(a)
Complete the table by stating whether the quantity is a vector or a scalar and by giving the full name of its unit.
Quantity
Vector or Scalar
Unit
Momentum
Weight
Kinetic Energy
Power
Assess your score
View Answer
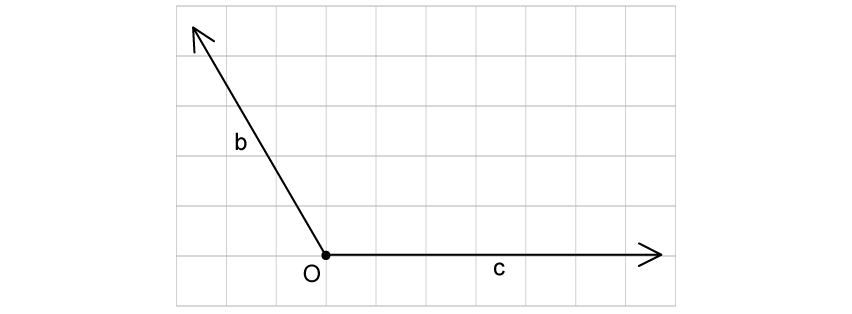
The diagram shows two forces b c O .
(b)
Draw a force triangle diagram to show the resultant force and state the value of this resultant force in terms of b c
Assess your score
View Answer
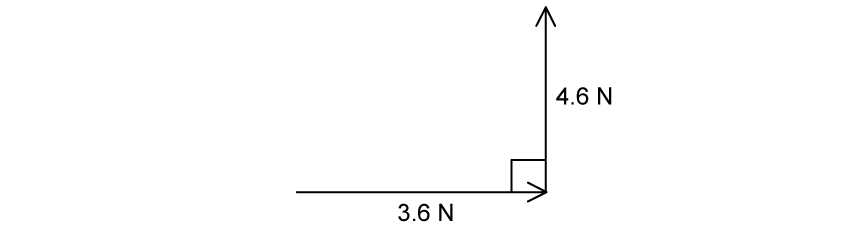
The diagram shows two different forces with magnitudes 4.6 N and 3.6 N perpendicular to each other acting on an object.
(c)
Calculate the magnitude of this resultant force.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Calculate the angle to the horizontal at which the resultant force acts.
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
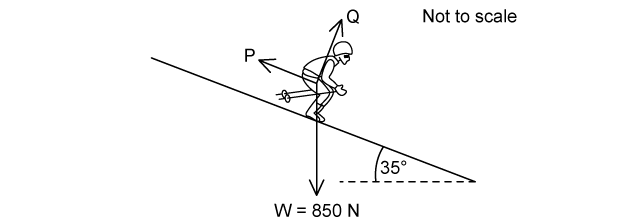
The diagram shows a skier travelling at constant speed down a slope of 35°
The force labelled P is parallel to the slope. The force labelled Q is perpendicular to the slope. Assume that there is no friction between the skis and the snow.
(a)
Draw the force triangle and identify the forces labelled P and Q .
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Calculate the magnitude of force Q
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Calculate the magnitude of the force P .
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Draw a new force diagram and calculate the new resultant force down the slope on the skier.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
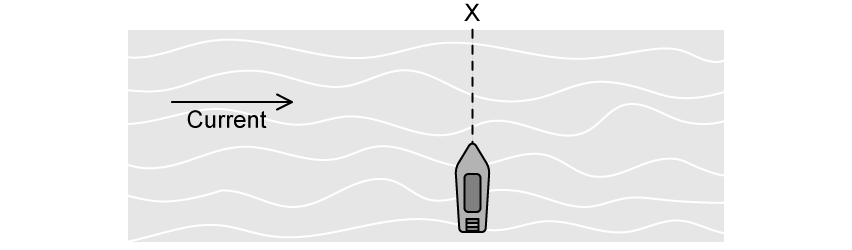
A man wants to cross a river in a motorboat. The speed of the motorboat in still water is
7.0 ms-1 . The river is 32 m wide. There is a current in the river whose speed with respect to the shore is 5.0 ms-1 .
(a)
Draw a vector triangle to show the velocities of the motorboat in still water, the current and the resultant velocity of the motorboat.
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Calculate the resultant speed of the motorboat.
Assess your score
View Answer
The man aims his boat at point X.
(c)
Determine the distance from X further down the river at which he reaches the shore.
Assess your score
View Answer
A woman in an identical boat leaves from the same spot as the man but wants to land at point X.
(d)
Determine the direction in which she must turn her boat to do this.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A cyclist cycles 15.0 km due east, followed by 23.0 km due north and then another 7.0 km east.
(a)
Draw a vector diagram to represent the cyclist’s journey.
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Calculate the resultant displacement travelled by the cyclist:
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Calculate the angle from where the cyclist started to due north of the cyclist final destination.
Assess your score
View Answer
The cyclist wants to return home.
(d)
What angle clockwise from north must he take to go home directly?
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
(a)
State whether impulse is a scalar or vector quantity and explain why.
Assess your score
View Answer
Electric charge can either be stated positive or negative.
(b)
State whether electric charge is a scalar or vector quantity and explain why.
Assess your score
View Answer
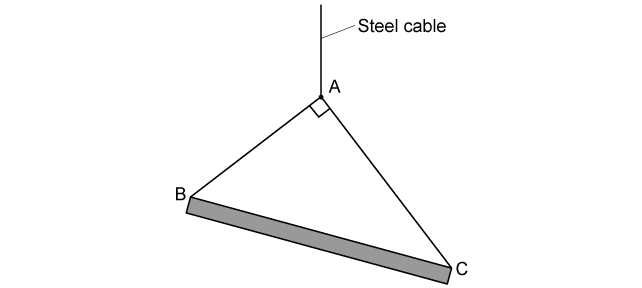
The diagram shows a uniform beam supported by two light cables, AB and AC , which are attached to a single steel cable from a crane. The beam is stationary and in equilibrium.
(c)
Draw the vector triangle for this situation labelling the tension in both cables and the weight of the beam.
Assess your score
View Answer
The tension in the cable AB is 9 N and the tension in the cable AC is 12 N.
(d)
Calculate the resultant force required in the beam BC to keep the system in equilibrium.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question