Question 1
Which is the correct unit for electromotive force?
Newton, N
Ampere, A
Volt, V
Coulomb, C
Which is the correct unit for electromotive force?
Newton, N
Ampere, A
Volt, V
Coulomb, C
A cell has an emf of 5 V and internal resistance 5 Ω and is connected to a lamp of resistance 200 Ω. What is the current in the cell?
0.10 A
0.050 A
0.025 A
0.024 A
Which statement correctly describes internal resistance?
The internal resistance of a cell is measured in amperes.
When the internal resistance is zero, the terminal pd of a cell is equal to its emf.
Internal resistance of a cell is due to resistance in the circuit wires.
Internal resistance within a cell increases its emf.
Which graph correctly shows the variation of terminal potential difference V of a cell with current I ?
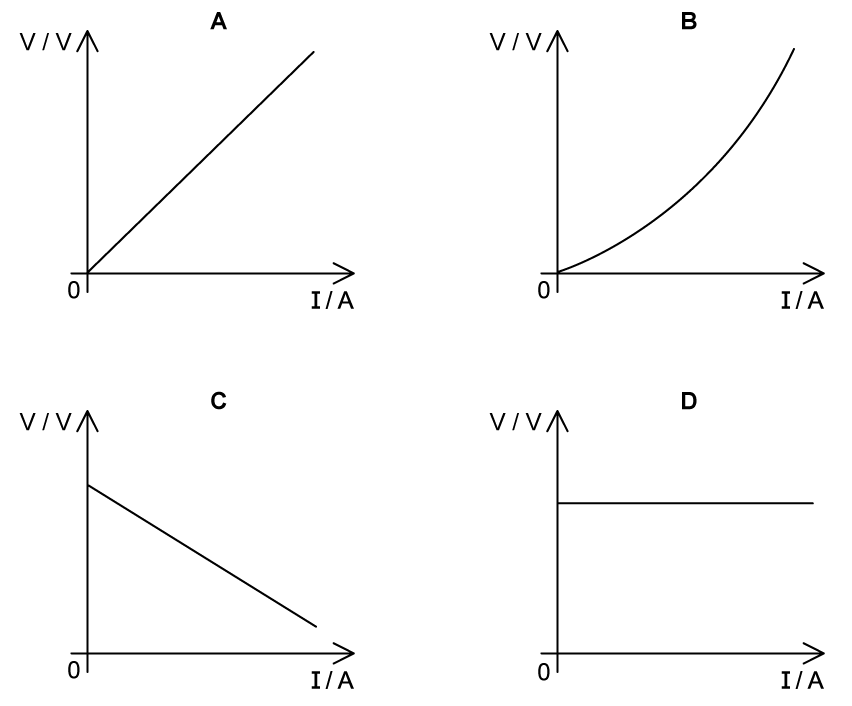
A graph showing the variation of terminal potential difference V of a cell with the current I flowing through it is shown:
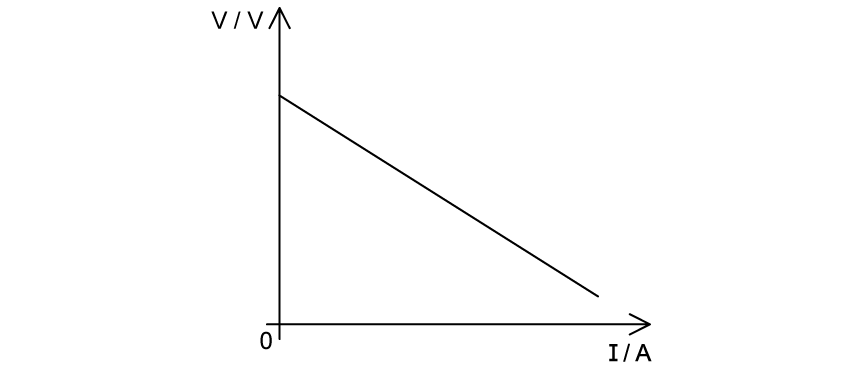
Which line identifies the quantity which is represented by the magnitude of the slope of the graph?
The internal resistance of the cell.
The terminal potential difference provided by the cell.
The current through the cell.
The external resistance in the circuit.
In a circuit-building investigation, two rechargeable 1.5 V AA batteries and one non-rechargeable 9.0 V C battery are used. What types of cells are these?
| rechargeable 1.5 V AA | non-rechargeable 9.0 V C | |
| A. | primary cell | primary cell |
| B. | primary cell | secondary cell |
| C. | secondary cell | primary cell |
| D. | secondary cell | secondary cell |
Primary and secondary cells both transfer energy due to the movement of electrons between the positive and negative terminals of the cell.
Which row correctly identifies the direction of flow of electrons when the cell is in use, powering a circuit?
| primary cell | secondary cell | |
| A. | from negative to positive | from positive to negative |
| B. | from negative to positive | from negative to positive |
| C. | from positive to negative | from negative to positive |
| D. | from positive to negative | from positive to negative |
For the discharge curve shown, which line most closely describes the discharging voltage of the cell over time?
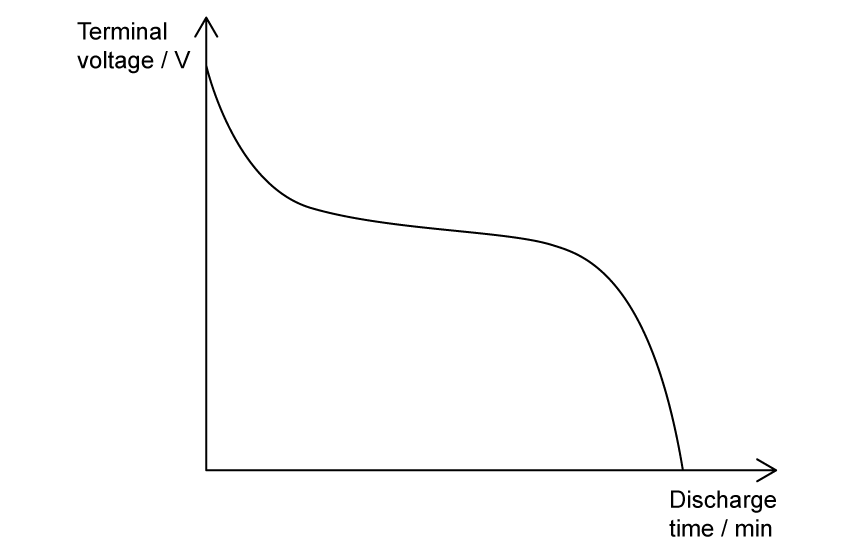
| at start of use | during most use | at end of use | |
| A. | slow | fast | plateaus |
| B. | fast | plateaus | fast |
| C. | plateaus | plateaus | fast |
| D. | fast | slow | slow |
Three discharge curves are shown, for three identical cells. The cells are connected to three different circuits, I, II and III.
By interpreting the graph, what can be said about the circuits?
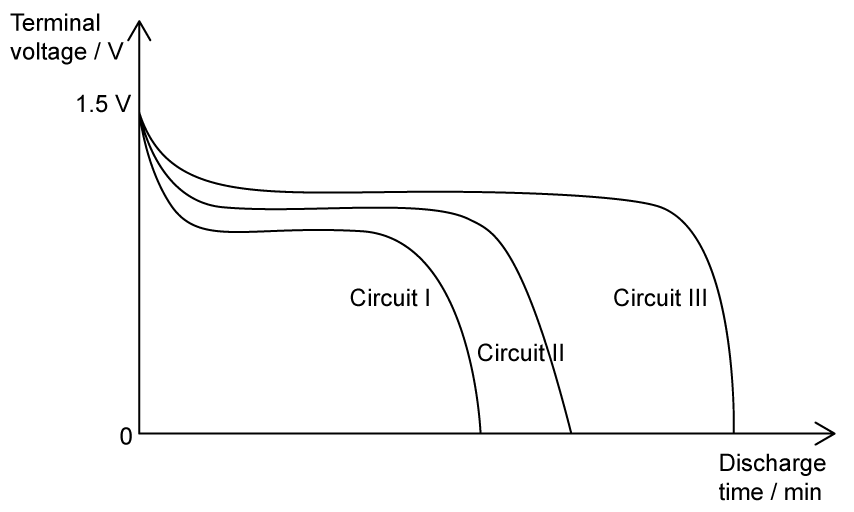
Circuit I draws less current than circuit III
Circuit II includes an ammeter
Circuit I draws more current than circuit III
Circuit II includes a voltmeter
Which of the following statements about the emfof a cell is correct?
The emf is measured in Newtons
, where R is the load resistance and r is the internal resistance
is the amount of chemical energy transferred to electric energy, per unit of charge through a cell
The emf of a cell is always less than its terminal – or output – potential difference