HL Respiration introduction
 Students are introduced to four important reaction types found in respiration; oxidation, reduction, phosphorylation and decarboxylation. There is a short presentation which helps to explain each reaction and put it into context. This is followed by a set of flashcards and a few IB-style questions to test understanding.
Students are introduced to four important reaction types found in respiration; oxidation, reduction, phosphorylation and decarboxylation. There is a short presentation which helps to explain each reaction and put it into context. This is followed by a set of flashcards and a few IB-style questions to test understanding.
Lesson Description
Guiding Question
What are these four key reactions in respiration:
- oxidation,
- reduction
- phosphorylation and
- decarboxylation?
Activity 1 - Introduction to the reactions
Read the slides on the ![]() HL respiration introductory presentation to introduce the four key reactions which will be useful in the analysis of the process of respiration.
HL respiration introductory presentation to introduce the four key reactions which will be useful in the analysis of the process of respiration.
Make notes on the four types of reactions found in repiration.
Four types of reaction in respiration.
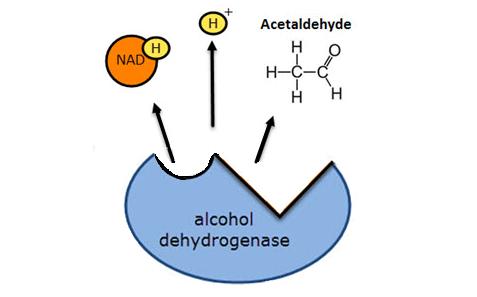
Reaction | Description | Example |
Oxidation | Oxygen is added | Dehydrogenation of alcohol |
Reduction | ||
Phosphorylation | ||
Decarbooxylation |
Activity 2: Test yourself with a few flashcards
Look at the flashcards below and test your knowledge of these four reactions before we look at respiration in earnest.
Activity 3 - IB style questions
Answer the following ![]() IB style questions about this respiration introduction
IB style questions about this respiration introduction
Teachers notes
This is a simple activity. The aim is to de-mystify some of the long and difficult sounding biochemical terms and to look first in detail at a few reaction types which occur in glycolysis and respiration.
The first activity is a few simple slides and students should make notes on these sides or about these slides. They need not be copied, it is the understanding of the four reactions which is most important.
There are many ways to approach the use of the flashcards. Try the "scatter" study mode for a bit of friendly competition.
The IB style questions involve some chemical symbols and molecule names which are not required in HL biology. However the questions focus on the types of reaction not the molecule names, these can simply be copied from the diagrams in the questions. The answers are; 1:D, 2:B, 3:A, 4:C, 5:C.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
