a)
Successive ionisation energies provide evidence for the arrangement of electrons in atoms. In the table below the successive ionisation energies of oxygen are given.
Ionisation number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Ionisation energy (kJ mol -1 )
1314
3388
5301
7469
10989
13327
71337
84080
i)
Give the equation, including state symbols for the third ionisation energy of oxygen.
[2]
ii)
Explain how this data shows evidence of two energy shells in oxygen.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Amorphous(unorganized solid form) boron is used as a rocket fuel igniter and in pyrotechnic flares.
i)
Write an equation, including state symbols to show the process that occurs for first ionisation of boron, B.
[1]
ii)
Suggest why the ionisation energy of boron is lower than that of beryllium going against the general trend in ionisation energies across the period.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Using the table in part (a) and sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet, calculate the wavelength, in nm, of the convergence limit in the spectral lines of an oxygen atom.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
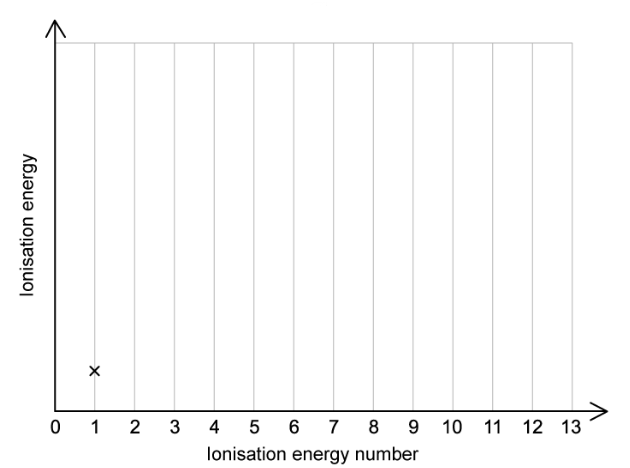
a)
Aluminium has 13 successive ionisation energies.
On the figure below, add crosses to show the 13 successive ionisation energies of aluminium. The value for the first ionisation energy is already completed.
You do not have to join the crosses.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
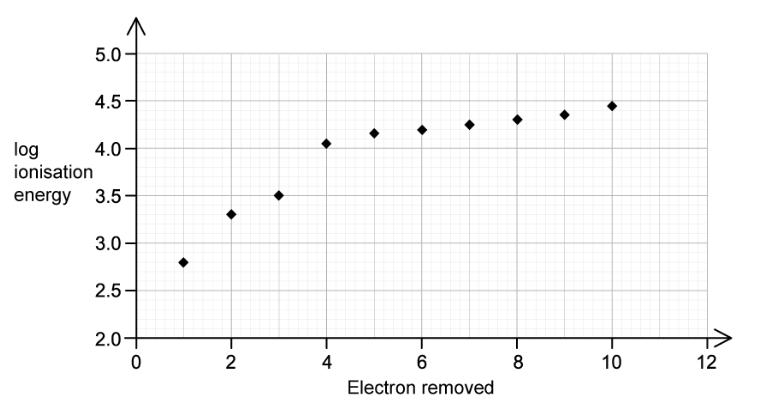
b)
This question is about ionisation energies of an element, X .
The figure below represents the log of the first ten successive ionisation energies of X plotted against the number of electrons removed.
State the group of the periodic table where element X is found.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Element A has the following first six ionisation energies in kJ mol -1 .
577, 1820, 2740, 11 600, 14 800, 18 400
i)
Explain how you know that element A is in group 3 of the periodic table.
[1]
ii)
Two elements B and C are in the same period as A , but B is in the group before A and C is in the group after A in the periodic table.
Give approximate first ionisation energies for elements B and C .
[1]
iii)
Explain, using ideas of electronic structure, the difference in ionisation energy values of element A compared to elements B and C .
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
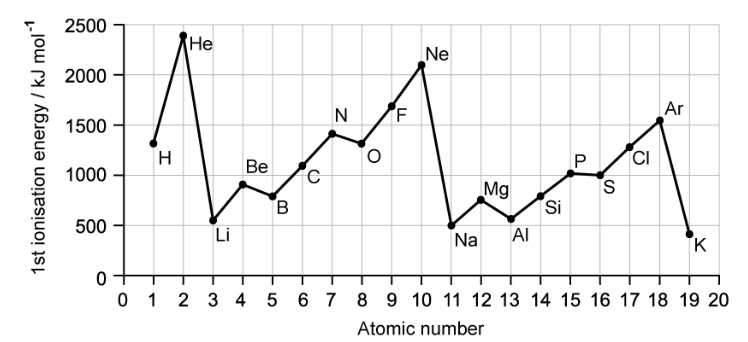
a)
The first ionisation energies of the elements H to K are shown below in the figure below
State and explain the trend in first ionisation energies shown by the elements with the atomic numbers 2, 10 and 18.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Compound J reacts with chlorine. The first five successive ionisation energies for an element J , are shown in the table below .
Energy number
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
Ionisation energy value / kJ mol −1
738
1450
7733
10543
13630
State the formula of the compound when element J reacts with chlorine.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
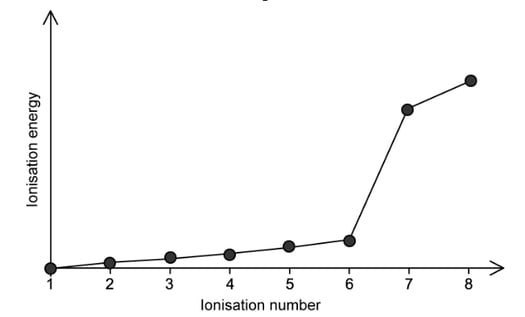
c)
The figure b elow shows the successive ionisation energies for a period 2 element.
With reference to electronic structures, state the identity of this element and explain your answer.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
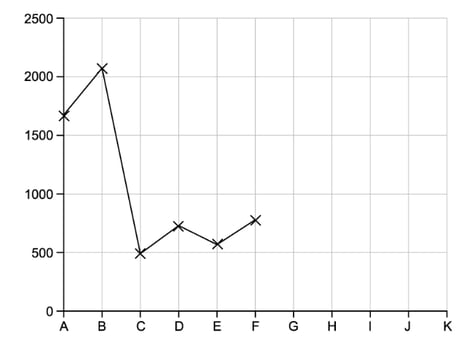
a)
Electrons in atoms occupy orbitals. The figure below shows the first ionisation energies for six consecutive elements labelled A – F in kJ mol-1 .
i)
Complete the graph of the first ionisation energies for the next five elements.
[3]
ii)
Explain why the value of the first ionisation energy for D is greater than for C.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
The sequence of the first three elements in the Periodic Table is hydrogen, helium and then lithium.
Explain why the first ionisation energy of hydrogen is less than that of helium but greater than that of lithium.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Using the figure in part (a) and sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet, calculate the frequency, in THz, of the convergence limit of a single atom of element C.
The prefix Tera, T, corresponds to a power of 1012 .
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
The table b elow shows the successive ionisation energies of an unknown element, X .
Ionisation number
Ionisation energy / kJ mol -1
1st
578
2nd
1817
3rd
2745
4th
11577
5th
14842
6th
18379
Deduce the group number and identity of element X and explain your answer with reference to its electron configuration.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
First ionisation energies decrease down groups in the Periodic Table.
Explain this trend and the effect on the reactivity of groups containing metals.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
The ionisation energy values show a general increase across period 4 from gallium to krypton.
i)
State and explain how selenium deviates from this trend.
[3]
ii)
Give one other element from period 2 or 3 which also deviates from this general trend, similar to selenium.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question