Topic 10 - Genetics HL revision list
This pages gives outline details of the content of the topic together with essential questions and student skills and applications. Helpful for revision.
10.1 Meiosis
Crossing over
- DNA replication makes a second chromatid in each chromosome in interphase before meiosis.
- Crossing over exchanges pieces of DNA between non-sister homologous chromatids and forms new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes formed in meiosis.
- Chiasmata are the crossing over points
Essential Questions
- How does a cell divide into four new cells and yet give all the new cells a copy of every gene?
- How does crossing over increase genetic variety in chromosomes?
- When does crossing over occur?
Chromosomes movements
- Details of chromosome movements in meiosis. ie:
- Homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I.
- Sister chromatids separate in meiosis II.
- Random orientation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I leads to independent assortment of alleles.
 Essential Questions
Essential Questions
- What are the steps in the movement of chromosomes in meiosis I and II?
- What are the differences between meiosis I and meiosis II?
- What are homologous chromosome pairs?
- How do homologous pairs orientate randomly?
Student skills and applications
- Drawing diagrams to show chiasmata formed by crossing over.
- Show sister chromatids still closely aligned, except at the point where crossing over occurred and a chiasma was formed.
10.2 Inheritance
Linked genes
- Genes are linked when they occur on the same chromosome.
- Unlinked genes show independent segregation in meiosis.
Essential Questions 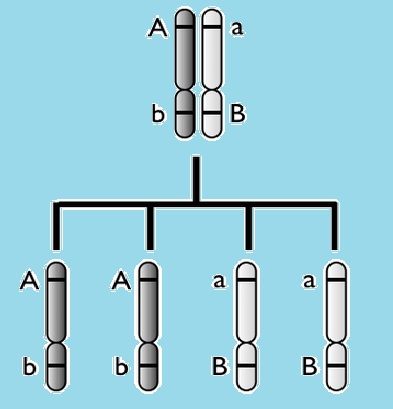
- What might happen during meiosis if two genes are located next to each other on a chromosome?
- If genes are unlinked how will ratios of offspring genotypes be different from offspring ratios in linked genes?
- How is independent segregation different to independent assortment?
Polygenic inheritance
- Variation between individuals of a species can be discrete or continuous.
- Phenotypes controlled by many genes (polygenic) show continuous variation. They may also be influenced by environmental factors.
- Chi-squared tests are used to calculate if differences between observed and expected frequencies are statistically significant.
Essential Questions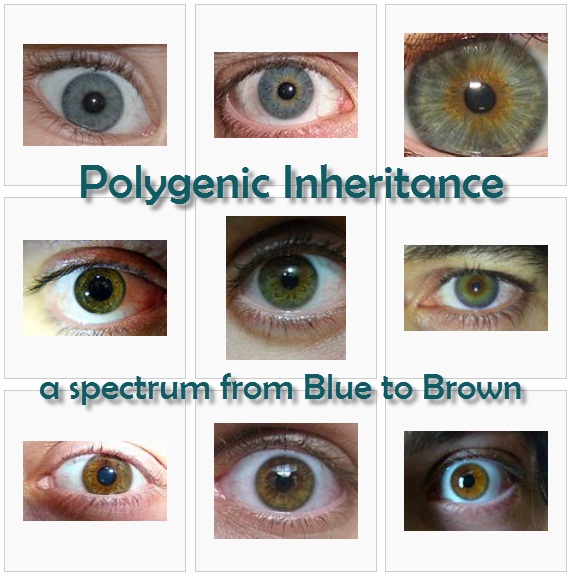
- If three genes control a single feature how many different combinations are there of alleles, assuming 2 alleles for each gene?
- Why do offspring phenotype ratios show continuous variation rather than simple 3:1 ratios?
Student skills and applications
- A awareness of Morgan’s discovery of non-Mendelian ratios in Drosophila.
- The ability to complete Punnett squares for dihybrid traits and analyse them.
- Ability to calculate predicted genotypic and phenotypic ratio of offspring of dihybrid crosses involving unlinked autosomal genes.
- The skill to identify recombinants in crosses involving two linked genes and to understand when they are shown as vertical pair in crosses of linked genes.
- The skill to use of a chi-squared test on data from dihybrid crosses.
10.3 Gene pools and speciation
Gene pools
- A gene pool consists of all the genes and their different alleles, present in an interbreeding population.
- Evolution requires that allele frequencies change with time in populations.
- Punctuated equilibrium implies long periods without appreciable change and short periods of rapid evolution.
Essential Questions 
- What is the difference between a gene pool and a population of individuals of a species?
- What is an allele frequency within a gene pool?
- Why is random interbreeding of organisms within a gene pool important in the evolution of characteristics within a species?
Speciation
- Reproductive isolation of populations can be temporal, behavioral or geographic.
- Speciation due to divergence of isolated populations can be gradual.
- Speciation can occur abruptly.
Essential Question(s)
- What is the difference between reproductive isolation of some individuals and random interbreeding?
- When two populations of a species are isolated why do we say they are separate gene pools?
- What must happen to cause these two gene pools to become two species?
- How can speciation happen both gradually and also quickly?
Student skills and applications
- Application: Identifying examples of directional, stabilizing and disruptive selection.
- Application: Speciation in the genus Allium by polyploidy.
- Skill: Comparison of allele frequencies of geographically isolated populations.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
