a)
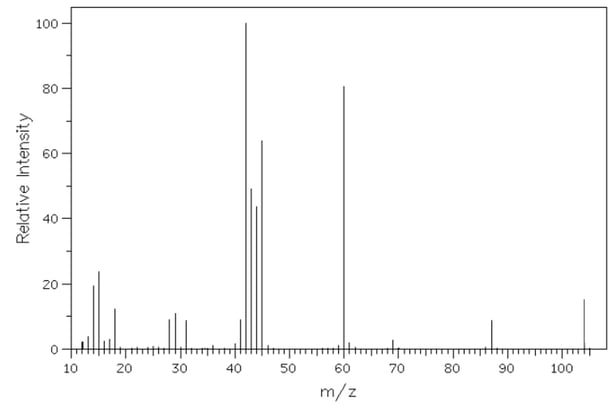
Malonic acid, C3 H4 O4 , is naturally occurring and found in many fruits and vegetables. It contains only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
The MS of malonic acid is show below.
Determine the relative molecular mass of malonic acid from the spectrum and account for the peak at m/z 45, using section 28 of the Data booklet to support your answer.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
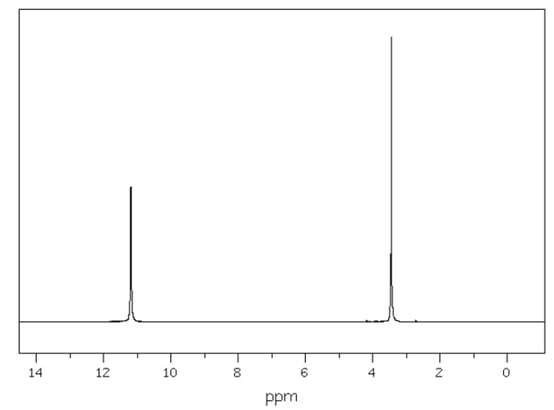
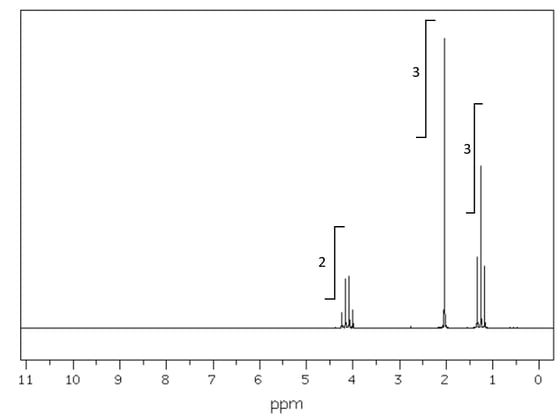
The 1 H NMR spectrum of malonic acid is shown below. Use section 27 of the Data booklet to help you with this question.
Suggest the identity of the proton environments seen in the spectrum and comment on the type of signals shown.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
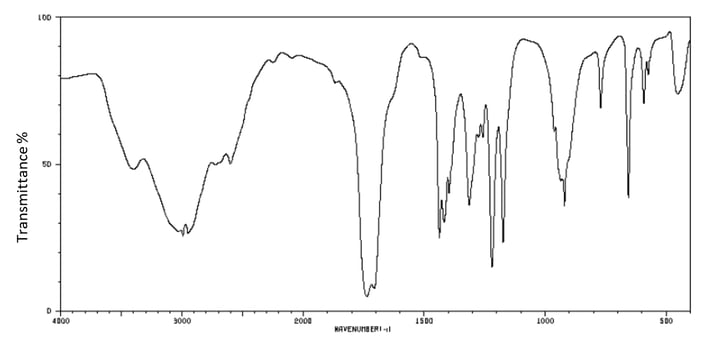
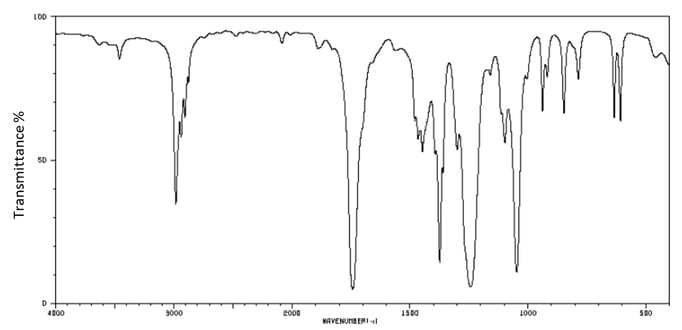
The IR spectrum of malonic acid is shown below:
i)
Identify two characteristic peaks and bonds that can be found in the spectrum of malonic acid.
[2]
ii)
Explain how the spectrum can be used to distinguish malonic acid from ethanoic acid.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Draw a displayed structure for malonic acid.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
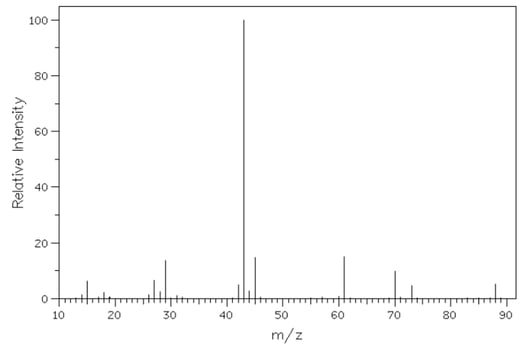
An organic compound, Q, of molecular formula C
x H
y O
z , has the following MS. Use section 28 of the Data booklet to help you answer this question.
i)
Determine the relative molecular mass of Q and account for the peaks at 15 and 29.
[2]
ii)
Comment on the size of the peak at m/z 43.
[1]
iii)
Write an equation for the formation of the fragment at m/z 29.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
The IR spectrum of Q is shown below.
Suggest which functional group(s) could be present in Q.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
The 1 H NMR spectrum of Q is shown below.
Explain the relative peaks heights and splitting patterns
[5]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
Suggest the identity of Q, giving your reasons.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Compound A, has molecular formula C
5 H
10 and occurs as 6 isomers. The table below shows the number of signals in the NMR spectrum of each isomer.
Isomer
Number of 1 H NMR signals
A
1
B
5
C
5
D
5
E
5
F
4
Suggest a structure for A and F.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
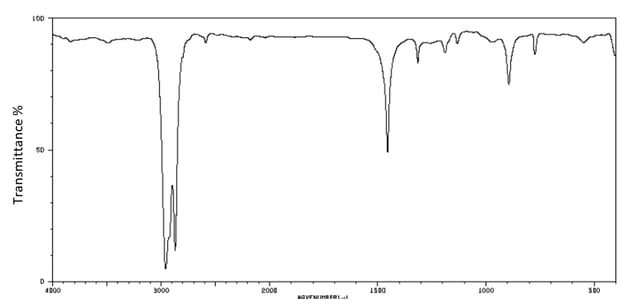
b)
The IR spectrum of A is shown below.
How does this spectrum distinguish A from the other isomers?
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Evaluate whether X-ray crystallography could distinguish between the isomers of A.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Oseltamivir is a drug used to treat and prevent influenza A and influenza B.
Predict the number of different proton environments in the molecule.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Predict the chemical shift and the splitting pattern seen for the hydrogens on the carbon atom circled in the diagram. Use section 27 of the Data booklet.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Predict three absorptions you would expect to see in the IR spectrum of oseltamivir. Use section 26 of the data booklet.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
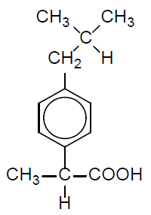
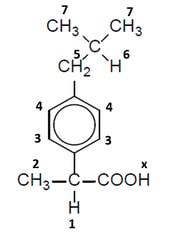
Ibuprofen is an important painkilling drug. The structure is:
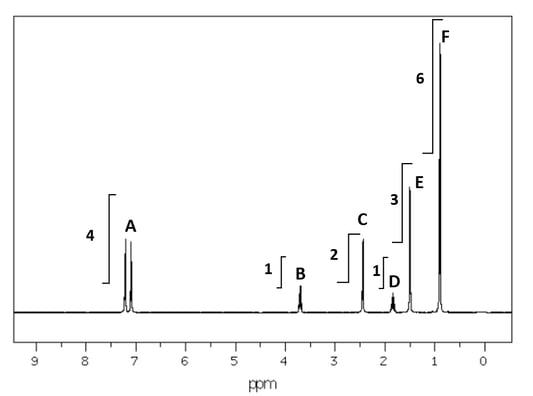
Part of the low resolution 1 H NMR spectrum is shown below.
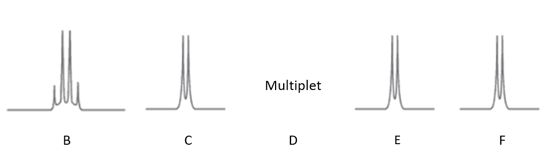
The high resolution expansion of the peaks in B-F is:
The protons responsible for the peaks are numbered 1-7:
Complete the table to show the assignment of the missing peaks.
Peak H atoms responsible
A
3 & 4
B
C
D
E
F
off spectrum
X
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
A sample of ibuprofen shows strong absorptions at 1716 cm-1 and 3345 cm-1 in an IR spectrum. Suggest the bonds responsible for these absorptions using section 26 of the data booklet.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
A sample of ibuprofen rotates plane polarised light. Identify the feature in ibuprofen responsible for this.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question