Assess your score
View Answer
4.7 × 1023 molecules of neon gas is trapped in a cylinder.
(b)
Calculate the number of moles of neon gas in the cylinder.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
The molar mass of neon gas is 20 g mol–1 .
(c)
Calculate the mass of the neon gas in the cylinder.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
The cylinder containing the neon gas has a volume 5.2 m3 and pressure of 600 Pa.
(d)
Calculate the temperature of the gas.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
(a)
State what is meant by an ideal gas.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
State the conditions for a real gas to approximate to an ideal gas.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Describe how the ideal gas constant, R, is defined.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
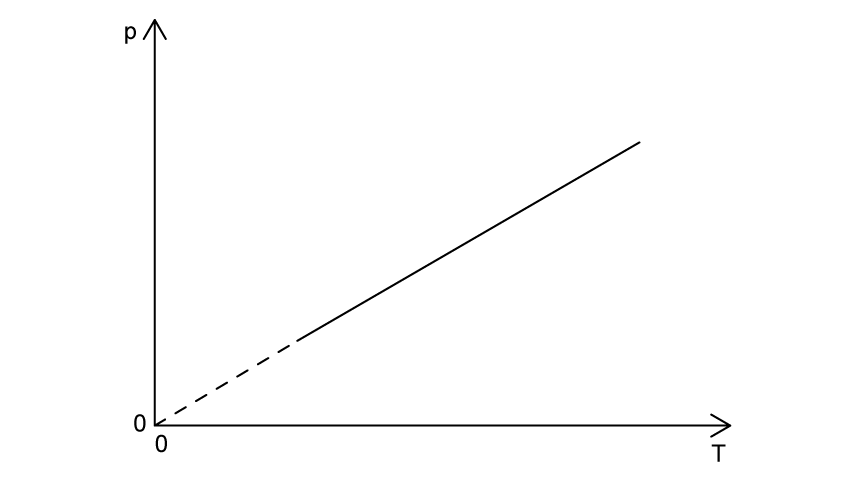
The graphs shows how pressure, p , varies with absolute temperature, T, for a fixed mass of an ideal gas.
(d)
Outline the changes, or otherwise, to the volume and density of the ideal gas as the absolute temperature increases.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
(a)
State three assumptions of the kinetic model of an ideal gas.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
A tank of volume 21 m3 contains 7.0 moles of an ideal monatomic gas. The temperature of the gas is 28 °C.
(b)
Calculate the average kinetic energy of the particles in the gas.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
The following paragraph explains, with reference to the kinetic model of an ideal gas, how an increase in temperature of the gas leads to an increase in pressure.
A ________ temperature implies ________ average speed and therefore higher ________. This increases the ________ transferred to the walls from ________ frequent collisions. This increased ________ per collision leads to an increased ________.
(c)
Complete the sentences using keywords from the box below.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Calculate the pressure of the gas described in part (b).
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
(a)
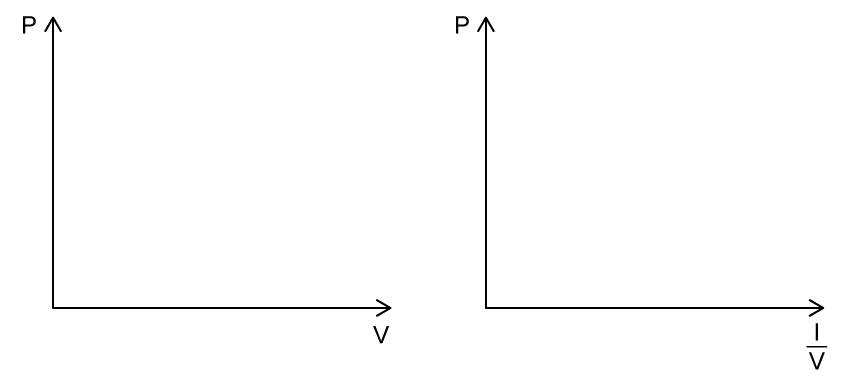
Sketch on both axes the change in pressure and volume for an ideal gas at constant temperature.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Sketch the graphs in part (a) at a higher temperature.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
For an ideal gas at constant volume, the pressure, p, and temperature, T, are directly proportional:
(c)
State the equation for an initial pressure p 1 at temperature T 1 and final pressure p 2 and temperature T 2 .
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
The final pressure of an ideal gas is 500 Pa and its temperature rises from 410 K to 495 K.
(d)
Calculate the initial pressure of the gas.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Assess your score
View Answer
When there are a large number of particles in a container, their collisions with the walls of the container give rise to gas pressure.
An ideal gas with a pressure of 166 kPa collides with the walls of its container with a force of 740 N.
(b)
Calculate the area that each particle collides on.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
An ideal gas is one that obeys the relationship
(c)
If the volume an ideal gas increases, explain how this affects the:
(i)
Pressure, if the temperature remains constant.
[1]
(ii) Temperature, if the pressure remains constant.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
The ideal gas equation can be rearranged to give
This relationship only holds true under a certain condition.
(d)
State the condition required for the equation to apply to an ideal gas.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question

constant