a)
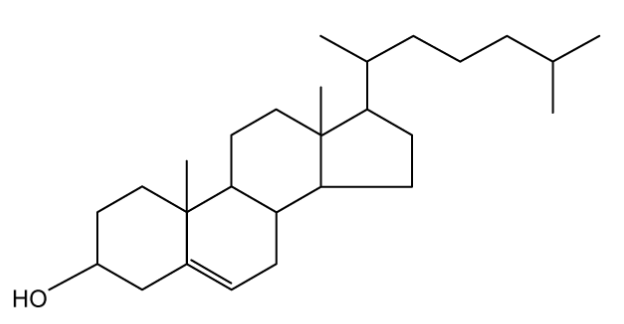
Cholesterol, shown below, is a fatty chemical used by the body to build healthy cells.
State the number of chiral carbons in the cholesterol structure.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
A student suggested that cholesterol could be tested with plane polarised light to show that it contains chiral centres.
Is the student correct? Justify your answer.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
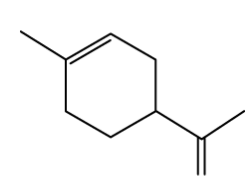
Limonene, shown below, is a naturally occurring hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C10 H16 and is commonly found in the rinds of citrus fruits such as grapefruit, lemon, lime and oranges.
Limonene exists as a pair of enantiomers; one enantiomer is responsible for a strong orange smell while the other is thought to smell like lemons.
Draw 3D representations of the two enantiomers of limonene.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
a)
1,1,1,2-tetrafluoro-but-2-ene is a compound containing hydrogen, carbon and fluorine atoms.
State the meaning of the term 'stereoisomers' and explain why 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoro-but-2-ene displays stereoisomerism.
[5]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Draw the E and Z isomers of 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoro-but-2-ene.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
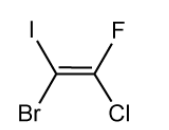
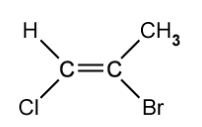
State the limitation of the cis-trans naming rules when it comes to the molecule shown below.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
d)
State the name of the molecule shown in part (c).
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Butenedioic acid is HOOCCH=CHCOOH. It has two stereoisomers, commonly known as malic acid and fumaric acid. Both acids are responsible for the sour taste in fruit.
Draw the two E-Z isomers of butenedioic acid in skeletal formulae and label them as E -butenedioic acid and Z -butenedioic acid.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
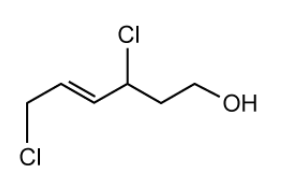
A student named the alcohol molecule shown below Z -1,4-dichlorohex-2-ene-6-ol.
State the errors the student has made in naming the molecule and give the correct IUPAC name.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Compounds with a carbon−carbon double bond are unsaturated. The figure below s hows an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
i) Name the isomer shown .
[1]
ii) Justify the CIP naming rule for this isomer.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
Lactic acid has the molecular formula of C3 H6 O3 , and the structural formula of CH3 CHOHCOOH.
Illustrate the types of isomerism shown by C3 H6 O3 .
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
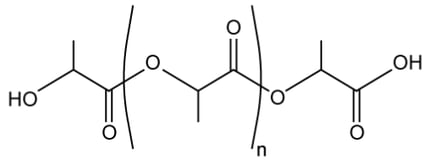
b)
The general structure of polylactic acid is shown below:
Draw two possible structures formed from two repeating units.
Your answer should keep the main polymer chain in the same plane but show the 3D representation of the chiral carbons.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
State, why the polymer formed from the uncontrolled condensation polymerisation of lactic acid, is not a racemate.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
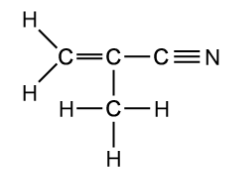
a)
Two isomers of 2-methylprop-2-enenitrile, C 4 H 5 N, display E/Z isomerism.
Draw and name the isomers.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
b)
Draw one repeating unit of the polymer formed by addition polymerisation of (E) -but-2-ene.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
c)
Explain why the polymer formed by ( E )-but-2-ene is the same as the polymer formed by (Z )-but-2-ene.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question