a)
The conversion of hydrogen and iodine into hydrogen iodide proceeds via a three step reaction mechanism:
I2 (g) (g) fast
H 2 (g) + I (g) 2 I (g) fastH2 I (g) + I (g) → 2HI (g) slow
Write the rate equation for this reaction and show how the mechanism is consistent with the stoichiometric equation.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
An investigation into the rate of reaction between hydrogen and iodine was carried out at 298 K and the data obtained is shown below.
Experiment
[H2 ] / mol dm-3
[I2 ] / mol dm-3
Initial rate/ mol dm-3 s-1
1
0.0258
0.0137
6.43 x 10-22
2
0.0258
0.0274
1.29 x 10-21
3
0.0516
0.0137
1.29 x 10-21
Determine the rate equation for the reaction and justify your answer.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Calculate the rate constant using Expt 2 data, including its units.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Using section 11 of the Data booklet, determine whether the forward reaction is favoured by an increase in temperature.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
The reaction between iodide ions and persulfate ions is a 'clock' reaction and often used to study reaction kinetics.
2I- (aq) + S2 O8 2- (aq) → I2 (aq) + 2SO4 2- (aq)
Deduce the redox changes taking place in the reaction.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
A persulfate-iodide clock reaction was studied and the following rate data obtained.
Experiment
[S2 O8 2- ] / mol dm-3
[I- ] / mol dm-3
Initial rate/ mol dm-3 s-1
1
0.25
0.10
8.0 x 10-3
2
0.10
0.10
3.2 x 10-3
3
0.20
0.30
1.92 x 10-2
Deduce the order with respect to persulfate ions and iodide ions.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Determine the rate equation for the reaction and calculate rate constant, including the units.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Four mechanisms are proposed for the persulfate-iodide reaction. Deduce which mechanism(s) is/are consistent with the rate equation in part c) and justify your answer.
I- (aq) + I- (aq) → I2 2- (aq) slow
I2 2- (aq) + S2 O8 2- (aq) → I2 (aq) + 2SO4 2- (aq) fast
Mechanism 2:
I- (aq) + S2 O8 2- (aq) → S2 O8 I3- (aq) slow
S2 O8 I3- (aq) + I- (aq) → I2 (aq) + 2SO4 2- (aq) fast
Mechanism 3:
I- (aq) + S2 O8 2- (aq) → S2 O8 I3- (aq) fast
S2 O8 I3- (aq) + I- (aq) → I2 (aq) + 2SO4 2- (aq) slow
Mechanism 4:
2I- (aq) + S2 O8 2- (aq) → I2 (aq) + 2SO4 2- (aq) slow
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
The reaction between nitrogen monoxide and hydrogen produces nitrogen and water:
2NO (g) + 2H2 (g) → N2 (g) + 2H2 O (g)
Rate data for this reaction is shown below.
Experiment
[NO] / mol dm-3
[H2 ] / mol dm-3
Initial rate/ mol dm-3 s-1
1
0.001
0.004
0.002
2
0.002
0.004
0.008
3
0.004
0.001
0.016
What is the molecularity of the reaction?
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
i)
Rate against concentration of NO.
[1]
ii)
Rate against concentration of H2
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Suggest a possible mechanism for the reaction.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Suggest a Lewis structure for N2 O2 and draw the shape of the molecule.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
The rate of reaction between manganate(VII) ions and oxalate ions, C
2 O
4 2- , can be investigated by measuring how the concentration of manganate(VII) varies with time.
2MnO4 - (aq) + 16H+ (aq) + 5C2 O4 2- → 2Mn2+ (aq) + 8H2 O(l) + 10CO2 (g)
The rate is first order with respect to oxalate ions and the general rate equation for the reaction is:
rate = k [MnO4 - ]p [C2 O4 2- ]q [H+ ]r
i)
Suggest how the change in manganate(VII) concentration can be measured.
[1]
ii)
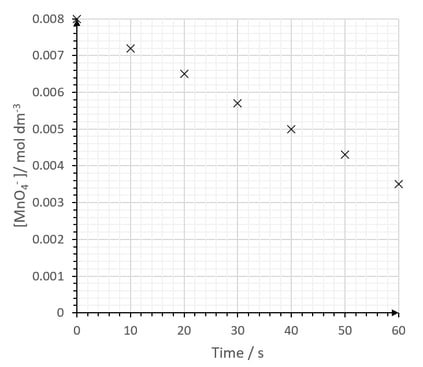
A student investigated how the concentration of manganate(VII) affected the rate of reaction and produced the following results. The oxalate ions and acid were in excess.
Determine the rate of reaction.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
The student used an acid concentration of 1.0 mol dm
-3 . She then varied it, keeping the other concentrations constant. She measured the rate of reaction and found the following results:
[H+ ]/ mol dm-3
Relative rate of reaction
0.5
0.0025
0.25
0.0013
0.01
0.0005
Identify the relationship between the relative rate of reaction and H
+ , and hence determine the order of reaction with respect to H
+ ions.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
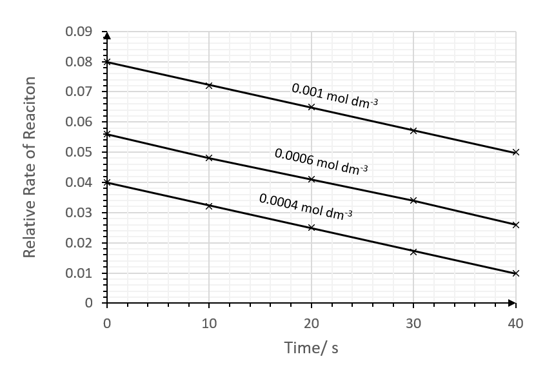
c)
The student varied the concentration of [MnO4 - ] and plotted the rate against time at three different concentrations:
i)
Deduce, with a reason, the order of reaction with respect to MnO4 -.
[2]
ii)
Write the rate expression for the reaction.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
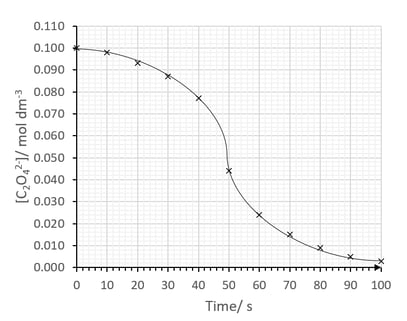
d)
The student then measured the reaction time for different concentrations of C2 O4 2- and obtained a curve as follows:
Comment on the shape of the graph.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
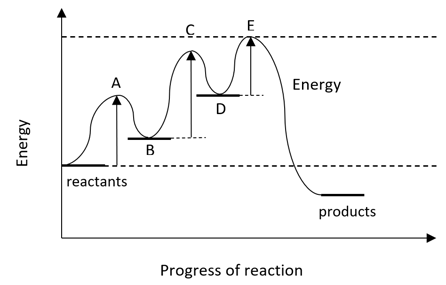
a)
A reaction proceeds by a three step mechanism. The energy profile for the reaction is shown below:
Explain the difference between points A, C, E and B, D on the profile.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Deduce which step is the rate determining step of the reaction, giving a reason.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question
2I (g) fast
H2I (g) fast