Changes to terminology
Introduction
If you are an experienced teacher of the old (pre-2014) programme then just how well prepared are you for the changes that have occurred in the current 2014 programme which was examined for the first time in May 2016? Obviously there are some new topics in the core/AHL such as the Winkler method in Topic 9 and the index of hydrogen deficiency in Topic 11 but are you also aware that you will need to change some of the terminology you used for the old programme even though the basic chemistry is still the same? Try the following 'fun' quiz. The answers to each question can be seen by clicking on the 'eye'
New terminology quiz
1. What is the oxidation number of copper in [CuCl4]2- ?
New syllabus: II
Old syllabus: +2
See 9.1 "Oxidation number and oxidation state are often used interchangeably, though IUPAC does formally distinguish between the two terms. Oxidation numbers are represented by Roman numerals according to IUPAC. • Oxidation states should be represented with the sign given before the number, e.g. +2 not 2+.
2. What is the name of:
-2-chlorobut-2-ene.png)
?
New syllabus: (E)-2-chlorobut-2-ene (or cis-2-chlorobut-2-ene)
Old syllabus: The geometric isomer cis-2-chlorobut-2-ene
See 20.3 "The term geometric isomers as recommended by IUPAC is now obsolete and cis-trans isomers and E/Z isomers should be encouraged in the teaching programme. In the E/Z system, the group of highest Cahn–Ingold–Prelog priority attached to one of the terminal doubly bonded atoms of the alkene (i.e. R1 or R2) is compared with the group of highest precedence attached to the other (i.e. R3 or R4). The stereoisomer is Z if the groups lie on the same side of a reference plane passing through the double bond and perpendicular to the plane containing the bonds linking the groups to the double-bonded atoms; the other stereoisomer is designated as E."
3. The periodic table is arranged in groups and periods. To which group does the element phosphorus belong?
New syllabus: 15
Old syllabus: 5
See 3.1 "The group numbering scheme from group 1 to group 18, as recommended by IUPAC, should be used."
4. What does the symbol ⦵, as used in ΔH⦵f and E⦵ for example, stand for.
New syllabus: Measured at SATP (Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure) 298 K and 100 kPa.
Old syllabus: Measured at STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure) 298 K and 1.01 x 105 Pa.
See 2014 data booklet Section 2. "STP conditions = 273 K and 100 kPa SATP conditions = 298 K and 100 kPa" Note that both SATP and STP are at 1.00 x 105 Pa. In the old programme it was 1.01 x 105 Pa (or 1 atm). In the past there was confusion also about the temperature. For the gas laws the temperature of 273 K was taken but 298 K was taken when referring to thermodynamic quantities such as ΔH⦵f even though ⦵ was usually referred to as 'standard conditions'.
5. What type of forces of attraction exists between octane molecules in liquid octane?
New syllabus: London (dispersion) forces
Old syllabus: van der Waals' forces
See 4.4 "The term “London (dispersion) forces” refers to instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces that exist between any atoms or groups of atoms and should be used for non-polar entities. The term “van der Waals” is an inclusive term, which includes dipole–dipole, dipole-induced dipole and London (dispersion) forces."
6. What is the molar volume of a gas at STP?
New syllabus: 2.27 × 10−2 m3 mol−1 (= 22.7 dm3 mol−1) measured at 273 K and 100 kPa
Old syllabus: 2.24 × 10–2 m3 mol–1 (= 22.4 dm3 mol–1) measured at 273 K and 1.01 × 105 Pa
See new data booklet.
7. Name three functional groups present in aspirin and the functional group present in propan-2-ol.
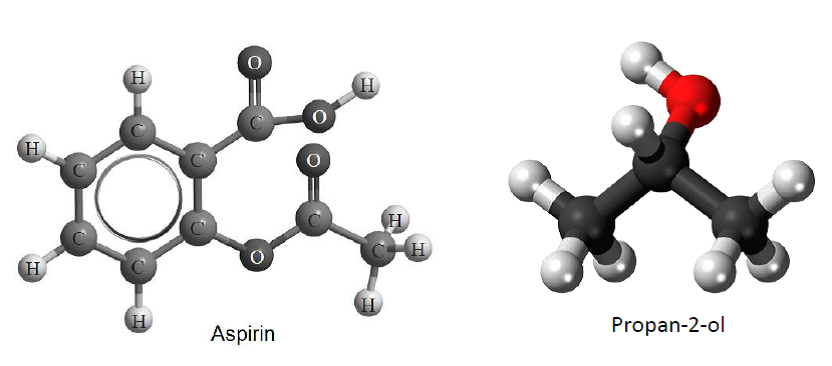
New syllabus: Aspirin - phenyl, ester and carboxyl; Propan-2-ol - hydroxyl
Old syllabus: Aspirin - benzene ring, ester and carboxylic acid; Propan-2-ol - alcohol
See 10.1 "The distinction between class names and functional group names needs to be made. E.g. for OH, hydroxyl is the functional group whereas alcohol is the class name."
8. Is scandium considered to be a transition element?
New syllabus: Yes
Old syllabus: No
See 13.1 and Section 14 of the new data booklet. The old syllabus specifically stated under assessment statement 13.2.2."Explain why Sc and Zn are not considered to be transition elements." The new syllabus just states that zinc is not considered a transition element.
9. ![]() What is the electron configuration of a potassium atom (Standard Level only)?
What is the electron configuration of a potassium atom (Standard Level only)?
New syllabus: 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 or [Ar]4s1
Old syllabus: 2.8.8.1
This is a slightly trick question as the old syllabus actually called it electron arrangement not electron configuration. See 2.2 "Full electron configurations (eg 1s22s22p63s23p4) and condensed electron configurations (e.g. [Ne] 3s23p4) should be covered."
10. When deducing the shape of a simple molecule or ion using VSEPR theory the term 'negative charge centre' was used on the old syllabus. What has this term been replaced by on the new syllabus?
New syllabus: Electron domain
See 4.3 "The term “electron domain” should be used in place of 'negative charge centre'."
So how did you do? If you got all ten correct then you are an ace teacher and should probably be running workshops! If you got zero then maybe you should either go on a workshop to refresh your knowledge or maybe just retire gracefully. I'll attach a pdf listing the main changes but of course they are all in the new guide (or data booklet).
![]() Main changes to terminology for the 2014 programme
Main changes to terminology for the 2014 programme

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team