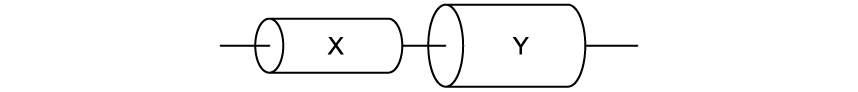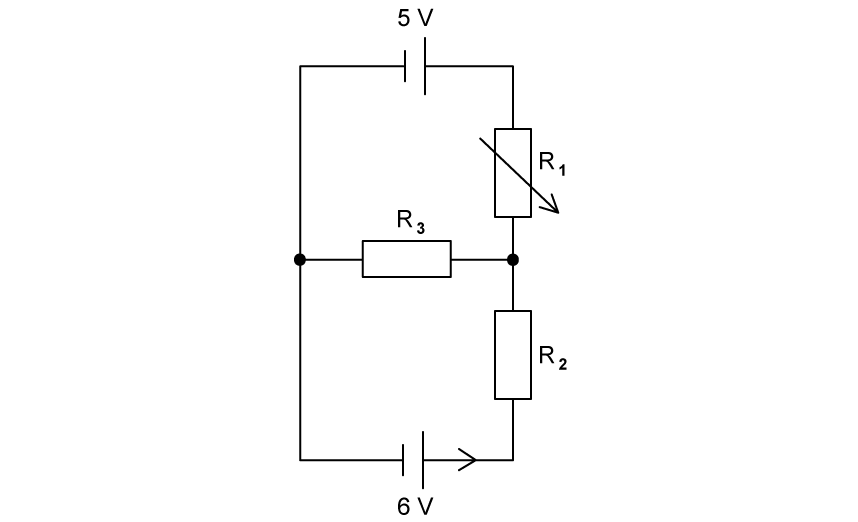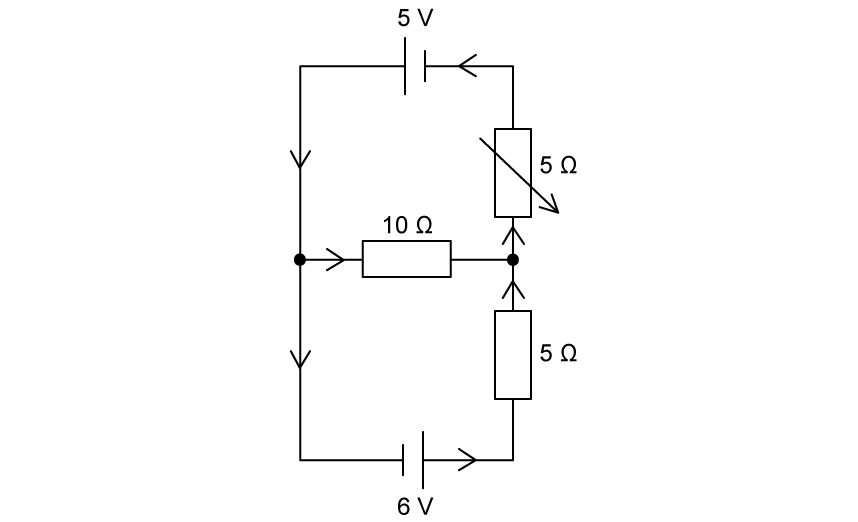Deborah is an aspiring electrical engineer who sets out to investigate the resistivity of a metal wire. The material of the wire is unknown.
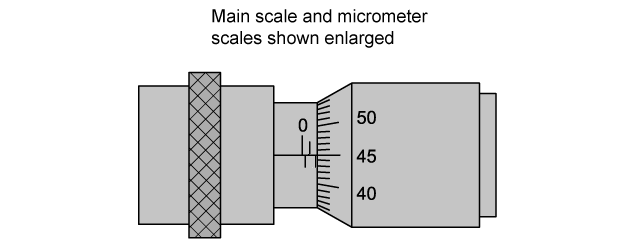
She measures the diameter of the wire using a micrometer screw gauge and takes a reading from the main scale and micrometer scale.
(a)
Determine the cross-sectional area of Deborah’s wire.
Assess your score
View Answer
Deborah then uses an ohmmeter to measure the resistance R for different lengths L of the wire.
Length L / cm
Resistance R / Ω
80.0
7.94
70.0
6.99
60.0
5.89
50.0
4.93
40.0
4.27
(b)
Use Deborah’s measurements to complete the final column in the table and then determine the resistivity of the wire.
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Suggest and explain two improvements to Deborah’s experimental method that would reduce the uncertainty in the final value of resistivity.
Assess your score
View Answer
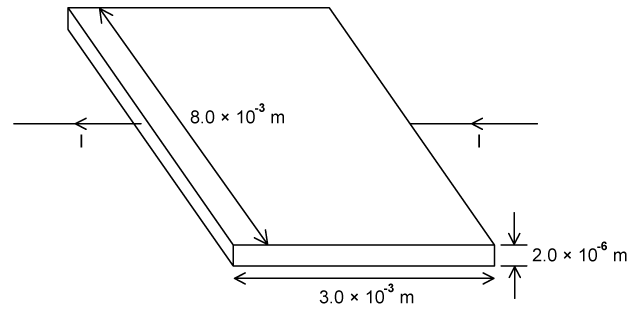
Deborah swaps the sample of wire used in her experiment for a thin film of carbon.
(d)
Calculate the current which passes through the carbon film in the diagram for an applied voltage of 2.5 mV.
The resistivity of carbon is 4.0 × 10–5 Ω m.
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
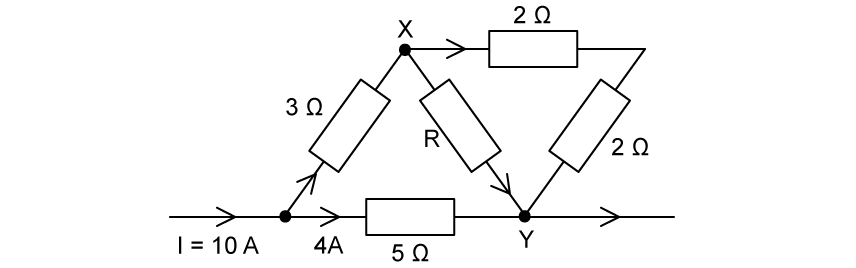
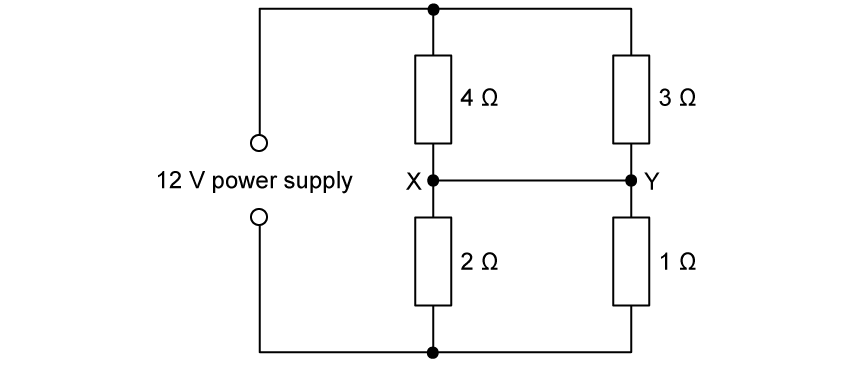
A current I = 10 A flows through a network of six resistors as shown.
The potential difference across the line XY is 8 V.
(a)
Calculate the value of the unknown resistance R .
Assess your score
View Answer
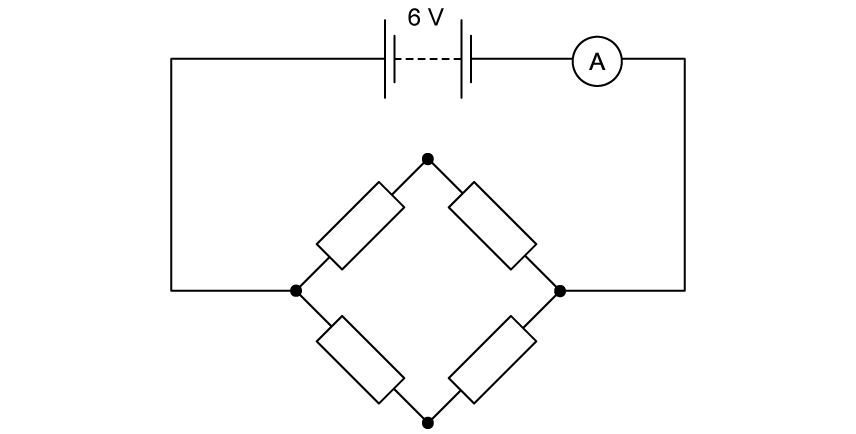
Another network, comprised of four identical resistors each of resistance 2 Ω, is connected to a 6 V battery with negligible internal resistance.
(b)
Determine the reading on the ammeter.
Assess your score
View Answer
A resistor is made by connecting two uniform cylinders X and Y of the same material and equal in length, in series.
Cylinder Y has a resistance of 5 Ω and is twice the diameter of cylinder X.
(c)
Calculate the total resistance of this series combination.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
State and explain why knowledge of quantities like resistivity is useful to scientists.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A variable resistor R1 has a resistance that varies between 0 and 10 Ω is connected to two resistors R2 and R3 and two cells of e.m.f. 5 V and 6 V.
(a)
Use Kirchhoff’s junction law to deduce an equation for three currents I1 , I2 and I3 at the junction between the resistors R1 , R2 and R3 .
Assess your score
View Answer
Initially, the variable resistor
(b)
If R2 is 5 Ω and R3 is 10 Ω, determine the current through resistor R2 .
Assess your score
View Answer
The terminals of the 5 V cell are reversed, and the variable resistor is set to a resistance of 5 Ω.
(c)
Using the current directions indicated, write:
(i)
Two unique equations using Kirchhoff’s circuit law for loops.
(ii)
One equation using Kirchhoff’s circuit law for junctions.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Hence, calculate the power dissipated in .
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
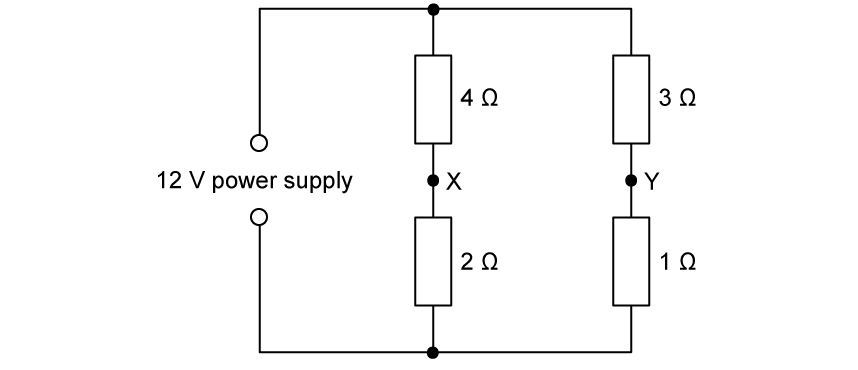
A circuit containing four resistors is connected to a 12 V power supply.
(a)
Show that the potential difference between X and Y is 1 V.
Assess your score
View Answer
A wire joins X and Y in the circuit.
(b)
Assuming current flows anticlockwise from the power supply, state and explain the direction of current along the line XY.
Assess your score
View Answer
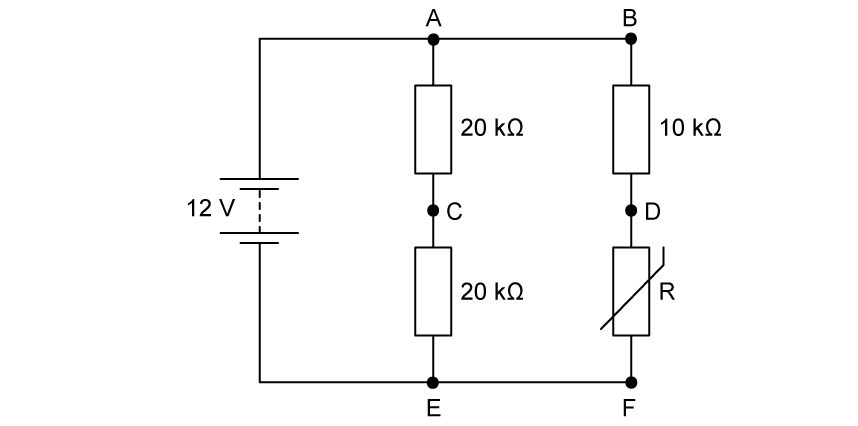
Another potential divider circuit includes a thermistor with resistance R .
The battery has an e.m.f. of 12 V, with negligible internal resistance. At room temperature, the resistance of the thermistor is 4.0 kΩ.
(c)
Calculate the current in the battery at room temperature, giving your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
For temperatures higher than room temperature, describe and explain how the power dissipated varies across:
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
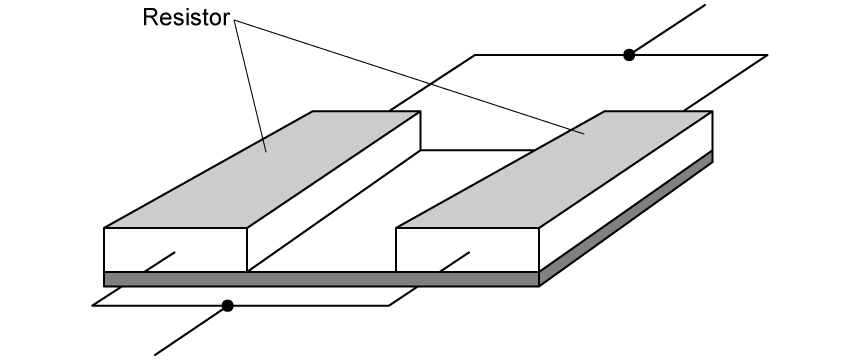
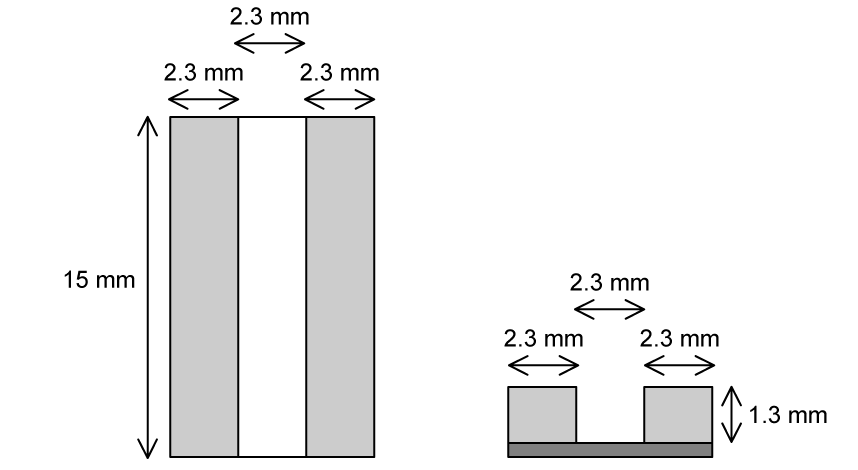
An electronic circuit contains two resistors connected as shown.
The material from which each resistor is made has a resistivity of 2.0 × 105 Ω m and both resistors have dimensions of 15 mm by 2.3 mm by 1.3 mm.
(a)
Calculate the total resistance of the electronic circuit.
Assess your score
View Answer
The circuit is designed such that changes to the dimensions of each resistor by a common factor are easily accomplished.
(b)
Show that if the dimensions of each resistor are increased by a factor of then the resistance decreases by the same factor.
Assess your score
View Answer
An electrical heating element is made of nichrome wire of resistivity 1.1 × 10–6 Ω m. It is required to dissipate 800 W when connected to the 230 V mains supply. The radius of the wire is 0.17 mm.
(c)
Calculate the length of wire required for the heating element.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Suggest two properties that the nichrome wire must have to make it suitable as an electrical heating element.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question