Question 1
Wavefront diagrams can be used to indicate the frequency of waves.
Which wave has the lowest frequency?
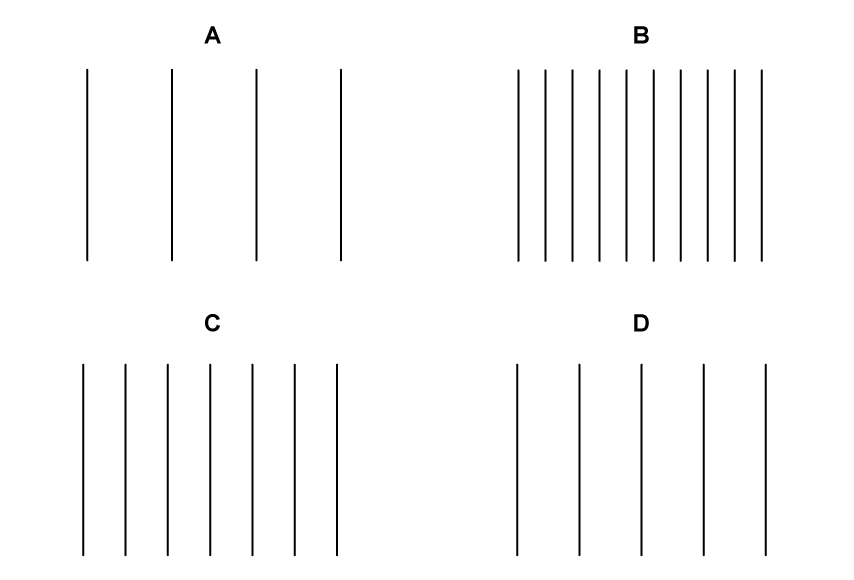
Wavefront diagrams can be used to indicate the frequency of waves.
Which wave has the lowest frequency?

Which of the following statements is the correct description of a ray?
The net displacement of a medium when two waves meet
A line that joins all the points on a wave that have the same phase
A line that indicates the direction of energy propagation
A line that indicates the plane of the oscillation of the electric field
A spherical wave emitted from a point source has an intensity, I, at a distance, r.
The relationship between intensity and the distance from the point source is given by
I =
What is the intensity of the wave at a distance of 3r?
Which phrase completes the following sentence about the relationship between the amplitude A and the intensity I of a wave?
The intensity of a wave is:
Directly proportional to A
Directly proportional to A2
Inversely proportional to A
Inversely proportional to A2
Which statement correctly describes the principal of superposition?
When two waves meet the resultant polarisation will be the sum of the individual polarisations
When two waves meet the resultant wavelength will be the sum of the individual wavelengths
When two waves meet the resultant intensity will be the sum of the individual intensities
When two waves meet the resultant displacement will be the sum of the individual displacements
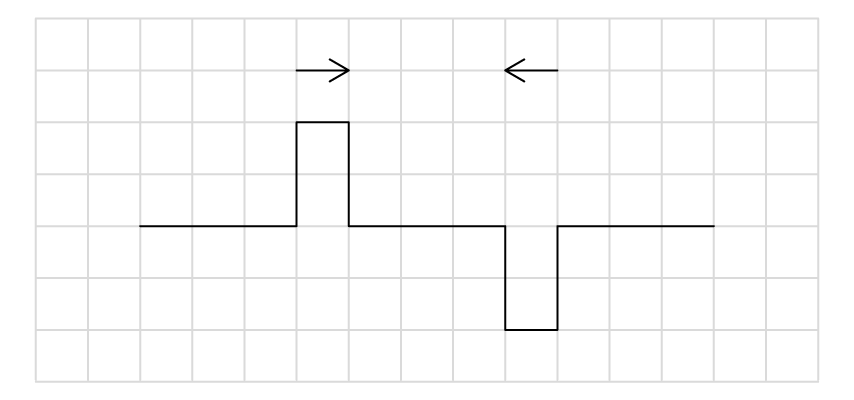
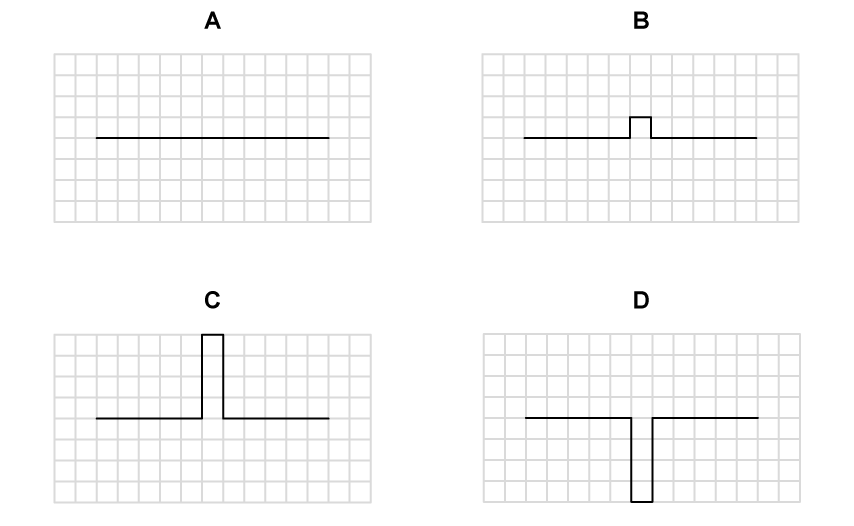
When two similar waves meet they superpose.
What is the correct resultant displacement for the superposition of the following waves?
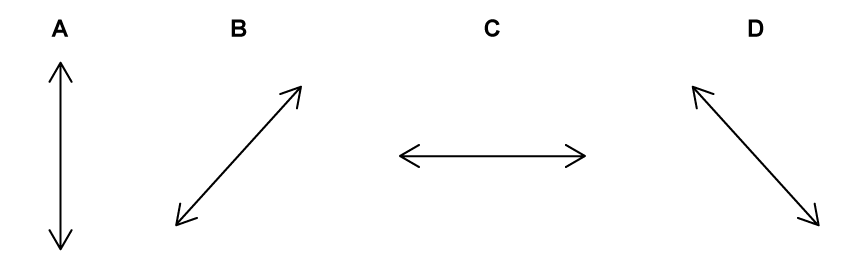
Unpolarised light is passed through a polarising filter as shown in the diagram.
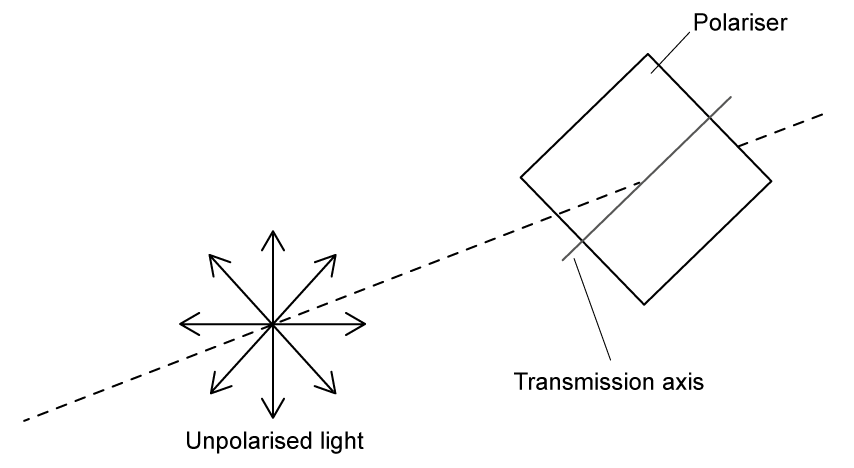

Which arrow shows the correct plane of the resulting polarised light?
Unpolarised light with intensity I0 is passed through a polarising filter.
Which expression shows the correct value of the resulting polarised light?
I0
2I0
I0 cos2θ
A physicist passes unpolarised light through a polariser and then an analyser as shown.
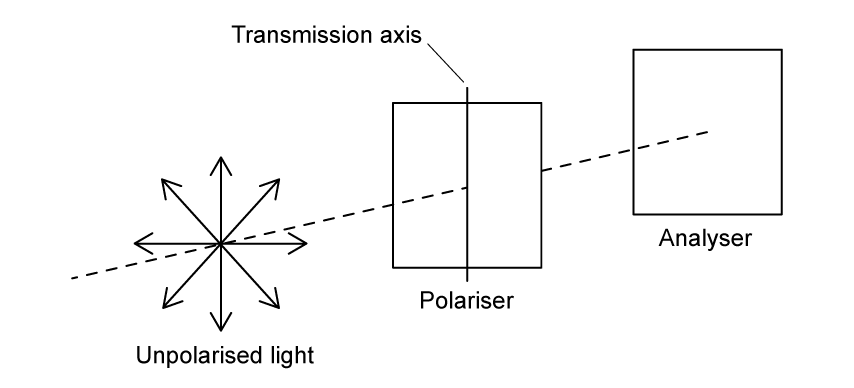
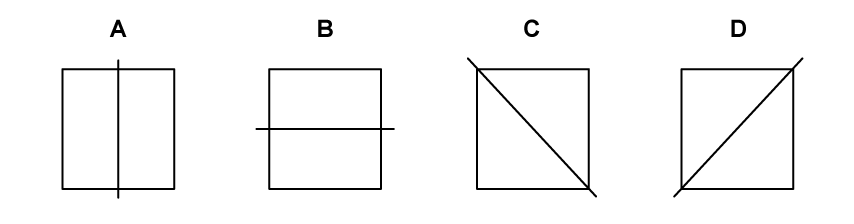
Which analyser does the physicist need to use so that the intensity of the analysed light is equal to the intensity of the polarised light?
Which law determines the intensity of analysed light?
Hooke's Law
Snell's Law
Hubble's Law
Malus's Law