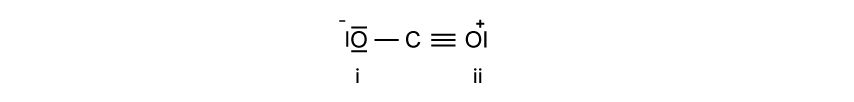a)
Sulfur can form bonds with six fluorine atoms to form sulfur hexafluoride, SF6 .
i)
How many electrons are in the outer shell of the sulfur in SF6 ?
[1]
ii)
State the minimum and maximum numbers of electrons possible in the outer shell of sulfur.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Sulfur has no lone pairs when bonded to fluorines in SF6 . Predict the molecular geometry of sulfur hexafluoride, SF6 .
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
State the F-S-F bond angles in SF6 .
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Phosphorus pentafluoride, PF5 , is also a molecule with an expanded octet around the central atom.
i)
Draw a Lewis (electron dot) structure for PF5
[1]
ii)
Predict the molecular geometry of PF5
[1]
iii)
State the F-P-F bond angle(s)
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Although noble gases do not normally react, a few compounds are possible. One is xenon tetrafluoride. 4 .
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Predict the molecular geometry and electron domain geometry for the XeF4 molecule.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Predict and explain the F-Xe-F bond angle in XeF4
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
The formal charge on an atom can be calculated by the following:
FC = (Number of valence electrons) - ½(Number of bonding electrons) - (Number of non-bonding electrons)
Calculate the formal charge on the xenon and the fluorines in xenon tetrafluoride, XeF4 .
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
 ) bond is formed
) bond is formedformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1437d7d1d97917cd627a34a6a0f%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%226.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) ) bond is formed
) bond is formed ) and pi (
) and pi (format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1437d7d1d97917cd627a34a6a0f%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%226.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) ) bonds.
) bonds. ) and pi (
) and pi (format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1437d7d1d97917cd627a34a6a0f%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%226.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) ) bonds in methane, CH4.
) bonds in methane, CH4. ) and pi (
) and pi (format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1437d7d1d97917cd627a34a6a0f%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%226.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) ) bonds in oxygen, O2.
) bonds in oxygen, O2.