Question 1
Which of the following can be used for a standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)?
| Electrode | Electrolyte solution | |
| A. | Graphite | 1 mol dm-3 H2SO4 |
| B. | Graphite | 1 mol dm-3 HCl |
| C. | Platinum | 0.5 mol dm-3 H2SO4 |
| D. | Platinum | 0.5 mol dm-3 HCl |
Which of the following can be used for a standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)?
| Electrode | Electrolyte solution | |
| A. | Graphite | 1 mol dm-3 H2SO4 |
| B. | Graphite | 1 mol dm-3 HCl |
| C. | Platinum | 0.5 mol dm-3 H2SO4 |
| D. | Platinum | 0.5 mol dm-3 HCl |
What are the ratios of gases produced at the electrodes in the electrolysis of dilute vs concentrated sodium chloride solution?
| Ratio of gas produced at cathode : anode in the electrolysis of dilute NaCl | Ratio of gas produced at cathode : anode in the electrolysis of concentrated NaCl | |
| A. | 1:1 | 2:1 |
| B. | 1:1 | 1:2 |
| C. | 1:2 | 1:1 |
| D. | 2:1 | 1:1 |
Which of the following could be used to electroplate a zinc medal?
1.0 mol dm-3 AgNO3 solution with a silver anode
1.0 mol dm-3 AgNO3 with a silver cathode
1.0 mol dm-3 CuSO4 solution with a copper cathode
1.0 mol dm-3 solution of SnCl2 and a tin anode
The diagram below shows the set-up of aluminium and silver cells in series:
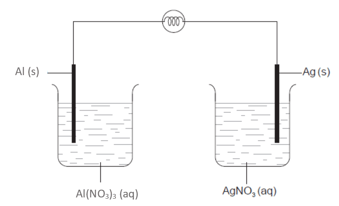
What calculation shows the loss in mass of the aluminium electrode if the silver electrode gains 0.25 g?
Al mass lost =
Al mass lost =
Al mass lost =
Al mass lost =
The oxidation of iron is a spontaneous process described by the overall equation:
Fe (s) + O2 (g) + H2O (l) → Fe(OH)2 (s)
(ΔGθ = -164 kJ mol-1 at 298 K)
The two half equations for the process are:
Fe2+ (s) + 2e- → Fe (s)
O2 (g) + H2O (l) + 2e- → 2OH- (s)
(ΔGθ = -nFEθ , F = 9.65 x 104 C mol-1)
Which is the correct calculation to work out Eθ in V?
Eθ =
Eθ =
Eθ =
Eθ =