a)
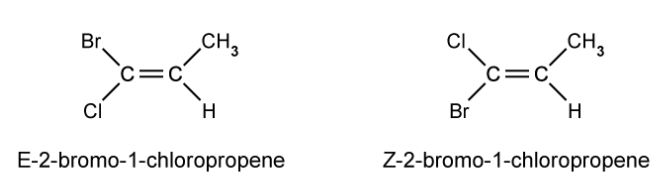
Draw the E and Z stereoisomers for 2,3-dichlorobut-2-ene.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
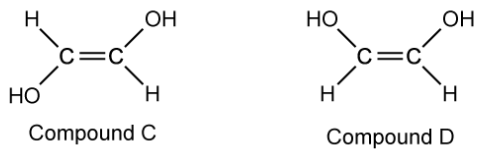
Name compounds C and D using the E / Z naming system.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
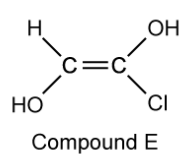
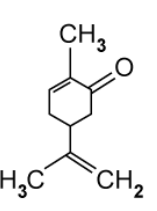
Compound E is a derivative of compound C .
Suggest why the cis/trans naming system fails with compound E .
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Describe the difference between conformational and configurational stereoisomers.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
The chemical and physical properties of optical isomers are identical. However, there are some other differences that can be used to distinguish isomers from each other.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Describe how you can detect optical activity in a sample.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
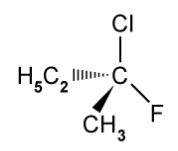
The structure of one optical isomer of a chlorofluorocarbon is shown below .
Draw the structure of the other enantiomer.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
State what is meant by the term a chiral carbon.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
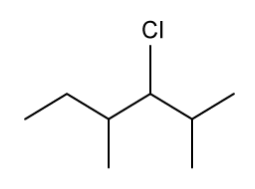
The skeletal structure of an organic compound is shown below.
Identify the chiral carbons.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
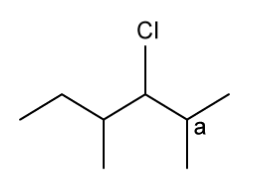
c)
Explain why carbon a cannot be a chiral carbon.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
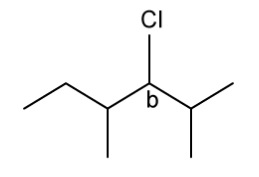
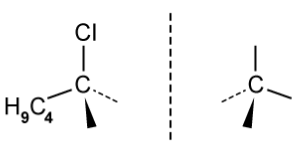
d)
The figure below identifies a different carbon, b , in the organic compounds structure.
Complete the figure below to show the 3D representations of the optical isomers formed at carbon b
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question