5 & 15. Energetics & thermochemistry (1)
 Energetics / thermochemistry (1)
Energetics / thermochemistry (1)
For each question choose the answer you consider to be the best.
1. When some solid ammonium nitrate was dissolved in water the temperature decreased
from 22 oC to 3 oC. What can be deduced from this observation?
A. The dissolving is endothermic and ∆H is positive.
B. The dissolving is endothermic and ∆H is negative.
C. The dissolving is exothermic and ∆H is positive.
D. The dissolving is exothermic and ∆H is negative.
2. Which of the following conditions normally apply to the standard enthalpy change for a reaction, ∆H![]() ?
?
I. A pressure of 100.0 kPa
II. A temperature of 298 K
III. One mol of all reactants and all products
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
3. Which statements are correct for all exothermic reactions?
I. The products are more stable than the reactants
II. The bonds in the products are stronger than the bonds in the reactants
III. The enthalpy of the products is less than the enthalpy of the reactants
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
4. Which is a correct statement concerning the reaction shown?
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) ∆H![]() = – 92 kJ
= – 92 kJ
A. 92 kJ of energy are absorbed for every mol of ammonia formed.
B. 92 kJ of energy are released for every mol of ammonia formed.
C. 46 kJ of energy are absorbed for every mol of ammonia formed.
D. 46 kJ of energy are released for every mol of ammonia formed.
5. The heat capacities (in kJ kg-1 K-1) of four elements are:
carbon (graphite) 0.709
copper 0.385
gold 0.129
iron 0.449
Which element will show the greatest increase in temperature if 2 kJ of heat is supplied to 0.100 kg samples of each element at the same initial temperature?
A. carbon (graphite)
B. copper
C. gold
D. iron
6. The heat produced when 0.010 mol of propanone was combusted raised the temperature of 250 g of water by 14 oC.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J g-1 K-1.
Which is the correct expression for value of the enthalpy of combustion of propanone (in J mol-1)?
A. − 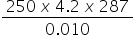
B. − 
C. − 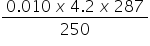
D. − (250 x 4.2 x 14 x 0.010)
7. When one mol of magnesium and one mol of hydrogen are combusted the enthalpy changes are – 602 kJ and - 242 kJ respectively.
Mg(s) + ½ O2(g) → MgO(s) ∆H = – 602 kJ
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(g) ∆H = – 242 kJ
What is the enthalpy change for the reduction of one mol of magnesium oxide by hydrogen?
MgO(s) + H2(g) → Mg(s) + H2O(g)
A. + 844 kJ
B. – 844 kJ
C. – 360 kJ
D. + 360 kJ
8. The enthalpy change for the dimerisation of two mol of nitrogen dioxide to form one
mol of dinitrogen tetroxide is – 57 kJ.
2NO2(g) → N2O4 ∆H![]() = – 57 kJ
= – 57 kJ
The enthalpy change for the formation of one mol of NO2(g) from its elements is + 33 kJ
½ N2(g) + O2(g) → NO2(g) ∆H![]() = + 33 kJ
= + 33 kJ
What is the enthalpy change for the formation of one mol of dinitrogen tetroxide from its elements?
N2(g) + 2O2(g) → N2O4(g)
A. + 9 kJ
B. – 9 kJ
C. + 24 kJ
D. – 24 kJ
9. Which of the following enthalpy changes can be calculated using only bond enthalpies and average bond enthalpies?
I. C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g)
II. C8H16(l) + H2(g) → C8H18(l)
III. CH4(g) + 4F2(g) → CF4(g) + 4HF(g)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
10. Ethane can react with chlorine in ultraviolet light to form chloroethane:
C2H6(g) + Cl2(g) → C2H5Cl(g) + HCl(g)
The relevant bond enthalpies are:

What is the enthalpy change, ∆H, for this reaction (in kJ)?
A. – 99
B. + 99
C. + 341
D. – 315
11. Which expression gives the correct value for the standard enthalpy change of combustion
of glucose in kJ mol-1?
C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
| Compound | C6H12O6(s) | CO2(g) | H2O(l) |
| ΔHf | – 1273 | – 394 | – 286 |
A. 6(-394) + 6(-286) –1273
B. 6(-394) + 6(-286) – (– 1273)
C. 6[(-394) + (-286) –1273]
D. 6[(-394) + (-286) – (– 1273)]
12. Which are endothermic steps in the Born Haber cycle for the formation of sodium bromide?
I. Br(g) + e- → Br-(g)
II. Na(g) → Na+(g) + e-
III. Na(s) → Na(g)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
13. Which is the correct equation for the lattice enthalpy of magnesium chloride?
A. Mg2+(g) + 2Cl-(g) → MgCl2(s)
B. Mg(s) + Cl2(g) → MgCl2(s)
C. Mg2+(g) + 2Cl-(g) → MgCl2(g)
D. Mg(s) + 2Cl(g) → MgCl2(s)
14. Which reaction in the Born Haber cycle for the formation of magnesium oxide is the most exothermic?
A. O(g) + 2e- → O2-(g)
B. Mg(s) + O2(g) → MgO(s)
C. Mg(g) → Mg2+(g) + 2e-
D. Mg2+(g) + O2-(g) → MgO(s)
15. Which compound has the highest lattice enthalpy?
A. NaF
B. NaI
C. MgO
D. MgS
16. Which reaction will have the largest positive entropy change?
A. H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g)
B. SO2(g) + 2O2(g) → 2SO2(g)
C. Mg(s) + ½ O2(g) → MgO(s)
D. PCl5(g) → PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
17. Which change does not lead to an increase in entropy?
A. Dissolving salt in water
B. Hydrogenating unsaturated fats
C. Boiling water
D. Melting ice
18. What is the standard entropy change (in J K-1 mol-1) for the following reaction?
NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s)
| NH3(g) | HCl(g) | NH4Cl(s) | |
| S | 193 | 187 | 96 |
A. – 96
B. + 96
C. – 284
D. + 284
19. Which are the correct signs for a reaction that is spontaneous at low temperatures but non-spontaneous
at high temperatures?

20. The standard enthalpy change, ∆H![]() , for a chemical reaction is – 100 kJ mol-1 and the entropy change
, for a chemical reaction is – 100 kJ mol-1 and the entropy change
at 27 oC for the reaction is + 10 J K-1 mol -1. What is the value of ∆G![]() (in kJ) for this reaction?
(in kJ) for this reaction?
A. – 2900
B. – 103
C. – 370
D. – 97
 Answers
Answers
1. A, 2. A, 3. D, 4. D, 5. C, 6. B, 7. D, 8. A, 9. B, 10. A,
11. B, 12. C, 13. A, 14. D, 15. C, 16. D, 17. B, 18. C, 19. C, 20. B.
Download the Energetics / thermochemistry ![]() Topics 5 & 15 MC (1) test
Topics 5 & 15 MC (1) test ![]()
Download the answer grid with the correct answers to cut out for Topics 5 & 15 MC (1) Answers ![]()

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team