Question 1
A fixed mass of an ideal gas is at temperature T K. The pressure is quadrupled, and the volume is halved. What is the temperature after these changes?
A fixed mass of an ideal gas is at temperature T K. The pressure is quadrupled, and the volume is halved. What is the temperature after these changes?
A fixed mass of an ideal gas undergoes an isovolumetric change. This leads to a decrease in the pressure of the gas.
Which row describes the change in internal energy of the gas and the direction of transfer of thermal energy?
|
|
Internal Energy |
Direction of thermal energy transfer |
|
A. |
greater |
to the gas |
|
B. |
greater |
from the gas |
|
C. |
less |
to the gas |
|
D. |
less |
from the gas |
A fixed mass of an ideal gas is initially at an absolute temperature, T and occupies a volume, V.
The gas is adjusted so that the final pressure of the gas is twice the magnitude of the initial pressure.
Which row of the table below, A to D, gives the correct expressions for the final volume and temperature of the gas?
|
|
Final volume of the gas |
Final temperature of the gas |
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
The graphs, A to D, show the variation of pV with θ for one mole of two different gases, nitrogen and chlorine, where p is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the gas and θ is the temperature in °C.
Which graph shows the correct variation of pV with θ for 1 mole of each gas?

X and Y are two flasks containing an ideal gas that are connected by a tube that has negligible volume compared with the volume of each flask. The volume of X is twice the volume of Y.
The temperature of the gas in X is kept at 200 K and the temperature of the gas in Y is kept at 400 K.
If the mass of the gas in X is MX and the mass of the gas in Y is MY, what is the ratio ?
An ideal gas of fixed mass has a pressure, p, and volume, V. The graph shows the variation of with V at a constant temperature.

Which line represents the same gas if the thermodynamic temperature and the amount of gas are doubled?

Given the following data:
What is the pressure of oxygen in a cubic container?
1 kPa
12 kPa
110 kPa
1200 kPa
A sealed cylinder of radius r and length L contains an ideal gas. The gas is at pressure p and temperature T. The radius of the cylinder is halved, and the temperature is altered to maintain the same pressure.
Which of these is an expression for the new temperature of the gas?
An ideal gas of N molecules is maintained at constant volume, V. The graph shows how temperature T varies with pressure p.
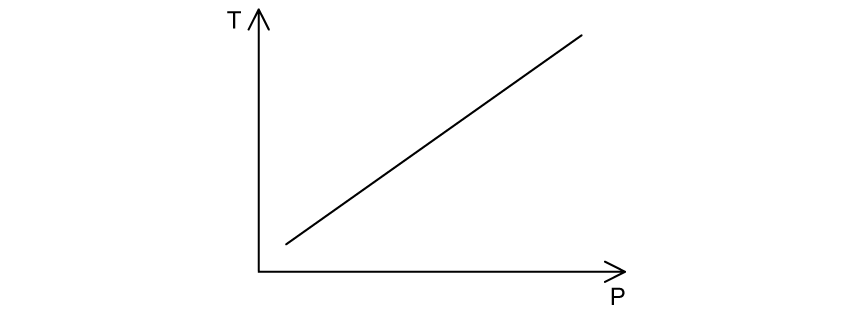
What is the gradient of the graph?