Which of the following statements about the rate-determining step are correct?
- It has the highest activation energy
- It can be used to deduce the rate expression
- It is the slowest step in the reaction mechanism
The rate information below was obtained for the following reaction at a constant temperature:
A + 2B → C + 2D
|
Experiment
|
Initial [A]
/ mol dm–3
|
Initial [B]
/ mol dm–3
|
Initial rate
/ mol dm–3 s–1
|
|
1
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
3.5 x 10-4
|
|
2
|
0.25
|
0.50
|
To be calculated
|
The rate equation for this reaction is rate = k [B]
What is the initial rate of reaction for experiment 2, in mol dm–3 s–1?
The rate equation for the reaction between A and B is:
Rate = k [A] [B]
What are the correct units for the rate constant of this rate equation?
The rate information below was obtained for the following reaction at a constant temperature:
5Br– (aq) + BrO3– (aq) + 6H+ (aq) → 3Br2 (aq) + 3H2O (l)
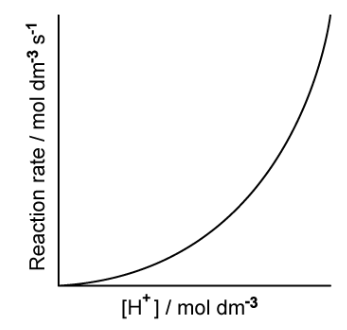
What is the order of reaction with respect to [H+]?
The mechanism for the following reaction between nitrogen(II) oxide and carbon monoxide is shown.
NO2 (g) + CO (g) → NO (g) + CO2 (g)
Step 1: NO2 + NO2 → NO3 + NO slow step
Step 2: NO3 + CO → NO2 + CO2 fast step
What rate expression is consistent with the mechanism?
