Question 1
A proton with velocity of 1.5 × 107 m s−1 moves normally into a uniform magnetic field of flux density 0.30 T. Which is the best estimate of the radius of curvature of the path of the proton?
5 × 10−38 m
5 × 10−3 m
5 × 10−1 m
5 m
A proton with velocity of 1.5 × 107 m s−1 moves normally into a uniform magnetic field of flux density 0.30 T. Which is the best estimate of the radius of curvature of the path of the proton?
5 × 10−38 m
5 × 10−3 m
5 × 10−1 m
5 m
The diagram shows a uniform electric field in which equipotential lines are placed 3.0 cm apart.
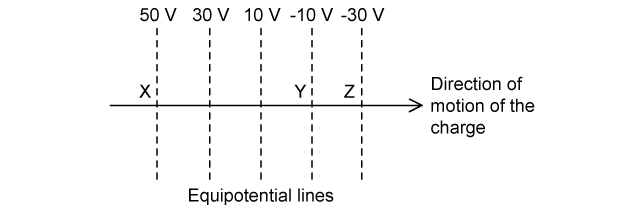
A charge of –6.0 nC is placed at the equipotential line X.
Which of the following statements is correct?
The charge is in an electric field directed from Z to X and has a gain of 4.8 × 10–7 J of kinetic energy moving from X to Z
The charge is in an electric field directed from X to Y and has a loss of 2.4 × 10–7 J of kinetic energy moving from Y to Z
The charge is in an electric field directed from X to Y and has a gain of 1.2 × 10–7 J of kinetic energy moving from Y to Z
The charge is in an electric field directed from X to Z and has a loss of 1.2 × 10–7 J of kinetic energy moving from Y to Z
The diagram shows four point charges at the corners of a square of sides 4a.
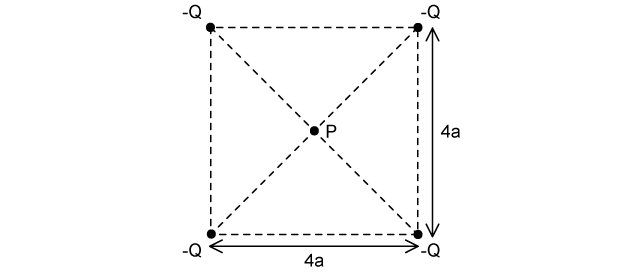
What is the electric potential at P, the centre of the square?
The Earth has radius, r and mass M. Which expression could be used to calculate the minimum time, T of one Earth-day for the material at the equator to just remain on the surface?
A space probe with mass m is launched from the surface of the Earth’s equator into orbit. The total energy Et given to the space probe is:
where G is the gravitational constant and M and rE are the mass and radius of Earth.
What is the height of the space probe’s orbit above the Earth’s surface?
rE
2rE
3rE
4rE
Two satellites, X and Y, of equal mass, orbit a planet at radii R and 2R respectively.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
X has more kinetic energy and more potential energy than Y
X has more kinetic energy and less potential energy than Y
X has less kinetic energy and more potential energy than Y
X has less kinetic energy and less potential energy than Y
A cable used in high-voltage electrical transmission has a radius of 3.0 mm. The diagram shows the circular cross-section of the cable with electrical field lines denoting areas of equipotential.
In the instant shown the potential of the cable is + 600 000 V.
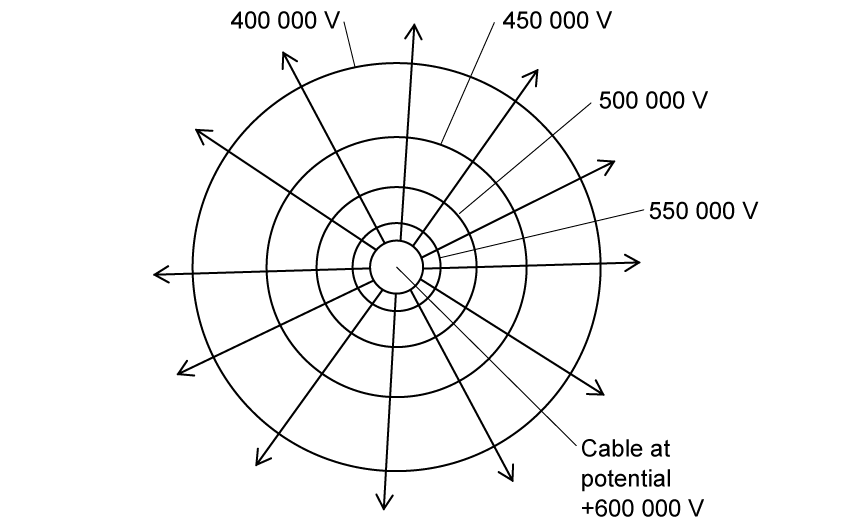
Assuming that the diagram has been drawn to scale, what is the the potential gradient near the surface of the cable?
-25 × 106 V m−1
-50 × 106 V m−1
-75 × 106 V m−1
-125 × 106 V m−1
Two identical negative point charges, P and Q, are separated by a distance of 6.0 mm. The resultant electric potential at point M, which is mid–way between the charges, is –40 V.
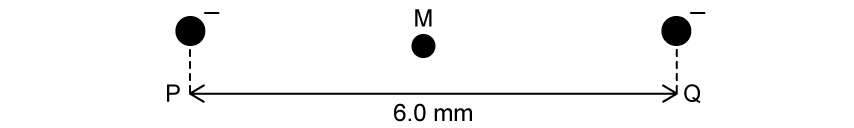
What would be the resultant electrical potential at a point 2.0 mm closer to Q?
–90 V
–72 V
–60 V
–48 V
Observations are made on two separate planetary system's suns of mass M1 and mass M2.
Their orbiting planets, P1 and P2 have masses of m1 and m2, and are observed to have identical orbits in shape and magnitude. P1 completes an orbit in a quarter of the time taken by P2.
Which statement can astronomers reasonably deduce?
M1 = M2 and 9m1 = m2
M1 = 16 M2 and m1 = m2
4 M1 = M2
M1 = 16 M2
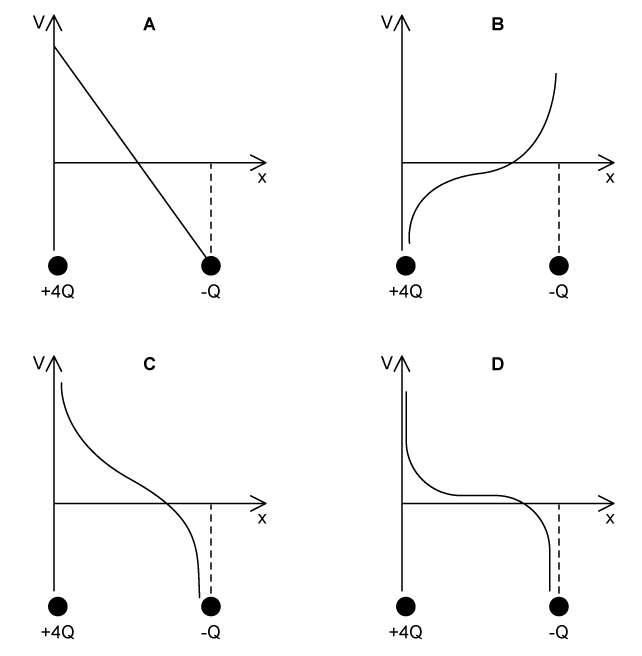
Two points charges of +4Q and –Q are placed 150 mm apart.
Which of the following graphs shows the variation of the potential V against the distance x along the line joining the two point charges?