(a)
Define the specific latent heat of fusion of a substance.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
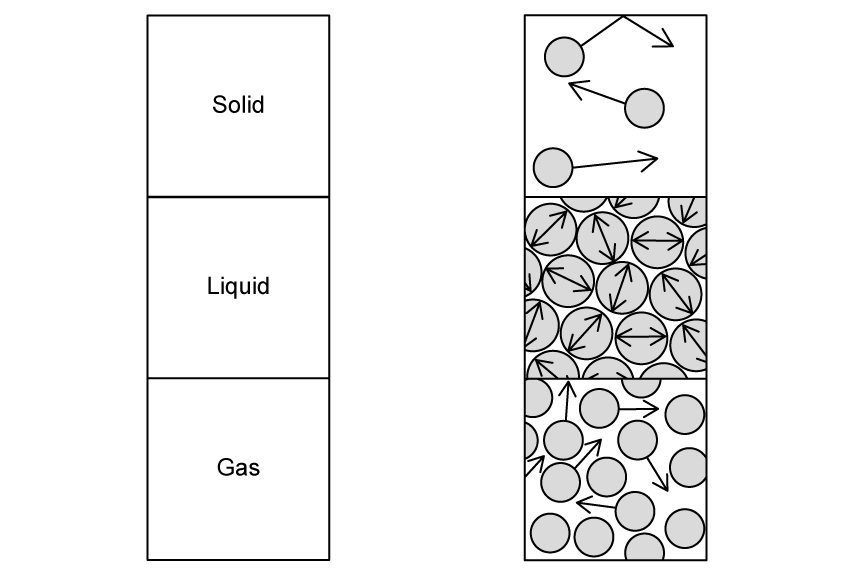
Draw a line to indicate which molecular model of matter matches with which state.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
The following statements are about the molecular model of matter.
The potential energy changes during change of _______.
Potential energy is greater for _______ than for _______ more energy is required to _______ bonds than just _______ them.
Therefore, specific latent heat of _______ is _______ than specific latent heat of _______ for any substance.
(c)
Complete the missing gaps using keywords from the list provided.
You may use any keyword once, more than once, or not at all.
weaken
fusion
break
greater
vaporisation
less
state
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
A 2.5 g block of ice is placed into a beaker of water where 825 J of energy is needed to melt the ice completely.
(d)
(i) Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice.
[3]
(ii) State an assumption that you have made in your answer to part (i).
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
Define specific heat capacity.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
The change in thermal energy, Q is given by the equation:
Q = mc ΔT
(b)
Define the following variables and state an appropriate unit for each:
[1]
[1]
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
A hot piece of copper is placed into a container of cold water. After a time, the copper and water reach thermal equilibrium.
(c)
Outline how it would be known when the copper and water reach thermal equilibrium.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
The following data are available:
Energy transferred to water = 5.6 kJ
Mass of copper = 0.72 kg
Specific heat capacity of copper = 389 J kg–1 K–1
(d)
Calculate the change in temperature of the copper.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
(a)
Define internal energy
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
The fraction of the internal energy that is due to molecular vibration varies in the different states of matter.
(b)
Arrange the following states of matter from highest to lowest fraction of internal energy due to molecular vibration.
Assess your score
View Answer
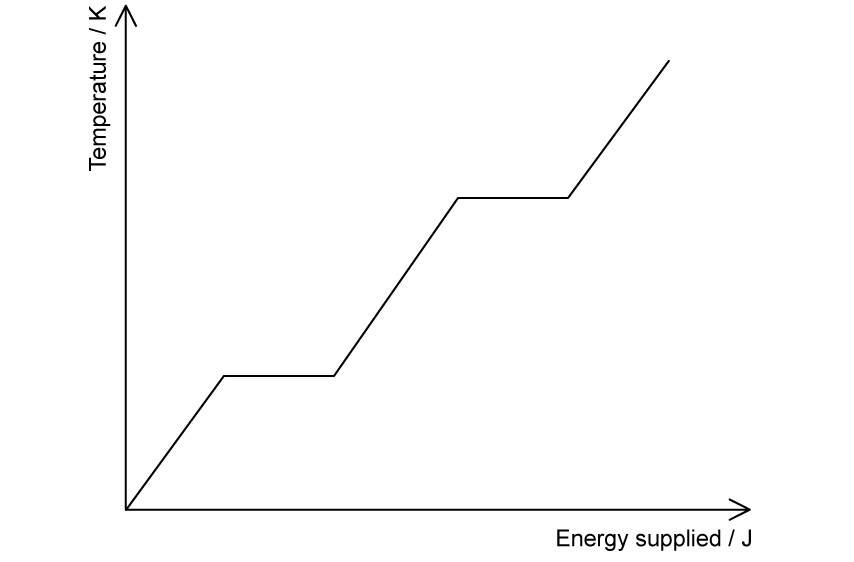
The heating graph shows the change in temperature against energy supplied for a specific substance.
(c)
Label the following on the graph:
(i)
Solid, liquid and gas
[1]
(ii)
Melting and boiling
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Label on the graph in part (c) the freezing point and the boiling point on the temperature axis.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
(a)
Define thermal energy.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
An immersion heater is placed in a beaker containing 350 g of water at a temperature of 15 °C. After some time, the temperature of the water is 42 °C. The thermal capacity of the beaker is negligible and the specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 × 103 J kg–1 K–1 .
(b)
Estimate the change in internal energy of the water.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
The water is further heated until it starts to boil at constant temperature.
(c)
Choose the correct word in the explanation for this scenario:
All the (internal / thermal) energy is used to (separate / fuse) the molecules and not to increase their average (potential / kinetic) energy
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
If water had a higher specific heat capacity, state two differences this would make to boiling water using an immersion heater.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
(a)
Define the latent heat of vaporisation of a substance.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Place a tick (✓
Evaporation Melting Freezing Condensation
Latent heat of vaporisation
Latent heat of fusion
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
The energy required to change the phase of a substance is given by
Q = mL
(c)
Define the following variables and state an appropriate unit for each:
[1]
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
3400 J of energy is needed to convert 16 g of oxygen from solid to a liquid.
(d)
Calculate the latent heat of vaporisation of oxygen.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question