Antibody production
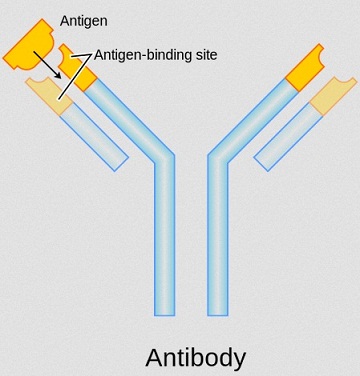 Antibodies and monoclonal antibodies.
Antibodies and monoclonal antibodies.
Two important ideas about antibodies are addressed in this lesson plan. Students first discuss ideas about immunity and mark a piece of student work using a mark scheme to consolidates their understanding of the production of antibodies. Structured worksheet extend this knowledge to monoclonal antibodies.
Lesson Description
Guiding Question
What do the T-helper cells which get infected by HIV do?
How does the immune system respond if the antigen has never been seen before?
Activity 1 - A few extra HL details of antibody production
Review the following HL details in the ![]() primary immune response presentation
primary immune response presentation
- antigen presentation by macrophages
- activation of helper T-cells leading to
- activation of B-cells which divide
- to form clones of antibody-secreting plasma cells and memory cells.
Activity 2 - Mark & improve a student answer about antibody production.
A students has written this answer to an IB Biology antibody question.
The question and mark scheme can be found on the ![]() antibody production HL student worksheet.
antibody production HL student worksheet.
- Explain how antibodies are produced? (8 marks)
Antibodies are produced in response to the presence of antigens in the body.
B-lymphocyces ( white blood cells) can produce antibodies if antigens enter the body.
Helper-T-cells help the lymphocytes by making them more active.
Plasma cells are the type of B-lymphocyte which circulates in the blood plasma and they make antibodies.
Another type of B-cell is called a memory cell, it remembers the antigen so the body can react better if the antigens come back later.
Antibody production by B-lymphocytes is called an immune response.
......................................................................................................................................................
Read the answer, and highlight the parts of the answer which correspond to the points a) to m) in the mark scheme.
Correct any errors and give suggestions how to improve the answer.
Mark Scheme
General points about the immune response
- antigens in the body stimulate an immune response;
- this response is the production of antibodies;
- antibodies are made by B-cells / lymphocytes / plasma cells;
Details about the role of macrophages
- a pathogen and its antigens are engulfed by macrophages;
- the antigen is presented on the macrophage membrane;
Details about the role of helper-T-cells
- helper T-cells bind to antigen (on macrophage);
- helper T-cells are activated;
- helper T-cells activate B-cells;
Details about the role of B-lymphocytes
- B-cells clone;
- into plasma cells and memory cells;
- plasma cells(a type of B-lymphocyte) produce specific antibodies to the antigen;
Details about immunity
- memory cells (a type of B-lymphocyte) live for many years giving immunity;
- Immunity allows a faster immune response if the antigen is encountered years later;
Compare marks with an IB examiner.
Click the eye icon to display.
In this box the answer has been marked by an IB examiner.
- Explain how antibodies are produced? (8 marks)
Antibodies are produced in response to the presence of antigens in the body. a)
B-lymphocyces ( white blood cells) can produce antibodies if antigens enter the body. c)
Helper-T-cells help the lymphocytes by making them more active. Too vague
Plasma cells are the type of B-lymphocyte which circulates in the blood plasma and they make antibodies. k)
Another type of B-cell is called a memory cell, it remembers the antigen so the body can react better if the antigens come back later. Too vague
Antibody production by B-lymphocytes is called an immune response. marking point b)
......................................................................................................................................................
TOTAL MARKS = 4
Sentences in the answer which were not precise enough
Helper T-cells "activate" the B-lymphocyes - this is better than, "helping" or "making more active"
Memory cells - "live for many years", "have receptors for the antigen" - but they don't have "memories"
Points missing from the answer
The role of macrophages - see the mark scheme for details
The role of T-helper cells.
With these additional four points the answer would achieve full marks.
Activity 3 - Histamines, allergic reactions and the dangers of blood cell antigens
What happens if antigens like plant pollen get into the body?
Some antigens cause a type of white blood cell (called a mast cell) to release a small protein called histamine. Histamine causes blood vessels to become more permeable leading to leakage of fluid into tissues, and swelling of the tissues. This leads to common allergic symptoms:
- A runny noes
- Watery eyes
- Nasal congestion
Read this nice simple explanation of histamine in response to the presence of dust mites from Cells Alive
Answer the following questions:
Questions on histamine production and allergies.
- What type of symptoms are produced in the nose, when histamine is released by cells of the nose?
.............................................................................................................................................. - What is the effect of histamine on blood vessels?
.............................................................................................................................................. - How could the release of histamine help the macrophages and lymphocytes of the immune system fight a potential infection?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
Activity 4 - Histamines, allergic reactions and the dangers of blood cell antigens
Antigens on the surface of red blood cells stimulate antibody production in a person with a different blood group.
Watch the video about blood types on this Study.com webpage.
Activity 5 - Video summary ( IB terminology but a little bit too detailed)
Teachers notes
Many of the details of the immune system will be known to students already if they have already learned the SL humans topic. The details in activity 1 are really all about the role of Macrophages and helper-T-cells. The short presentation gives emphasis to these two cells.
Activity 2 is an different way to help students to understand the biological details by correcting a student's answer.
This also gives an opportunity to talk about exam technique. The danger of giving human characteristics to cells of the immune system is illustrated in the student answer. The marked example also makes reference to this.
Activity 3 is really optional but it makes for a good plenary. The video includes details of interleukins to communicate between macrophages, B-cells and T-cells which are not mentioned in the IB guide. However the other vocabulary is well matched with the IB Biology guide.
The following are additions:
- Histamines cause allergic symptoms. This is a nice simple explanation of histamine from Cells Alive
- Application: Antigens on the surface of red blood cells stimulate antibody production in a person with a different blood group.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
