The distance from the Earth to the Sun is 1.5 × 1011 m. The mass of the Earth is 6 × 1024 kg and the mass of the Sun is 3.3 × 105 times the mass of the Earth.
(a)
Estimate the gravitational force between the Sun and the Earth.
Assess your score
View Answer
Mars is 1.5 times further away from the Sun than the Earth and is 10 times lighter than Earth.
(b)
Predict the gravitational force between Mars and the Sun.
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Determine the acceleration of free fall on a planet 20 times as massive as the Earth and with a radius 10 times larger.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Calculate the orbital speed of the Earth around the Sun.
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
A satellite orbits the Earth with mass M above the equator with a period, T equal to 48 hours. The mass of the Earth is 5.972 × 1024 kg.
(a)
Derive an equation for the radius, r of the satellite’s orbit.
Assess your score
View Answer
The mean radius of Earth is 6.37 × 106 m.
(b)
Calculate the height of the satellite above the Earth’s surface.
Assess your score
View Answer
The Hubble Space Telescope is in orbit around the Earth at a height of 490 km above the Earth’s surface.
(c)
Calculate Hubble’s speed.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Calculate the magnitude of the gravitational field on the Hubble Space Telescope at this height above the Earth’s surface.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Europa, a moon of Jupiter, has an orbital period of 85 hours and an orbital radius of 670 900 km.
(a)
Outline why Europa moves with uniform circular motion.
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Show that the orbital speed of Europa is 14 km s–1 .
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Deduce the mass of Jupiter.
Assess your score
View Answer
Ganymede is the largest of Jupiter’s Moons. It has an orbital period of 7.15 days and an orbital speed of 10.880 km s–1 .
(d)
Calculate the orbital radius of Ganymede in terms of billions of km.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
(a)
Define Newton’s universal law of gravitation.
Assess your score
View Answer
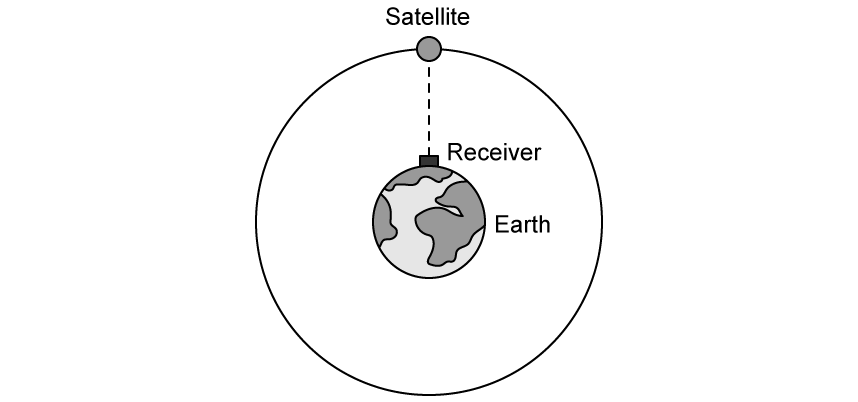
The diagram shows a satellite orbiting the Earth. The satellite is part of the network of global–positioning satellites (GPS) that transmit radio signals used to locate the position of receivers that are located on the Earth.
When the satellite is directly overhead the microwave signal reaches the receiver 62 ms after leaving the satellite.
(b)
Calculate the height of the satellite above the surface of the Earth.
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Explain why the satellite is accelerating towards the centre of the Earth even though its orbital speed is constant.
Assess your score
View Answer
The radius of Earth is 6.4 × 106 m.
(d)
Calculate the gravitational field strength of the Earth at the position of the satellite.
Mass of Earth = 6.0 × 1024 kg
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
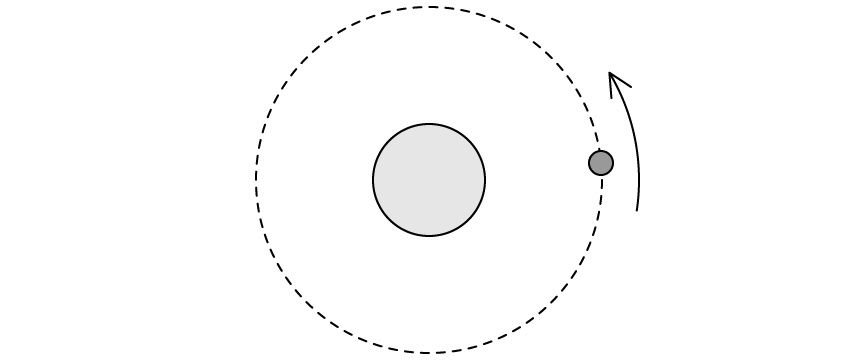
A satellite is in a circular orbit around a planet of mass M .
(a)
Sketch arrows to represent the velocity and acceleration of the satellite.
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Show that the angular speed, ω is related to the orbital radius r by
r
Assess your score
View Answer
Because of friction with the upper atmosphere, the satellite slowly moves into another circular orbit with a smaller radius before.
(c)
Suggest the effect of this on the satellites angular speed.
Assess your score
View Answer
Titus and Enceladus are two of Saturn’s moons. Data about these moons are given in the table.
Moon
Orbit radius / m
Angular speed / rad s-1
Titan
1.22 9
Enceladus
2.38 8
5.31 -5
(d)
Determine the mass of Saturn.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question