 Assignment:
Assignment:  Questions on Topic 20.2: Synthetic routes
Questions on Topic 20.2: Synthetic routes
This page of questions can be marked as direct student access either for assigning as a test or for students to work on in their own time. If you do not wish to use student access, links to downloadable versions of the questions and, separately the worked answers, can be found at Printable versions of written tasks.
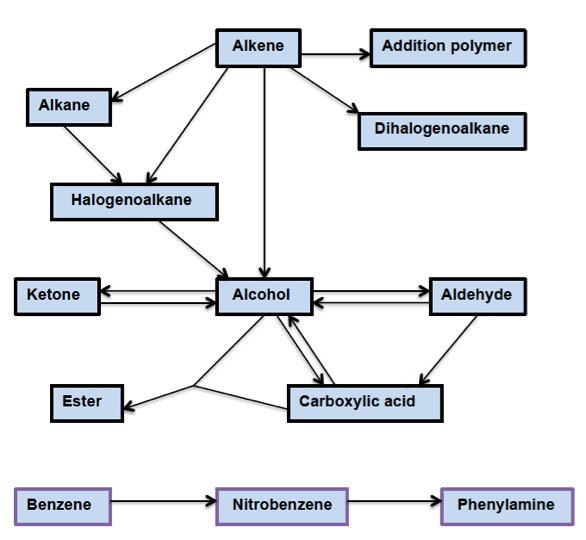
Starting with 2-methylpropane deduce a synthetic pathway to make 2-methylpropanoic acid.
CH3CH(CH3)CH3 → CH3CH(CH3)COOH
For each step specify the reagents and any necessary conditions and write an equation for each step.
10 lines
Step 1: React with chlorine in ultra violet light and separate 1-chloro-2-methylpropane from any other chlorinated products.
CH3CH(CH3)CH3 + Cl2 → CH3CH(CH3)CH2Cl
Step 2: React 1-chloro-2-methylpropane with warm dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to give 2-methylpropan-1-ol.
CH3CH(CH3)CH2Cl + NaOH → CH3CH(CH3)CH2OH + NaCl
Step 3: Oxidize 2-methylpropan-1-ol by refluxing with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution to give the required product
(via 2-methylpropanal).
CH3CH(CH3)CH2OH + H2O → CH3CH(CH3)COOH + 4H+ + 4e−
Design a synthetic route to make butanone starting with but-1-ene.
CH3CH2CHCH2 → CH3CH2COCH3
Knowing that the first step involves the addition of hydrogen bromide to but-1-ene state the name of the mechanism for the first two steps.
10 lines
Step 1: React but-1-ene with hydrogen bromide to form 2-bromobutane (formed in preference to 1-bromobutane according to Markovnikov’s rule).
Mechanism: Electrophilic addition.
Step 2: React 2-bromobutane with warm dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to give butan-2-ol.
Mechanism: a mixture of S
N1 and S
N2.
Step 3: Oxidize butan-2-ol by refluxing with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution to give butanone.
You are provided with ethanal and any inorganic reagents and laboratory equipment you require but no other organic compounds. Design a method to synthesise ethyl ethanoate from ethanal.
CH3CHO → CH3COOC2H5
For each step specify the reagents and any necessary conditions.
10 lines
Step 1: Oxidize some of the ethanal by refluxing with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution to give ethanoic acid.
Step 2: Reduce the rest of the ethanal with sodium borohydride (or lithium aluminium hydride) to give ethanol.
Step 3: Warm the ethanol and the ethanoic acid formed in
Steps 1 and
2 in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid to produce the desired ester.
Show how phenylamine can be synthesised from benzene.
5 lines
Step 1: Covert benzene into nitrobenzene by warming (keep below 50 oC) with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid.
Step 2: Reduce nitrobenzene to phenylamine by using tin and concentrated hydrochloric acid then react the phenylammonium chloride intermediate with sodium hydroxide solution.
Propyl ethanoate is used as a solvent and has the characteristic smell of pears.
Design a synthetic route to make propyl ethanoate starting from 1-chloropropane and chloroethane as the only organic compounds available.
10 lines
Step 1: React 1-chloropropane with warm dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to give propan-1-ol.
Step 2: React chloroethane with warm dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to give ethanol.
Step 3: Oxidize the ethanol obtained in Step 2 by refluxing with acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution to ethanoic acid.
Step 4: React the ethanoic acid with the propan-1-ol obtained from Step 1 by warming in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid to give the ester.
 Assignment:
Assignment: ![]() Questions on Topic 20.2: Synthetic routes
Questions on Topic 20.2: Synthetic routes 
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team