Question 1
Using conservation of charge, determine which of the following is the correct quark composition of a proton?
sss
uud
ddd
uds
Using conservation of charge, determine which of the following is the correct quark composition of a proton?
sss
uud
ddd
uds
Which of the following particles has a baryon number of zero?
antineutron
neutron
kaon
proton
Beta-minus decay can be represented in terms of fundamental particles
What type of particle is particle X?
quark
photon
lepton
hadron
Which of the following was not an observation made by the Rutherford-Geiger-Marsden experiment?
Most of the α-particles went straight through the foil
Some α-particles deflected through small angles of less than 10°
Only a small number of α-particles deflected straight back at angles greater than 90°
The gold foil emits alpha particles
Which of the following is a correct statement about Feynman diagrams?
The vertical axis represents time
Gauge bosons are represented by a wavy/dashed line, or a helix
Only three particles may go into or out of a vertex
Particle lines can cross over
Which of the following is not conserved during weak interactions?
Baryon number
Lepton number
Strangeness
Charge
The Feynman diagram shows a particle interaction involving a W+ boson.
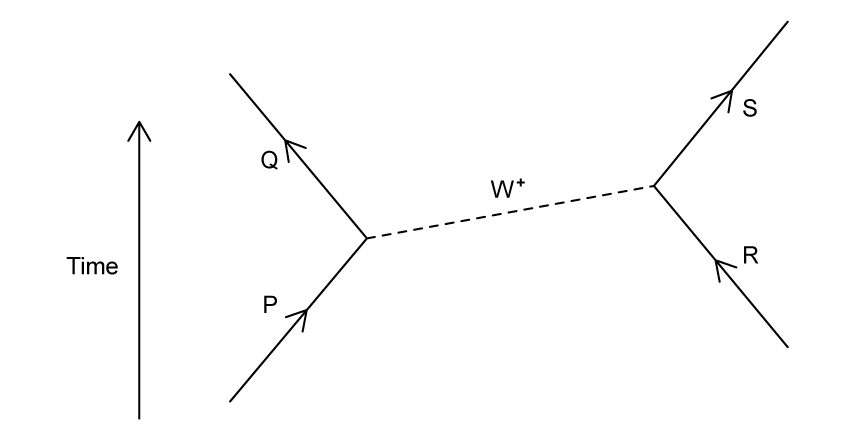
Which two particles are the products of the interaction?
Q and S
P and Q
P and S
R and S
The standard model classifies particles into hadrons, leptons, mesons and baryons. The diagram below shows some examples of these types of particles.
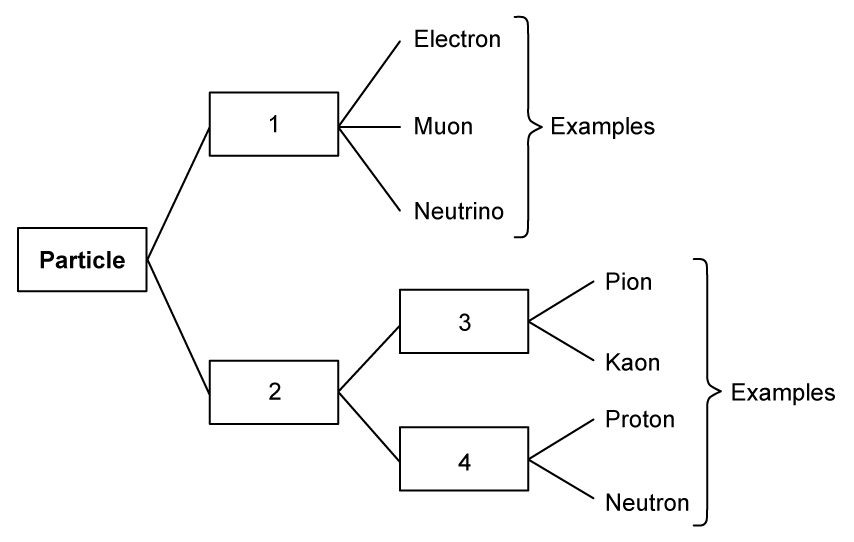
Which row shows the correct position of each type of particle in the diagram?
|
Hadrons |
Baryons |
Leptons |
Mesons |
|
| A |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| B |
2 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
| C |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
| D |
3 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
Which answer is not a feature of the strong nuclear force?
The strong nuclear force is repulsive at nucleon separations closer than around 0.5 fm
The strong nuclear force is attractive up to around 3.0 fm
The strong nuclear force has an infinite range
The strong nuclear force reaches a maximum attractive value at around 1.0 fm