Which statement is not true about circular apertures?
Circular apertures allow a cone of light to enter a region behind the aperture
Circular apertures allow light to act like a point source
The diffraction of light through a circular aperture produces a diffuse disc surrounded by fainter concentric circular rings
The diffraction pattern produced by circular apertures produces a central linear fringe with subsequent alternating dark and light fringes
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Next Question
What does the Rayleigh criterion describe?
The diffraction of light through a single slit
The diffraction of light through a double slit
The diffraction of light through multiple slits
The minimum separation between two light sources that can be resolved into two distinct objects
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
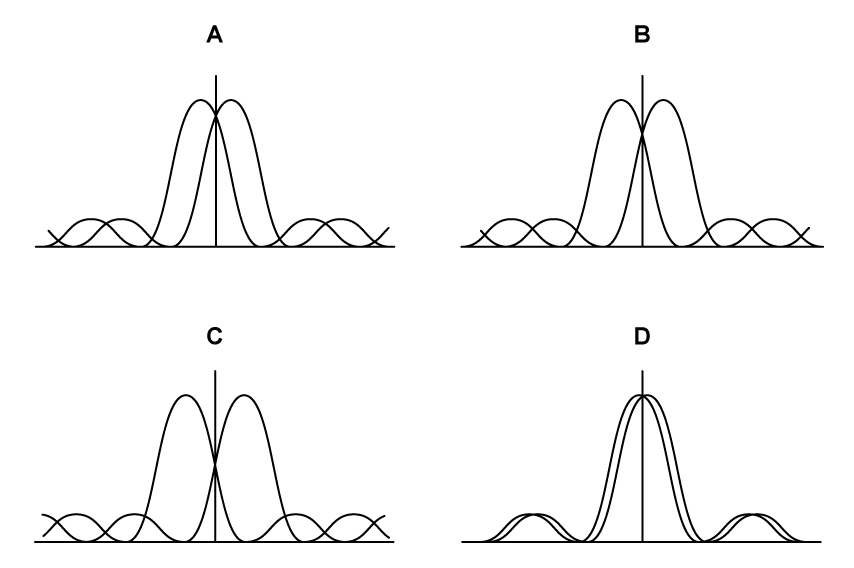
The diagram below shows the light from two point sources, s1 and s2 passing through a circular aperture.
What name is given to the angle shown as θ ?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Light from two sources with wavelength λ is passed through a circular aperture with diameter b , producing an angle of diffraction θ .
According to the Rayleigh criterion, how would the angle of diffraction be affected if the diameter of the aperture was doubled?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Which of the following options would not increase the resolution of two objects?
Decreasing the wavelength of the light
Increasing the angular separation of the objects
Increasing the diameter of the aperture
Increasing the angle of diffraction
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
The Rayleigh criterion can be presented as:
Which option provides the correct quantities represented in the expression?
s
d
λ
b
A.
Distance between sources
Distance between source and aperture
Wavelength
Diameter of aperture
B.
Distance between source and aperture
Distance between sources
Wavelength
Diameter of aperture
C.
Wavelength
Diameter of aperture
Distance between sources
Distance between source and aperture
D.
Diameter of aperture
Wavelength
Distance between source and aperture
Distance between sources
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
The Rayleigh criterion can also be applied to diffraction gratings.
Incident light with an average wavelength of 600 nm is incident on a diffraction grating. The difference between the wavelengths is 25 nm. How may slits would the grating need to have to resolve fully the second order of diffraction?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Which of the following objects can be resolved according to the Rayleigh criterion?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
The Rayleigh criterion can be expressed as:
A telescope is aimed at two objects that are known to be 10 cm apart. The angle of diffraction is 4.5 × 10−5 rad.
Can the objects be resolved at a distance of 10 km?
Yes, because
No, because
Yes, because
No, because
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
It is not possible to view an object smaller than the wavelength used to see it.
Which of the following can be used to resolve objects smaller than the wavelengths of visible light, such as atoms?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question