Question 1
In the table below, which row shows the correct conversion between the Kelvin and Celsius temperature scales?
| Kelvin temperature / K | Celsius temperature / °C | |
| A. | 0 | –270 |
| B. | -273 | 0 |
| C. | 150 | -123 |
| D. | 210 | -163 |
In the table below, which row shows the correct conversion between the Kelvin and Celsius temperature scales?
| Kelvin temperature / K | Celsius temperature / °C | |
| A. | 0 | –270 |
| B. | -273 | 0 |
| C. | 150 | -123 |
| D. | 210 | -163 |
Thermal energy is transferred from a solid. Three properties of the solid are
Which of the above properties determine the decrease in temperature of the solid?
II only
I and III only
I and II only
I only
What are the units of the ratio ?
J K
No units
K–1
K
The strength of intermolecular forces varies between in the different states of matter.
What is the order from highest to lowest strength of intermolecular forces?
solid > liquid > gas
solid > gas > liquid
liquid > gas > solid
gas > liquid > solid
Molecules fuse from water vapour to form water. The vapour and the water have the same temperature.
What is the change of the average potential energy and the change of the average random kinetic energy of these molecules when they move from the vapour to the water?
| Average potential energy | Average random kinetic energy | |
| A. | decreases | decreases |
| B. | no change | decreases |
| C. | decreases | no change |
| D. | no change | no change |
Which of the following correctly identifies the properties of the molecules of a substance that determine the substance’s internal energy?
The total gravitational potential energy and random electrostatic potential energy
The total potential energy and random kinetic energy
The random kinetic energy
The total potential energy
The specific latent heat of vaporisation is the energy required to change the phase of
one kilogram of a liquid to gas.
a solid at constant temperature.
one kilogram of a gas to liquid at constant temperature.
a gas at constant temperature.
A sample of solid aluminium is heated beyond its melting point. The graph shows the variation of temperature with time.
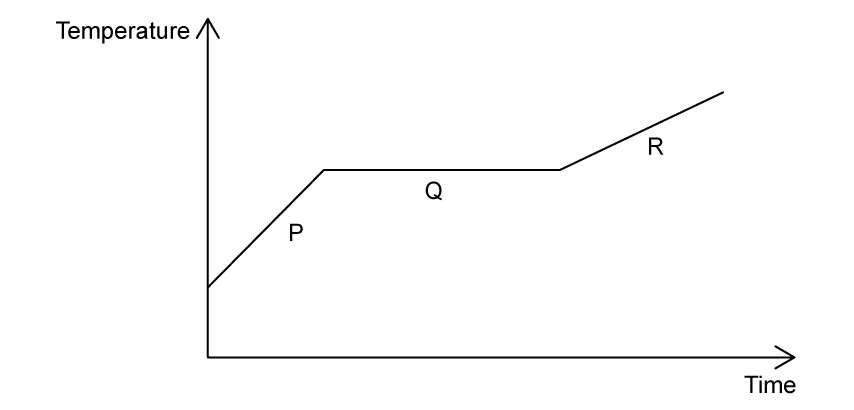
During which stage(s) is the aluminium melting?
Q only
P, Q and R
P only
P and R only
What is the correct comparison of the specific latent heat of fusion Lf to the specific latent heat of vaporisation Lv for any substance?
Lf = Lv
Lf > Lv
Lf < Lv
Depends on the substance.
Which of the following is numerically equal to the specific heat capacity of a substance?
The thermal energy required to increase the temperature of unit mass of the substance by 1 °C
The thermal energy required to increase the temperature of the substance by 1 °C
The sum of the random kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules in the substance
The thermal energy required to evaporate the substance