Consider these standard electrode potentials.
Fe2+ (aq) + 2e- format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1aa495e18c7e3a21a4e48923b92%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x21CC%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) Fe (s) EΘ = -0.45 V
Fe (s) EΘ = -0.45 V
Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1aa495e18c7e3a21a4e48923b92%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x21CC%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) Cu (s) EΘ = +0.15 V
Cu (s) EΘ = +0.15 V
Which is the correct working to determine EΘcell?
Which of the following is not a condition for the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)?
Hydrogen gas with a pressure of 100 Pa
Which combination would electroplate an object with silver?
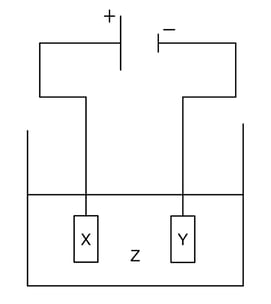
| |
X |
Y |
Z |
| A. |
Object to be plated |
Silver |
Silver chloride |
| B. |
Silver |
Object to be plated |
Hydrochloric acid |
| C. |
Object to be plated |
Silver |
Water |
| D. |
Silver |
Object to be plated |
Silver nitrate |
What are the products for the electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride solution using inert electrodes?
| |
Anode |
Cathode |
| A. |
O2 (g) |
H2 (g) |
| B. |
H2 (g) |
O2 (g) |
| C. |
Cl2 (g) |
H2 (g) |
| D. |
H2 (g) |
Cl2 (g) |
A voltaic cell is made by connecting two half-cells represented by the half-equations below.
Al3+ (aq) + 3e- format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1aa495e18c7e3a21a4e48923b92%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x21CC%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) Al (s) EΘ = -1.66 V
Al (s) EΘ = -1.66 V
Sn2+ (aq) + 2e- format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1aa495e18c7e3a21a4e48923b92%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2210.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%26%23x21CC%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) Sn (s) EΘ = +0.14 V
Sn (s) EΘ = +0.14 V
Which statement is correct about this voltaic cell?
The cell representation is Al (s) l Al3+ (aq) II Sn2+ (aq) I Sn (s)
The Al3+ (aq) / Al (s) electrode is the cathode
The cell representation is Al3+ (aq) l Al (s) II Sn (s) I Sn2+ (s)
The Sn2+ (aq) / Sn (s) electrode is the anode
Fe (s) EΘ = -0.45 V
Cu (s) EΘ = +0.15 V
