a)
Tetrafluoroethene, C2F4, and tetrafluorohydrazine, N2F4, are fluorides of adjacent elements in the Periodic Table.
Draw the Lewis (electron dot) structures for C2F4 and N2F4 showing all valance electrons.
[2]
b)
Predict and explain the F-C-F bond angle in tetrafluoroethene and the F-N-F bond angle in tetrafluorohydrazine.
[5]
c)
Tetrafluorohydrazine is a polar molecule but tetrafluoroethene is not.
Explain the difference in molecular polarity.
[4]
a)
Draw the Lewis (electron dot) structure of the carbonate ion, CO32-.
[3]
b)
Deduce the number of possible resonance structures for the carbonate ion, CO32-, and draw two of them.
[3]
c)
Discuss how the bonding in the carbonate ion, CO32-, evidences the presence of the resonance structures.
[3]
d)
Organic molecules can also show resonance. The methanoate ion, HCOO-, shows similar resonance forms to the carbonate ion, CO32-.
The corresponding organic acid, methanoic acid, also has resonance structures.
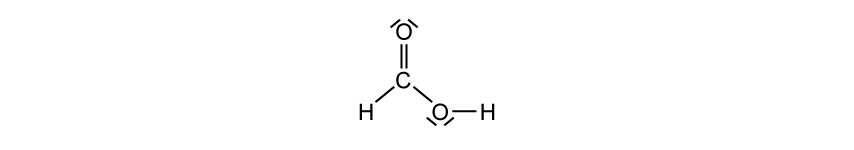
Draw another resonance structure of methanoic acid.
[2]
