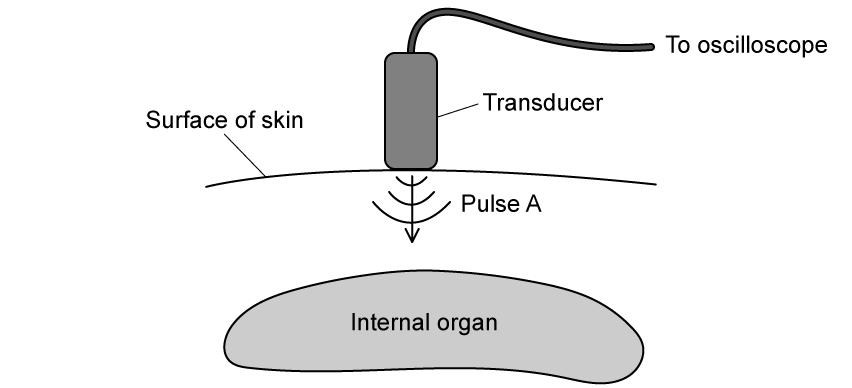
Question 1a
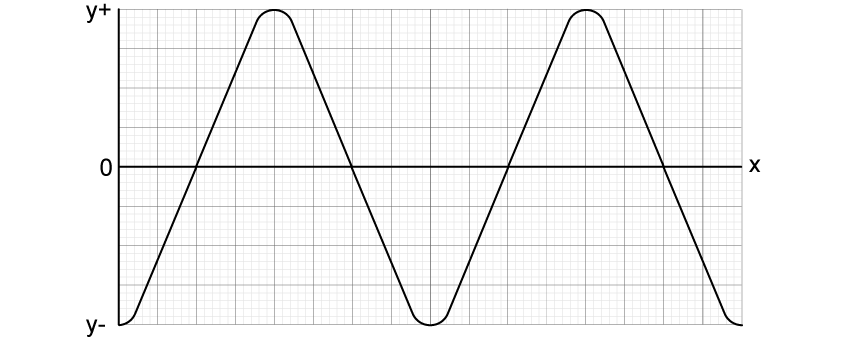
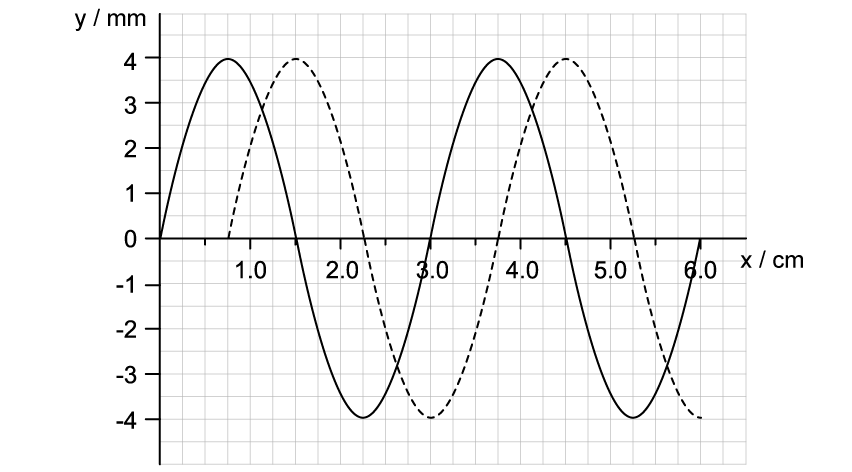
A wave on the surface of a ripple tank moves from the source at the rear of the tank to the front. The graph shows the variation with distance x of the displacement y of the surface of the water.
The solid line shows displacement at t = 0 and the dashed line shows the displacement at t = 0.154 s.
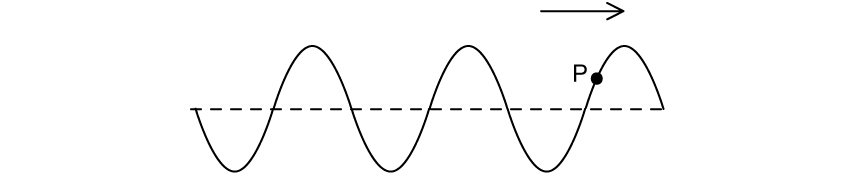
(a) Describe the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves.
Question 1b
(b) Calculate for the wave on the ripple tank

(i) the speed
[2]
(ii) the frequency
[2]
Question 1c
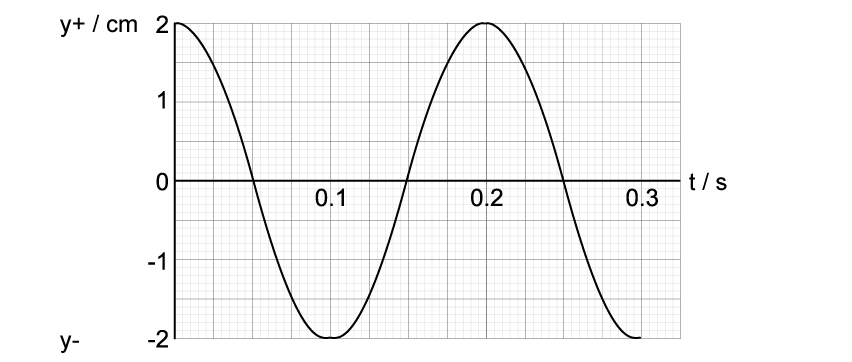
The graph shows the motion of the water waves at a point where displacement ≤ 6.0 cm.
Question 1d
The initial amplitude of the ripples is 0.38 cm.