Investigating strawberries with a glucose test meter
 This page explores a use of affordable glucose test meters to estimate glucose concentrations in strawberries. These amazing gadgets use nanotubes lined with enzymes to turn glucose molecules into electrical signals. Designed to test the glucose concentration in tiny blood samples, they help many people in the management of type II diabetes. With a little care they work equally well as a tool to measure the glucose concentration of strawberries. This activity introduces the glucose test meter and connects it to the understanding of enzymes, reduction, oxidation and electrical signals in DP Biology. A simple glucose testing experiment leads to a final activity helping students to use design thinking to create ideas for an Individual investigation using this protocol.
This page explores a use of affordable glucose test meters to estimate glucose concentrations in strawberries. These amazing gadgets use nanotubes lined with enzymes to turn glucose molecules into electrical signals. Designed to test the glucose concentration in tiny blood samples, they help many people in the management of type II diabetes. With a little care they work equally well as a tool to measure the glucose concentration of strawberries. This activity introduces the glucose test meter and connects it to the understanding of enzymes, reduction, oxidation and electrical signals in DP Biology. A simple glucose testing experiment leads to a final activity helping students to use design thinking to create ideas for an Individual investigation using this protocol.
Lesson Description
Guiding Questions
- What is a glucose test meter?
- Why do so many people need to test their glucose regularly?
Activity 1 - Introduction to the glucose test meter
A knowledge of redox reactions and hydrogen carriers associated with enzymes is important in the metabolism and respiration topic. An understanding of the metabolism of glucose is not covered in topic 8 but is important in understanding glucose metabolism and diabetes in topic 6 Human physiology. The slides below introduce Blood glucose test meters.
Look through the slides and answer the questions which follow.
Note the different command terms Define, Discuss, Describe Outline Explain and Suggest.
Questions
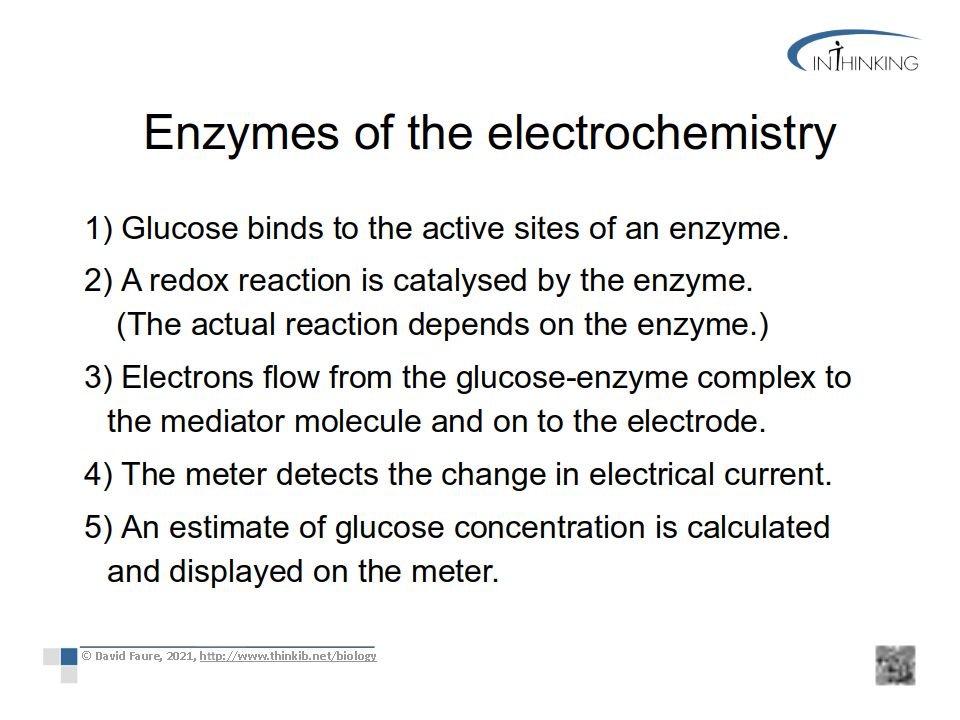
- Describe the how an enzyme can bind to a glucose molecule in the test strip. (2 marks)
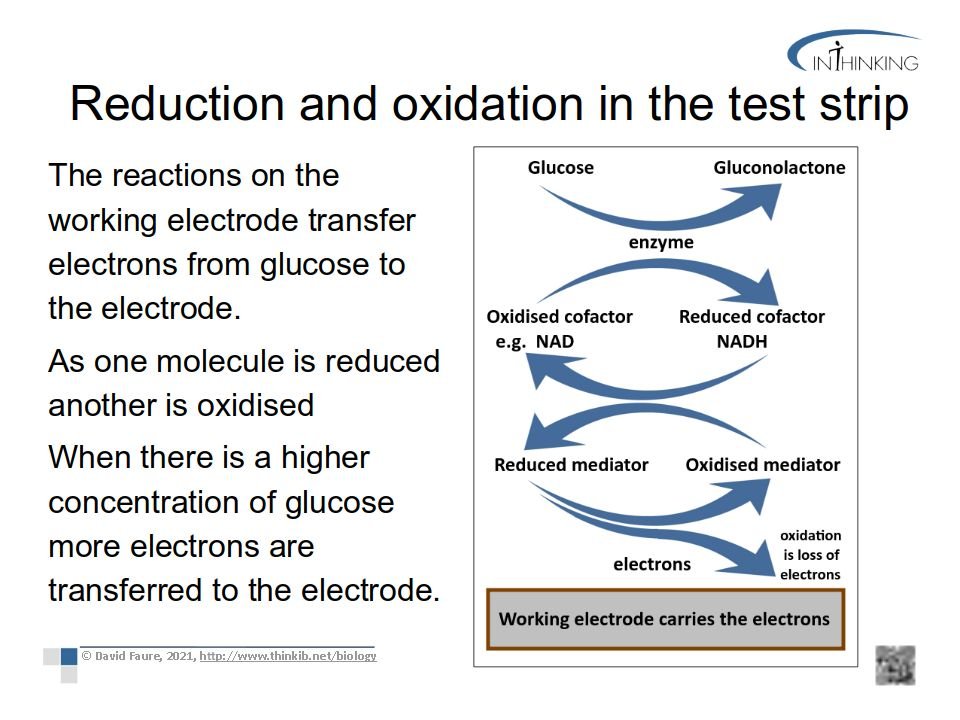
- Outline the enzymes glucose oxidase and glucose dehydrogenase both oxidise glucose using your knowledge of oxidation and reduction. (2 marks)
- Suggest why a hydrogen carrier, like NAD, is also required when the enzyme glucose dehydrogenase is used in a test strip. (2 marks)
- Discuss whether the release of electrons detected by this electronic meter is a more reliable estimate of glucose concentration than a colour change in a chemical indicator, or not? (4 marks)
Click the eye icon to display some model answers. How do your answers compare?
- Describe the how an enzyme can bind to a glucose molecule in the test strip. (2 marks)
The active site of the enzyme has a shape which allows the substrate to bind to it
Induced fit is also thought to occur where the active site changes when the substrate binds. - Outline the enzymes glucose oxidase and glucose dehydrogenase both oxidise glucose using your knowledge of oxidation and reduction. (2 marks)
Oxidation is the addition of oxygen to a molecule or the removal of hydrogen. (Oxidation is loss of an election too)
So the enzyme oxidase adds oxygen and dehydrogenase removes hydrogen.
These are both processes which oxidise the glucose molecule, and remove an electron. - Suggest why a hydrogen carrier, like NAD, is also required when the enzyme glucose dehydrogenase is used in a test strip. (2 marks)
When dehydrogenase removes hydrogen from glucose the NAD, hydrogen carrier is reduced by the hydrogen.
NAD becomes NADH (more precisely NADH + H+) - Discuss whether the release of electrons detected by this electronic meter is a more reliable estimate of glucose concentration than a colour change in a chemical indicator, or not? (4 marks)
The release of electrons following these redox reactions seems very accurate as many factors are controlled in the manufacture of the test strip, e.g. volume of blood in the sample, concentration of enzymes in the strip.
A numerical value on a continuous scale is more precise than a colour scale in discontinuous bands.
There are other chemicals which can affect the glucose concentration estimate, e.g. antioxidants like Vitamin C.
Temperature also affect the activity of enzymes, but it also affects the rate of reaction of inorganic chemicals.
Activity 2 - Experiment to measure the glucose concentration of a strawberry.
This activity introduces several concepts in biochemistry, the idea of reducing the scale of a test to very small volumes and the use of electrochemistry instead of colour chemistry in biochemical analysis.
This simple protocol describes how to measure the glucose concentration of a strawberry. It could be adapted to compare different berries, drinks or simply to introduce the quantitative possibilities of this type of test.
Testing of human blood, or other body fluids is not allowed in the Animal Experimentation guidelines published by the IB. Do not use sterile lancets or other methods of extracting blood because of the risks of transmitting blood bourne pathogens.
Fortunately strawberries are red, like blood, and they pose no health risk in the lab, so long as they are not eaten !
Use ![]() Measuring glucose concentration in fruit student worksheet to prepare a sample of strawberry, with a 1 in 20 dilution and then to test its glucose concentration with the blood glucose meter.
Measuring glucose concentration in fruit student worksheet to prepare a sample of strawberry, with a 1 in 20 dilution and then to test its glucose concentration with the blood glucose meter.
Activity 3 - How to use this method as a start for a Research question in an IA.
Sometimes the best place to begin devising a research question for an IA is with a piece of apparatus or a standard method which looks really useful. Blood glucose meters testing blood concentration is a neat technique.
To turn a single test on one strawberry into a research question requires some curious observation, and a little creativity.
Try this creative thinking activity. It is designed to help us think laterally and to observe closely.
The style of questions could be a useful tool to help with any IA topic.
Think about these six questions in turn.
Answer as many of them as you can in the space below.
- What surprises you about the fact that strawberries (or other fruit) contain glucose?
- What are the most important uses that plants make of glucose?
- What interest in glucose do animals have? Do animals like glucose?
- What could happen to glucose in a strawberry if the strawberry isn't eaten?
- Can you think of inconsistencies in strawberries (or other fruit)?
- Which factors (size, shape, ripeness, colour, density, etc.) might influence the concentration of glucose in a strawberry?
Consider your answers and try to convert one of them into a Research question.
Include an independent variable, a dependent variable and details about the scope of your question.
The page Focusing a research question will help you to turn any ideas into a focussed research question.
Teacher's notes
Activity 1 aims to help students make links to their learning in topic 6 and 8 about glucose metabolism and metabolic pathways, including the factors which affect enzymes. The slides could be projected in class, or students could look at them individually and then answer the questions.
The questions are intended to help stimulate a discussion in class rather than providing a tool for assessment. The suggested answer can be revealed easily to help those students finding the questions difficult, or by the teacher wanting to move the discussion to a conclusion.
Activity 2 provides simple step by step instructions for students to carry out a simple test of the blood glucose level using a blood glucose meter. There are two hypotheses suggested, and the conclusion prompts students to consider whether the data they collect supports the null hypothesis or the alternative hypothesis. There is also a consideration of the uncertainties and how they might alter the confidence in the conclusion.
Activity 3 is a creative thinking activity to help students think of ideas for an IA topic using this glucose testing technique. The questions in the activity have been adapted from ideas about design thinking and tailored to the testing of glucose concentration in strawberries, or other fruit.
If this page is used as a task from the Student access section of the site, then the answers written by students will be saved and teachers will be able to comment on them or grade them. Of course student can write answers separately too.
If students need a little prompting here are some suggestions of possible IA topics.
Measure the glucose content in sports drinks and compare the glucose content to sporting performance.
Us a glucose meter to measure glucose concentration in a solution and calculate the activity of an enzymes like amylase or maltase enzymes.
Monitor the rate of respiration in yeast in different environmental conditions.
Evaluate reliability of the blood glucose meter at different temperatures / different pH values. The meter documentation will give a working range of pH and temperature.
Test whether the presence of vitamin C will affect the accuracy of the glucose meter.
For further information.
TopTenReviews gives a detailed summary of the pros and cons ot glucose test meters including the price of test strips which can vary from 0.10€ each to almost 1.00€.
This page gives useful information about dilutions and the best way to store and use the test strips which might help any teachers or students trying to get their glucose meter to work. Determination of Glucose in Beverages using a Blood-Glucose Meter by Erin Gross. The downloadable files on this page contain useful information about reliability and a calibration curve using know concentrations of glucose.
The article by J. Wang and C. Maccà “Use of blood-glucose test strips for Introducing Enzyme Electrodes and Modern Biosensors” J Chem Ed 1996, 73(8), 797-799. is a good academic source for the use of these blood glucose meters.
 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team