A trampolinist bounces up and down on their trampoline.
Which row states the energy transformations that take place in the system when the trampolinist bounces down on the trampoline and back up again. Assume that air resistance is negligible.
Gravitational potential → elastic potential → kinetic → elastic potential → gravitational potential
Gravitational potential → kinetic → elastic potential → kinetic → gravitational potential
Kinetic → gravitational potential → elastic potential → gravitational potential → kinetic
Gravitational potential → kinetic → elastic potential → gravitational potential
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Next Question
An object falls from rest from a height h close to the surface of the Moon. The Moon has no atmosphere.
When the object has fallen to height
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
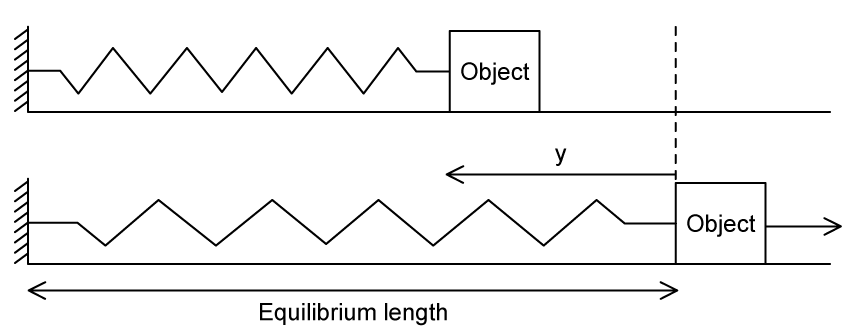
A horizontal spring of spring constant k and negligible mass is compressed through a distance y from its equilibrium length. An object of mass m that moves on a frictionless surface is placed at the end of the spring. The spring is released at speed v and returns to its equilibrium length.
What is the value of y ?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A student states three scenarios in which she thinks no work is done on an object.
A pulling force on a sledge being pulled at an angle.
A charged particle in a magnetic field.
A drag force acting a car.
Which of the above scenarios is / are correct?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
The power generated by the nuclear reactions in the core of the reactor is 35 GW.
If the efficiency of the power station is 60%, how much power goes into producing wasted energy?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
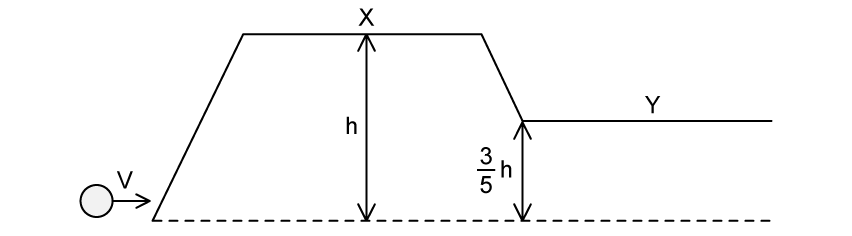
A mass with speed v travels up to point X then down to Y.
Assuming air resistance is negligible, what is v of the mass at point Y?
2
4
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A student of mass 50 kg climbs a vertical ladder 4.0 m tall in a time of 8.0 s. What is the power developed by the student against gravity?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
The efficiency of an electric motor is 80 %. When lifting a body, the amount of energy wasted is
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A lift is operated by an electric motor. It moves between the 21st and the 5th floor at a constant speed. One main energy transformation during this journey is:
Electric energy → Gravitational potential energy
Gravitational potential energy → Kinetic energy
Electric energy → Thermal energy
Kinetic energy → Electric energy
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A spring of mass m and spring constant k rests on top of a vertical spring whose base is attached to the floor.
What is the energy stored by the spring?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question