a)
A molecule of oleic acid is shown.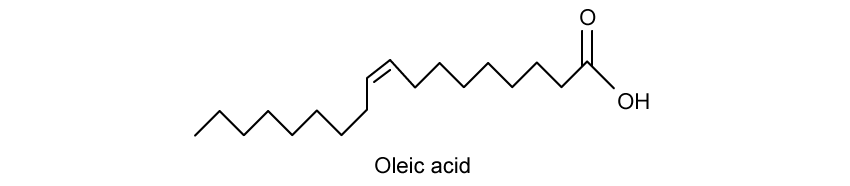
Oleic acid is a fatty acid which occurs naturally in different animals and plants.
Oleic acid exhibits
stereoisomerism. Explain the meaning of this term and identify why oleic acid has stereoisomers.
b)
Crotonic acid is another fatty acid which has a similar structure to oleic acid. The molecular formula of crotonic acid is C4H6O2.
i)
State the empirical formula of crotonic acid.
ii)
Crotonic acid has a carboxylic acid functional group. Draw the displayed formula of the positional and branch-chain isomers of crotonic acid.
iii)
Identify which of the isomers you have drawn shows E / Z isomerism..
c)
Give the IUPAC names of the E / Z isomers of crotonic acid.
d)
Draw the structure of the Z-isomer of crotonic acid and mark the C-C=C bond angle
a)
A chemist is analysing a collection of organic compounds. The structural formulae of these compounds are shown.
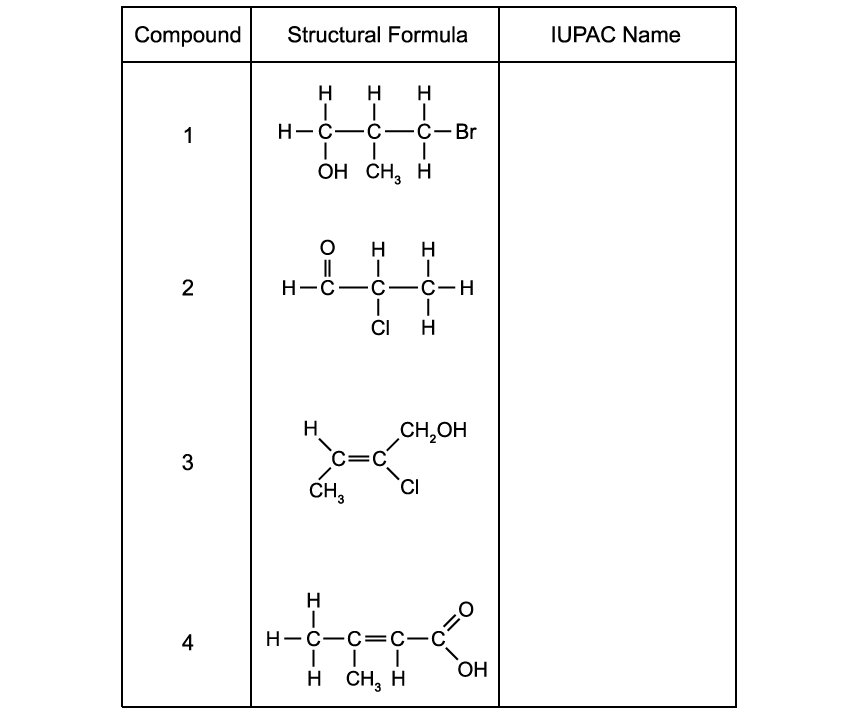
Give the IUPAC name for the compounds to complete the table.
b)
This question refers to the compounds in the table in part (a)
(i)
Identify the compounds which have chain isomers and draw their isomers.
(ii)
State the empirical formula of compound 3.
(iii)
Does compound 4 exhibit stereoisomerism? Explain your answer.
c)
Which of the bond(s) shown in the following structure is/are in the
Z configuration?
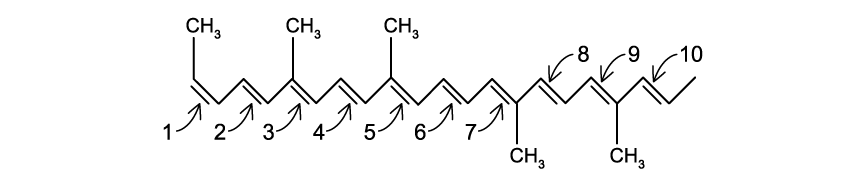
d)
Explain why the reaction between E-but-2-ene and bromine produces the same product as Z-but-2-ene with bromine.
a)
Draw and label the cis / trans isomers of 1,2-dichlorocyclohexane. Explain why this molecule has cis / trans isomers
b)
Mark the location of any chiral centres in limonene.
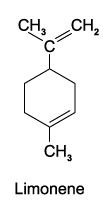
c)
Two unsaturated isomers of C4H5N, display stereoisomerism.
Draw and name the isomers.
d)
Draw an isomer of C4H5N that does not exhibit stereoisomerism.
a)
2-methylbut-2-ene can be converted into 2-methylbutan-2-ol, a liquid that smells of camphor.
State the reagents needed to convert 2-methylbut-2-ene into 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
b)
The reaction in part (a) produces a small amount of an isomeric co-product, X, which is optically active.
i)
State the meaning of optical activity.
ii)
Draw the structure of X.
c)
What does optical activity indicate about the structure of X?
d)
Explain how optical activity can be detected using a polarimeter
a)
Dichloroethene exists as two stereoisomers. Draw the structures of these isomers.
b)
Explain why dichloroethene has stereoisomers.
c)
Draw the structures of the stereoisomers of 1-bromo-1-chloroethane, C2H4BrCl, and show the relationship between them.
d)
Explain the differences in chemical and physical properties between the isomers of C2H4BrCl



