Metallic bonding questions
 Assignment:
Assignment: ![]()
![]() Questions on Topic 4.5: Metallic bonding
Questions on Topic 4.5: Metallic bonding
Explain why graphite, an allotrope of the non-metal carbon, is a good conductor of electricity whereas diamond which is also an allotrope of carbon is a very poor conductor of electricity.
i. Define the term malleable.
ii. Explain why gold conducts electricity and is a malleable metal.
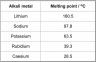
Explain why the melting points of the alkali metals decrease as the atomic number of the metal increases.

Tin, Sn, and lead, Pb, are both in group 14. Both are metals. Suggest one reason why lead, which has a higher atomic number than tin, has a higher melting point.
The precise melting point of an alloy depends upon its exact composition. Stainless steel contains between 5 and 13% chromium. Suggest one reason why the melting point of stainless steel (1510 oC) is very similar to the melting point of steel (1425 - 1540 oC).

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team