Question 1
In which of these circuits can full-wave rectification be achieved?
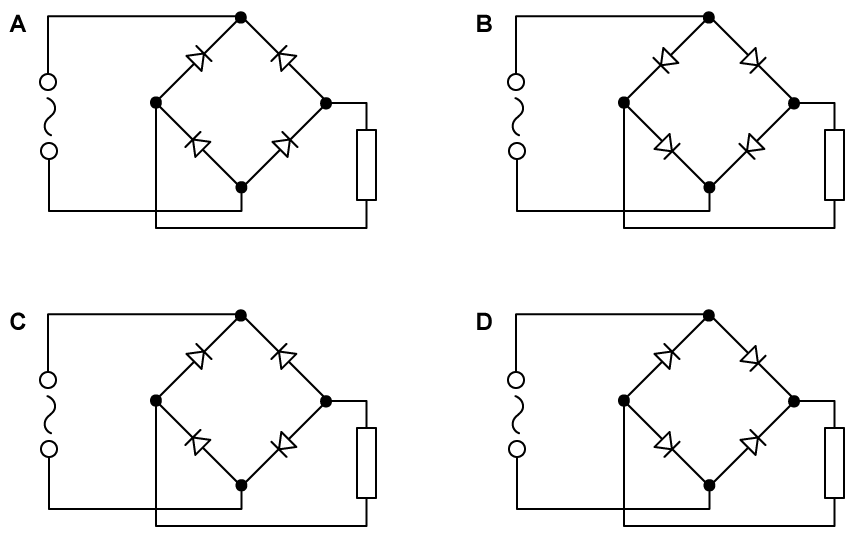
In which of these circuits can full-wave rectification be achieved?

The sinusoidal current shown below flows through an 90 Ω resistor. It has an rms value of 2 A.
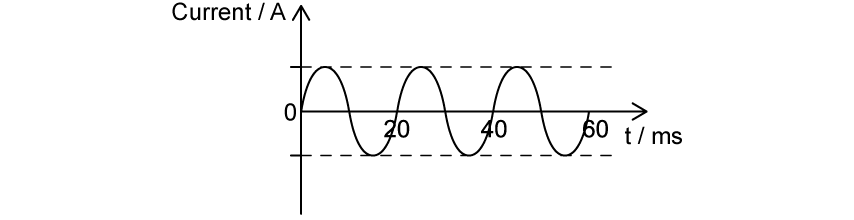
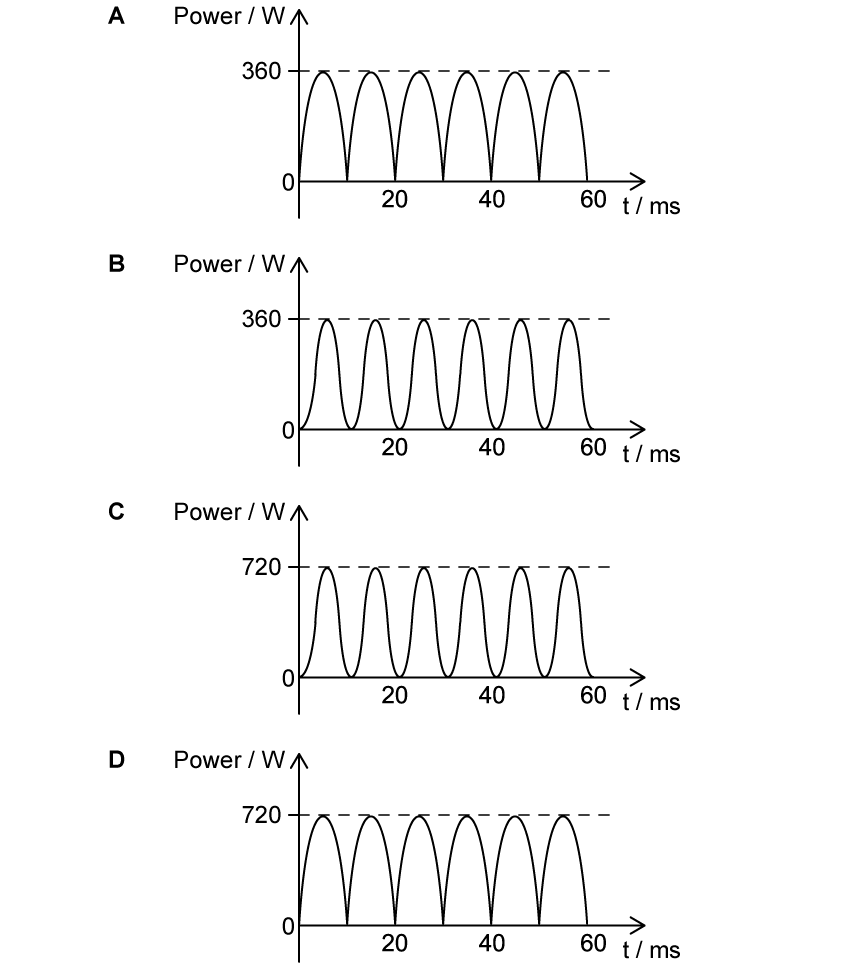
Which graph correctly shows the power dissipated in this resistor?
A cathode-ray oscilloscope screen with a grid of 1cm squares displays an alternating potential difference waveform. The gain and time base dials are set to show the full waveform on the screen.
Which mathematical expression correctly describes the waveform of the potential difference?
A coil, P, is connected to an alternating supply of potential difference. Another coil, Q, is placed nearby and connected to an oscilloscope.
A thick iron loop is now introduced, such that it passes through the centre of coil P and the centre of coil Q.
Which of the following shows the effect on the oscilloscope trace of introducing this new component?
| Height of trace | Number of cycles on screen | |
| A. | increase | increase |
| B. | increase | stays the same |
| C. | stays the same | increase |
| D. | stays the same | stays the same |
A step-up transformer is being tested before its use in a power distribution system that passes underwater.
The secondary coil has 200 turns and is connected to a sample section of insulated power cable. The four metre-long cable has a resistance of 1050 Ω m-1. This is passed under a tank of water containing 5 L of water. The primary coil has 10 turns and is connected to a supply of alternating current.
In 16 seconds, the temperature of the water increases from 23.5 °C to 24.5 °C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg-1 °C-1
Assuming of the average power dissipated in the cable is transferred to the water's thermal store, what is the rms current of the alternating supply connected to the primary coil?
A
A
A
A
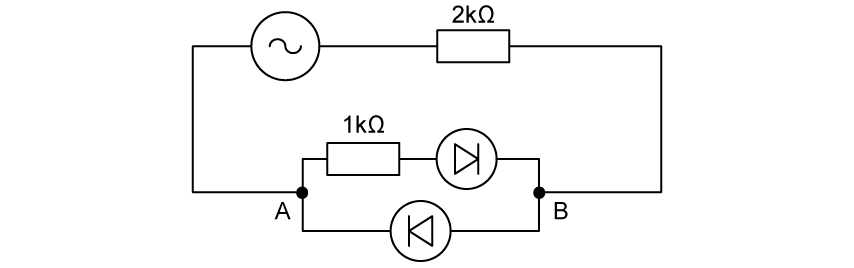
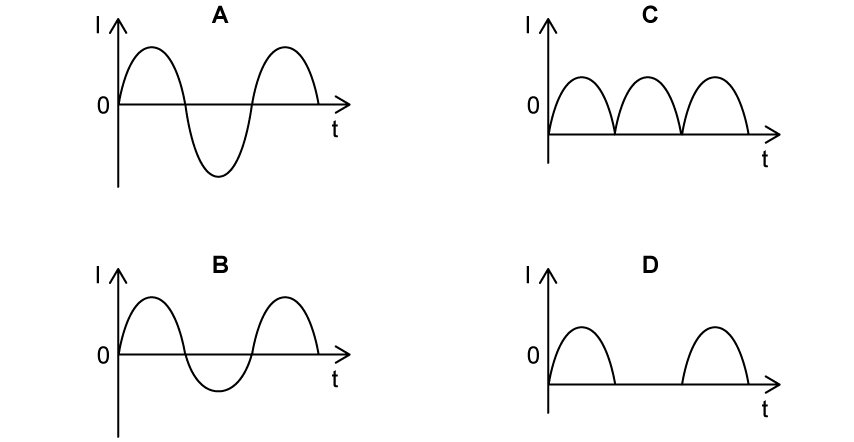
Which of the following graphs best represents the variation of current I with time t through the segment AB in the circuit below?
A power station generates power P to be delivered to a city distance L away using cables with a total resistance of R. This power is generated at voltage Vp and then stepped up by an ideal transformer before travelling along the cables.
The turns of the coils are in a ratio of N : 1, where N > 1. The station spends £0.10 per kW h of energy produced.
How much money is lost by the station in one hour due to power loss in the cables?
The graph shows the output voltage from a half-wave rectifier. The load resistor has a resistance of 2.0 kΩ. An engineer wishes to smooth the output voltage by placing a capacitor in parallel across the load resistor.
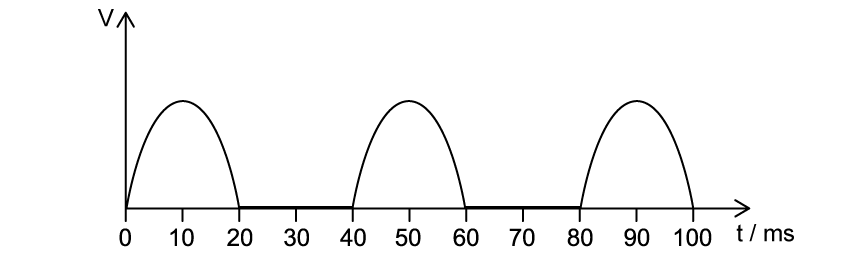
Which capacitor would be best for this task?
30 pF
40 nF
50 mF
6 F
The voltage of an a.c. source varying with time t is shown in the graph below.
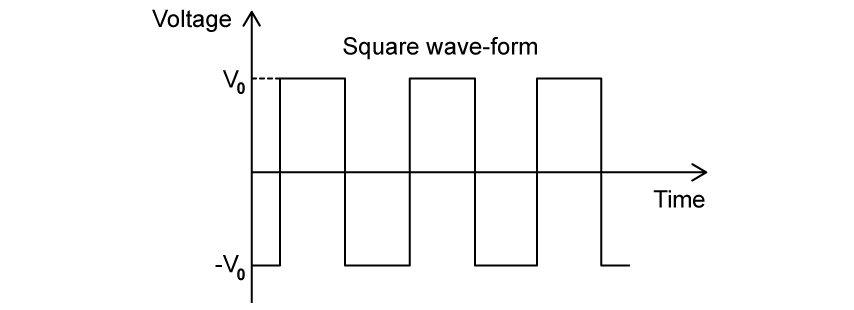
Which of the following gives the correct expression for the root-mean-square voltage, Vrms, if the peak voltage is V0?
Power is generated in a power station, stepped up and then transmitted around the country via transmission cables before being stepped down again to be used in homes.
The total power incident on one transmission cable is 1000 MW. The cable is 100 km long and has a resistance of 0.02 Ω per km. As the electricity is transported along the cable 50% of the power is lost by the time it gets to the transformer. The primary coil has 3000 turns and the secondary coil 300 turns.
How much current will be present in the transmission wire as it comes out of the transformer?
5 A
50 A
500 A
5000 A