Question 1
What force does a particle of an ideal gas experience with a pressure of 166 kPa on an area of 2.0 m2?
83 000 N
332 000 N
0.083 N
0.332 N
What force does a particle of an ideal gas experience with a pressure of 166 kPa on an area of 2.0 m2?
83 000 N
332 000 N
0.083 N
0.332 N
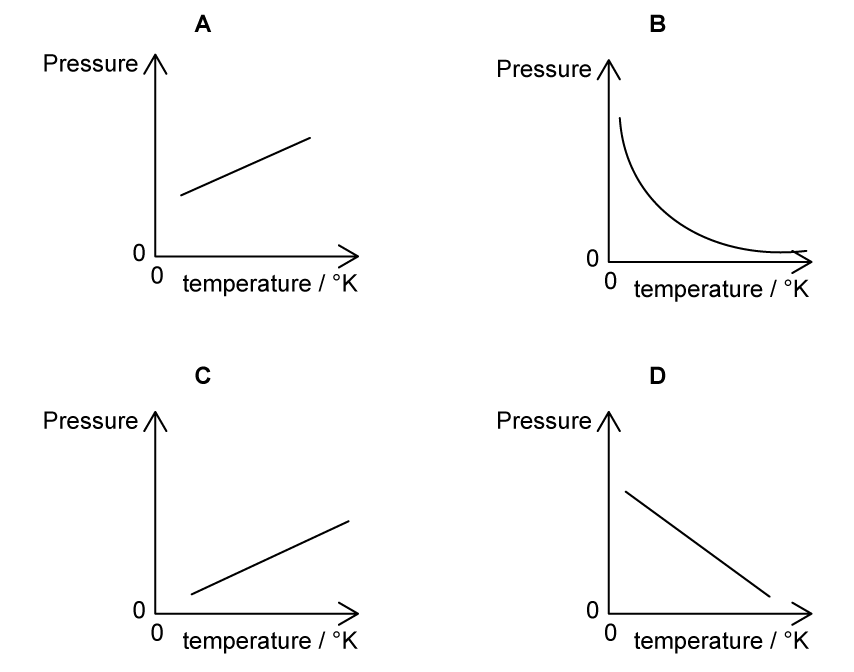
A fixed mass of an ideal gas is trapped in a cylinder of constant volume and its temperature is varied. Which graph shows the variation of the pressure of the gas with temperature in kelvin?
Which row gives the correct definitions for n, N and NA?
| n | N | NA | |
| A. | number of molecules | Avogadro's constant | Avogadro's constant |
| B. | Avogadro's constant | Avogadro's constant | number of molecules |
| C. | Avogadro's constant | number of moles | number of molecules |
| D. | number of moles | number of molecules | Avogadro's constant |
A sealed container contains a mixture of helium and neon gas.
The ratio of is 5.
What is the correct ratio for ?
1
5
Dependent on the concentration of each gas
Which statement describes a correct assumption for the kinetic model of an ideal gas?
The kinetic energy of a given molecule of the gas is constant.
The forces between each gas molecule varies.
The intermolecular potential energy of the molecules of the gas varies.
The momentum of a given molecule of the gas varies upon a collision with the container.
The volume of an ideal gas in a container is decreased at constant temperature.
Which of the following statements are correct about the molecules of the gas?
I. Their average kinetic energy increases.
II. The frequency of the collisions per unit area of the container wall increases.
III. The pressure of the gas increases.
I only
I and III only
II and III only
I and II only
Which of the following is not an assumption of the kinetic model of ideal gases?
All particles in the gas have different speeds.
The duration of collisions between particles is long in comparison to the time between the collisions.
There are no intermolecular forces between the particles in the gas.
Collisions with the walls of the container are elastic.
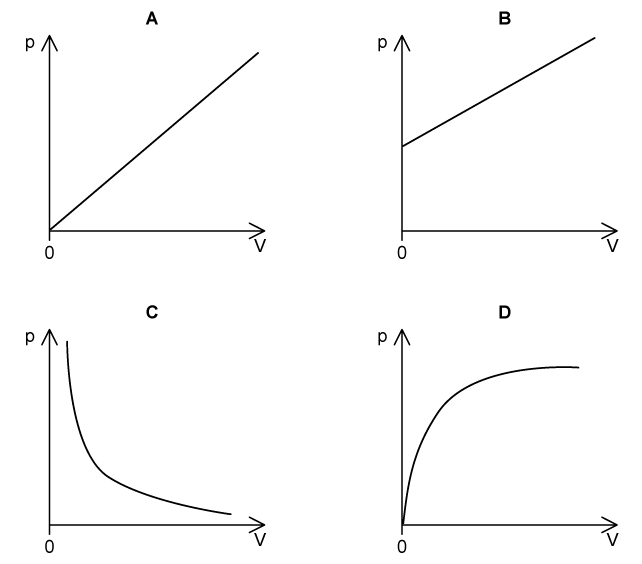
Which graph shows the correct relationship between the volume, V ,and pressure, p, of a gas kept at a constant temperature?
Which condition allows the behaviour of a monatomic gas, such as argon, to approximate to that of an ideal gas?
Low pressure.
High temperature.
High density.
Very low temperature.
Which of the following is not an equation used for an ideal gas?
pV = nRT
= constant
= constant
= constant