a)
Iron is a transition element that forms several ions with iron in different oxidation states.
Deduce the condensed electron configuration of the iron cation that can form the complex ion [Fe(CN)6]4−.
[1]
b)
Co(III) has the same electron configuration as the iron cation in part(a).
Explain why, despite this, solutions of the two ions are different colours.
[2]
c)
Rhenium forms salts containing the perrhenate(VII) ion, ReO4−.
Suggest why the existence of salts containing an ion with this formula could be predicted. Refer to section 6 of the data booklet.
[1]
d)
Rhenium is used with platinum to speed up reactions used in the production of gasoline.
Predict two other chemical properties you would expect rhenium to have, given its position in the periodic table.
[2]
a)
Chromium (III) picolinate, shown below, is often used in tablets as a nutritional supplement for chromium.
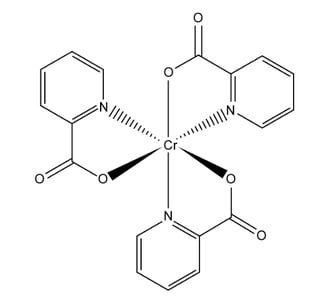
i) Draw the structure of the ligand in chromium(III) picolinate.
[1]
ii) State the coordination number of chromium in chromium(III) picolinate.
[1]
b)
A complex of cobalt has the following composition by mass:
Co, 21.98%; N, 31.35%; H, 6.81%; Cl, 39.86%
i)
Calculate the empirical formula of this complex.
ii)
The formula of this cobalt complex can be expressed in the form [Co(L)m]x+(Cl−)n.
Suggest the chemical formula of [Co(L)m]x+.
[3]
c)
Ni(ClO4)2 reacts with water to form the complex ion [Ni(H2O)6][ClO4]2.
Explain this reaction in terms of an acid-base theory.
[2]
d)
Nickel(II) forms a complex ion with water, [Ni(H2O)6]2+
i)
Outline how the bond is formed between Ni2+ and H2O during the formation of the complex.
[1]
ii} State the geometry of the complex formed.
[1]
