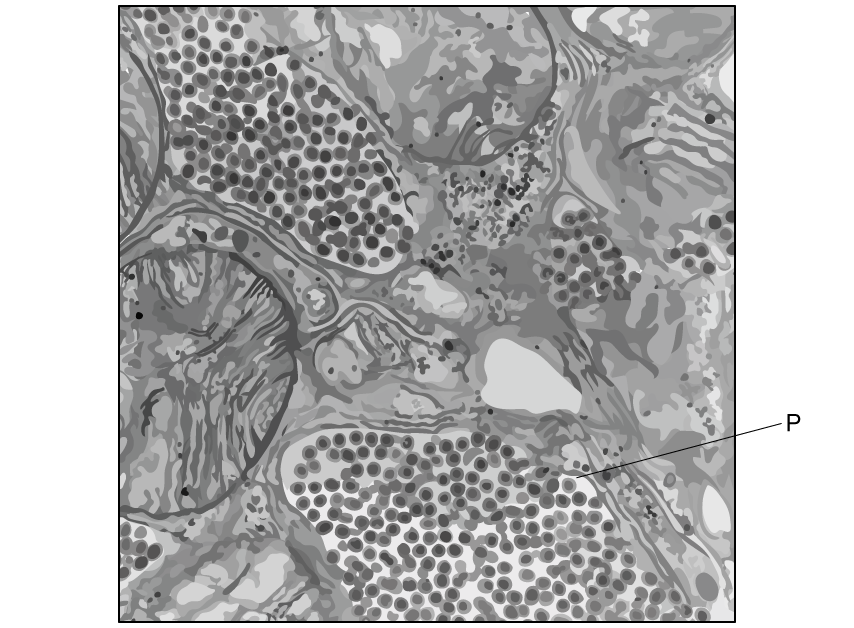
The electron micrograph below is of a salivary gland of a mosquito.
Identify the structures labelled P .
[1 mark]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Draw a labelled biological diagram of the bacterial cell below.
Pradana Aumars, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
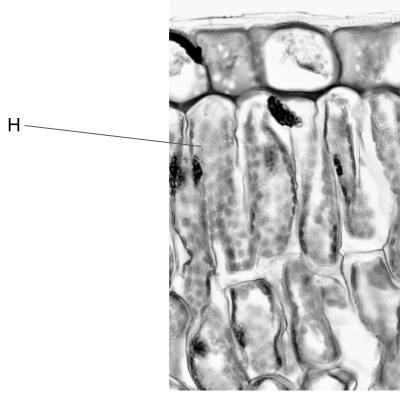
The image below is an electron micrograph of some cells.
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4d/Angiosperm_Morphology_Adaxial_Epidermis_in_Ligustrum_%2836845195186%29.jpg/800px-Angiosperm_Morphology_Adaxial_Epidermis_in_Ligustrum_%2836845195186%29.jpg?20180623001402
Deduce, with a reason, the function of cell H .
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
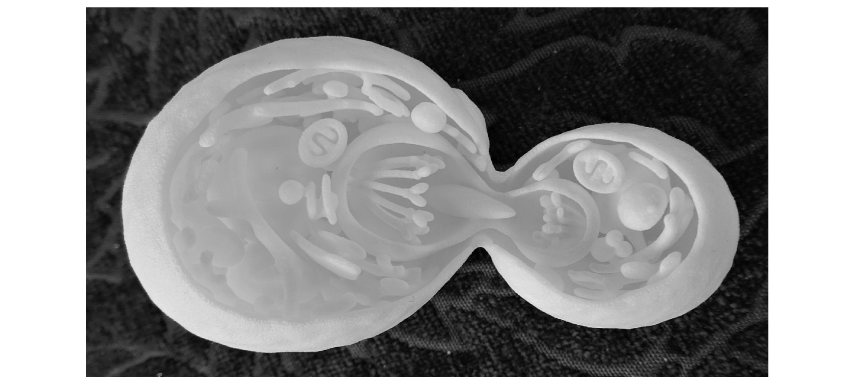
The image below is a 3D-printed model of a cell dividing.
Rosser1954, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Deduce, with a reason, whether this model represents an animal cell, plant cell or neither.
[2 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
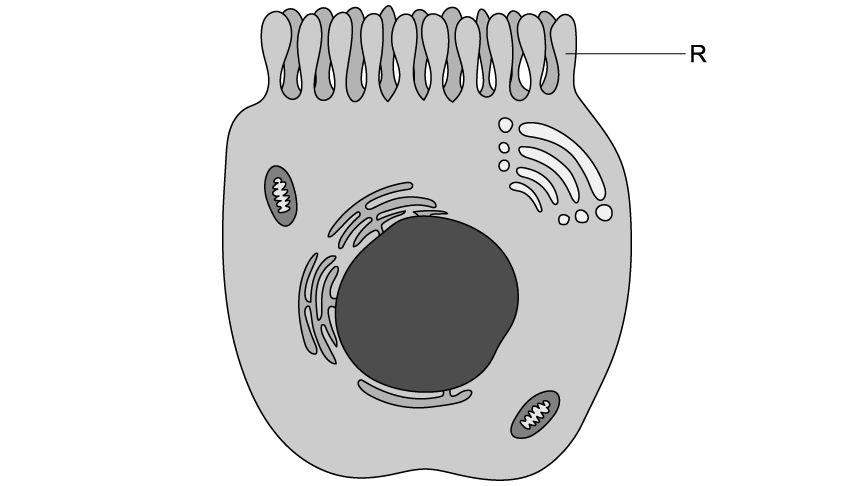
This is an electron micrograph of an immune cell, responsible for specific immunity.
i) Identify R
[1 mark]
ii) Deduce, with a reason, the function of this cell.
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
One mark is available for clarity of communication throughout this question.
a)
A student was examining this electron micrograph of a cell. They identified it as a plant cell.
Evaluate the student’s decision to identify this as a plant cell.
[3 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Explain the Oparin-Haldine hypothesis scientists proposed for the origin of the first cells.
[5 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Euglena gracilis is a unicellular eukaryotic cell that is both heterotrophic and autotrophic.
Discuss the theory that suggests how an organism could have evolved to be a eukaryotic cell that is both heterotrophic and autotrophic.
[7 marks]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question